Heat sinks are a very important component for keeping hot components cool. It can either include a fan or with the help of different other means, heat sinks ensure that the heating parts can go for long without burning out.
So, where we can employ the use of these components? Heat sinks are widely used in laptops, computers, lighting devices, airplanes, and many other devices.
We have already been engaging in a lot of traditional heat sink manufacturing processes. However, the good news is that we can also 3D print a heat sink.
Doing so would help in optimizing the design of these components for better results. And, at the same time, these could be made lighter and smaller.
3D printing has become a great alternative for so many applications. There are niches, where 3D printing has replaced conventional methods with better outputs.
And, it is growing faster to make more changes to the already existing workflows within different industries. When talking about the small parts, such as heat sinks, the design specifications are very precise.
And, 3D printing excels are accomplishing parts that need accuracy and precision.
This is the reason why a lot of institutions and experts are researching ways to improve the overall output of heat sinks for making these even more efficient and reliable.
Let us find out how to 3D print heat sink and what are the various considerations one must take to achieve the desired outcome.
What are the Types of Heat Sink?
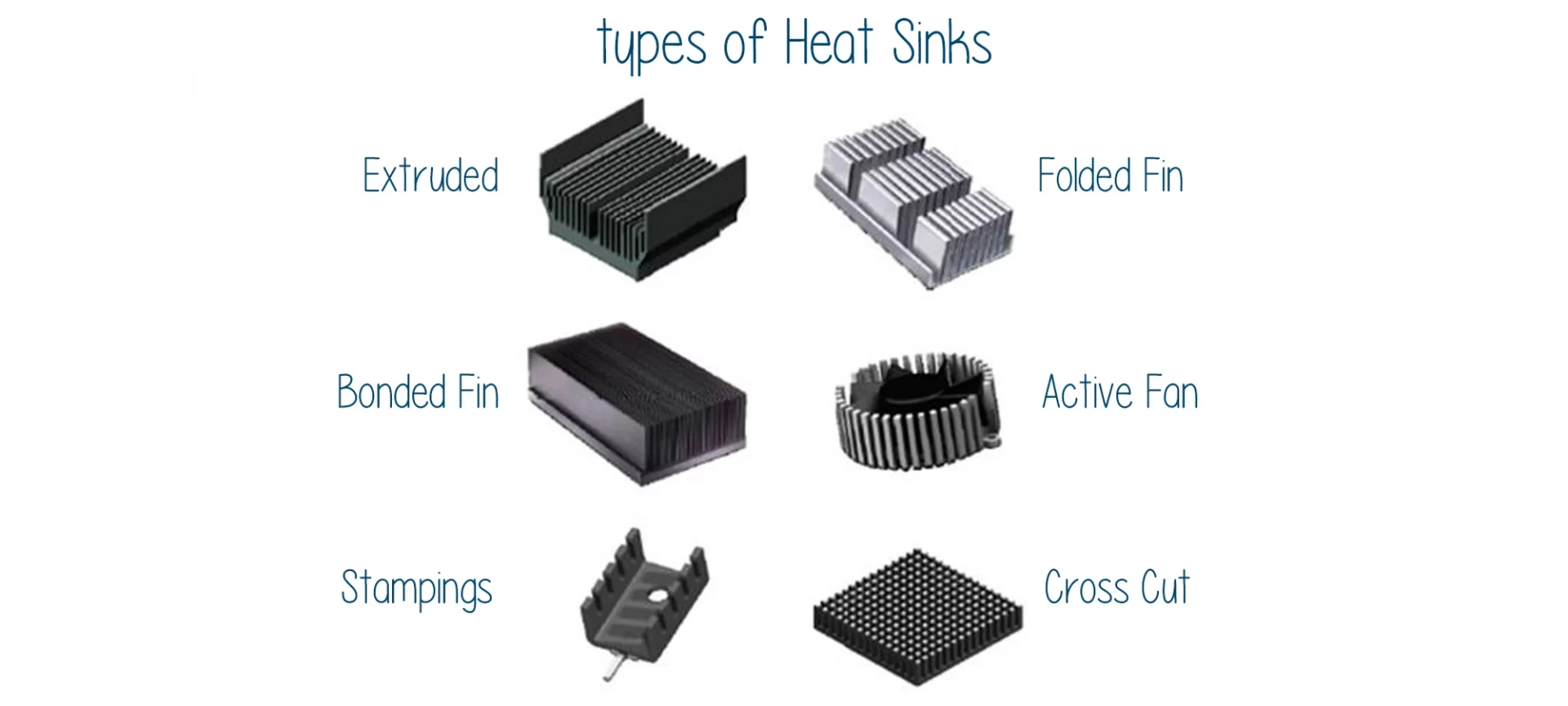
There are two standard types of heat sinks. One is the Active heat sink and the other is the Passive heat sink. The active heat sinks work with a power supply and often include a fan of their design.
On the contrary, passive heat sinks do not possess mechanical components. Usually, these are made of metals such as aluminum to utilize the concept of the convention for dissipation of heat.
Devices that Utilize Heat Sinks
Now that you have got an idea of what heat sinks are, lets progress to their usage. These components are widely available for varying applications.
Only within a computer, different parts make use of heat sink to stay cool and working. For example, CPU, video card, memory, hard drive, power supply, and many others.
Apart from that, heat sinks are commonly used for lighting devices, aircraft, etc.
Few Recent Studies to 3D Print Heat Sink
Heat sinks guarantee longer life for various devices including light fixture. Usually, these are crafted with the help of materials having high thermal conductivity.
For instance, copper, aluminum, etc. The role of these components is to conduct heat from the heated devices and divert it to their extremes. After the heat touches the extremes, it finally reaches the air flowing overhead.
The entire process is extremely crucial for the longevity of the devices that heat up on continual use. And, it is pretty evident that heat sinks are not just a spare part, but contributes hugely to the entire internal design of these devices.
Hence, researchers tried to find the potential of 3D printing in designing the better version of heat sinks that we already have.
In a recent study from two different contributors, a lot of facts were analyzed. Bringing the gist of all: can we 3D print heat sink? The answer is yes. But, what would it entail and how can we do that?
Experts from the USA, along with the researchers from Europe tested few designs to conclude that the 3D printed heatsinks aren’t just lighter and smaller but way more successful. The conventional heatsinks cannot have such benefits at all.
There are two projects working for the same cause, jointly proves that one can easily 3D print heat sink. One project was done at the Oak Ridge National Laboratory and the other was accomplished by the University of Tennessee in Knoxville.
One of the studies deems that the 3D printed aluminum heat sinks can not only match but can even supersede the thermal conductivity belonging to the standard heatsink made with aluminum.
The later has come up with genetic algorithms using the freedom of complex shapes possible with 3D printing for designing heat sinks. These are sure to perform better than their conventional counterparts.
3D Print Heat Sink: Benefits and Limitations
We do know that 3D printing has its own advantages and disadvantages, especially when printing with metals.
And, when it comes to heat sinks, where the performance depends a lot on the design of the component, we must look for the pros and cons of establishing a connection between 3D printing and manufacturing of heat sinks.
Benefits
As we know that 3D printing is an additive manufacturing technology that means that the material is added and not subtracted. Hence, when working with metals, and employing 3D printing, one could highly reduce the wastage of materials.
Another important reason for bringing 3D printing for manufacturing heat sinks is that it could help create complex designs that aren’t possible otherwise.
Not just that, it could also reduce the overall weight of these components making them lighter yet stronger and more efficient.
One can 3D print heat sink with fully dense parts and allowing the highest precision of internal features. This is not possible with traditional manufacturing.
In addition, 3D printing is a highly reliable choice. It may take the maker to fine-tune the design a few several times to get the right model in place.
However, once done, there remains almost no room for error. The 3D printer will design the component without any changes all the time.
This is a huge pro of 3D printing. And, in need of slighter change, one just has to change the 3D design and the parts would be enhanced as desired.
Limitations
We already talked a lot about the benefits. However, there are a few limitations as well. And, you must not ignore them.
Did we ever think why the lighting industry is still far behind when accepting 3D printing for heat sink manufacturing compared to the early adopters, aerospace, and automotive niche?
This is because 3D printing does provide better precision and offer lightweight results, but lacks speed.
Build times can be very high for printing with metals than it takes to build parts with plastic polymers. Plus, you may have to test multiple designs to finally find the one that suits your needs.
This would again complex the entire process, making the workflow tedious and time taking.
The other constraint is the cost of metal 3D printing. Not every industry can afford a 3D print heat sink. And, the mass production is also a question mark as of now.
How to 3D Print Heat Sink?
Before you decide to get a 3D print heat sink, you must come up with a suitable 3D design. And, there are certain tips you can always keep up your sleeves when working with metal 3D printing (discussed later).
Let us take an example of a DIY laptop heatsink to understand the 3D printing process.
Choose a Design or Build Yourself: There are various designs available on the internet for laptop heatsink. Laptop Stand by merthancioglu, 3D Printed Portable Laptop Cooler Pad and many other 3D designs are available online. You can either use any of these or create your own. You can also make changes to these designs for a few modifications.
Slice the Design: Use the 3D printer slicer software to create G-Code for the 3D printer. Using the slicer software, you must slice the layers for printing.
3D Print Heat Sink: You can feed the G-code to the 3D printer to start printing. If there are any settings that need to be done such as bed leveling or calibration, you must complete those prior to starting the print. After the printing completes, you can check the working of the DIY laptop heatsink all by yourself.
What to Consider When Printing with Metal?
As mentioned before, you must expect a fair amount of failures before you can perfect design, in case you are working from scratch to model a heat sink.
In the midst of all these, there are few usual pitfalls that turn designs into a nightmare. And, these can easily be excluded from your 3D printing process. Taking special consideration of these constraints, one can easily overcome a few of the common mistakes.
The Correct Wall thicknesses
Even if it’s metal, you cannot expect thinner walls to stay strong for long. These will collapse when printing under their very own weight.
Hence, one must ensure that the walls aren’t thinner than 0.5 mm. When doing so, a huge percentage of the battle against failed attempts will already fall in your favor.
Hollows
Every 3D printer is different with varying constraints. Hence, the limitations levied for holes may also differ. Apart from that, the limitation will also vary depending on the metals used, as well as the design of the parts.
If you go by the books, you must not include gaps under 0.5 mm. In case the holes and gaps are smaller, they may become susceptible to merging together with the sides and filling into the empty spaces.
Moreover, if you plan to design gaps greater than 10mm, you must use support to successfully accomplish the task.
Designing Overhangs
Once again, overhangs are tricky. And, if you include these in your design, you must not exceed the maximum length of 0.5 mm. In addition, the structures facing downward must have chamfer having a concave shape (convex shape will also do the job).
Use of Support Materials
Usually, support structures serve two purposes. The first reason is to provide a base for hanging parts of the 3D design to the build plate. And, also for heat dissipation.
Hence, if there are any areas in your design that are below 45 deg. from a horizontal surface, it would need a support structure. This is the same along with all the metals you choose.
Working with Part orientation
You must know that with 3D printing, the parts created will have varying mechanical properties alongside different orientations. For instance, if you consider, the X and Y plane, the parts will showcase higher tensile strength compared to the Z direction.
This is why one must take extra caution when deciding the part orientation of the 3D model. It becomes even more important if you are printing a part that has to go through varying degrees of tension and pressure.
Not just that, the orientation also affects the surface finish of the parts. The face attached to the surface will end up with a poorer surface finish when compared to the open surfaces, not in contact with the print surface.
Hence, if you are printing an object that needs to be impressive in certain areas, you must not forget to consider the part orientation. Moreover, the supports will also end up affecting the surface finish of the objects after removed. So, you must take care of that too.
The Conclusion
3D printing has proved every now and then that it is not going to stop. It will keep changing the way we work and design parts.
From medical to aerospace, technology has widened its application and will continue to grow further. There is no way, one can ignore the various perks that the niche has to offer.
This is why bringing 3D printing for enhancing the performance of heat sinks does not feel very surprising. Does it?
As we know that heat sinks are also a common component utilized widely for saving electronics and heated parts from failing.
In such a case, finding an apt design that could not only increase the efficiency of the overall device but could also be easy to design is the need of the hour.
Many researchers are already working on it. And, hopefully, we would find more industries, like aerospace and automobile, connecting with the cause sooner.
Until then, you can try to design and 3D print heat sink and explore the onset of a new future-ready to embark soon.







