3D printing is an additive manufacturing process where each layer combines to the next layer for creating the final part. However, there are different 3D printing processes available for users with varying 3D printer “ink” choices.
As well as the cost of these materials varies widely. Some are affordable and others are highly expensive. When talking about the 3D printing processes, one may come up with different versions of it.
This is because there has been a huge development since the first process came into existence. Many patents have been accepted and the industry has evolved to bring a lot of great alternatives for users, in terms of functionalities as well as material options.
Here is an article listing some of the most common 3D printing processes and the different 3D printer materials used for these technologies.
Types of 3D Printer Materials for Varying 3D Printers
Among all the different processes, let us concentrate on the most basic and common ones. 3D printing processes differ in terms of the technology used to combine different layers together to form an object.
Fused Deposition Material
Fused Deposition Modeling, abbreviated as FDM is the most common of all among consumers. These are the cheapest, hence, easily accessible to masses.
These printers are available at different price ranges, starting from as low as $150. Sometimes, FDM machines are also referred to as Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF).
These printers work with filament spools. The filament spool is loaded and fed through the nozzle to reach the printer’s bed after being melted inside the extruder. To do so, the nozzle is heated to a temperature just above the melting point of the filament, the 3D printer material.
This molten filament is deposited on the printer’s bed, one layer at a time. Once the layer sets, another layer is deposited above the first one. These layers combine and the process continues until the object is completely printed.
FDM Material
FDM 3D printers can print with many material choices. And, the new ones are developed every now and then. Here is a list of filaments available for FDM printers.
PLA

This is the cheapest filament of all. PLA is derived from cornstarch and is biodegradable. The material is very easy to tame and can be worked out without a heated bed requirement.
The material is available in various colors. However, being susceptible to heat, PLA isn’t as durable as other FDM filaments such as ABS.
But, it does have many other qualities that make it equally competitive as any other filaments. It contracts less, hence, is simple to print with.
ABS

ABS is a bit expensive than PLA, however, still affordable for professional applications. The material is very popular among consumers and provides excellent results.
It is durable than PLA as well. Moreover, the material is strong and lightweight at the same time. This is also available in a huge range of colors.
However, this does have a drawback. ABS emits harmful fumes when heated and must be used in a closed design 3D printer. Or, there must be enough ventilation to null the harmful effects of these gases.
Nylon

Unlike many other filaments that are rigid, Nylon has a touch of flexibility alongside a commendable strength which makes this material a premium choice for users.
The material is being used for specific as well as artistic applications. Either its engineering or art, nylon can be useful in many ways.
However, one must smoothen the surface of prints created with nylon as they have roughness after being printed. You can expect the highest layer bonding in nylon as compared to the other FDM 3D printer materials.
PET

You may have touched PET but aren’t aware of it. The material mostly used for printing water bottles. PET is often regarded as an alternative to ABS.
However, PET does not emit fumes as ABS and can be worked without much hassle. The material results in stronger and flexible parts.
As PLA, PET also can be printed with a heated bed. It provides glossy touch to the printed parts. Above all, the material is food safe.
PEEK

If you are looking to create high-resistant parts, you are in the right place. PEEK can withstand high stress, temperature, as well as chemicals.
Not just that, the objects printed with this material can also be exposed to harmful radiations such as X-rays and it would have no adverse effect on the parts.
It does create robust parts, however, it can be easily fabricated at the same time. However, not every 3D printer can extrude the material. It needs up to 400°C of temperature to melt. And, is usually used with professional 3D printers.
PVA

PVA isn’t used for printing objects but is helpful in creating soluble supports. The reason it is being so popular as a support structure material is that it dissolves in water.
This means, that users do not require any special chemical to remove the supports from the final part. PVA can be dissolved in tap water.
HIPS

HIPS is usually used for support structure like PVA. However, it does have other applications too. The material dissolves in the chemical Limonene.
HIPS is extremely durable and makes as a great option for applications requiring high impact resistance. HIPS, like ABS, emit vapors when printed. Hence, one must take the necessary precautions when printing this material at home.
ULTEM

The material has similar properties to that of PEEK. And, must be used with professional 3D printers. It is used for applications that seek high-performance.
The parts are highly resistant to temperature, stress as well as chemicals. And, the material is easy to fabricate. It does require high temperatures to extrude.
Hence, isn’t safe to work at home. Because of its high performance, and robustness, the material is utilized for specific applications within industries like aerospace, medical, automotive, and many others.
PETG

This material is from the PET family. PET is combined with glycol to create PETG, hence the name. This is done to realize a variety of desirable effects, for example, properties like high transparency.
Additionally, the material can be melted at a lower temperature and can be printed at a higher flow speed. This helps in accomplishing the prints at a higher rate.
There are other qualities too. The material is resistant to changing weather. Hence, can be utilized for outdoor applications. PETG is also food-safe 3D printing material like PLA and PET.
Composites
These filaments aren’t just made of a single material. However, they are a combination of more than one material to provide 3D printed parts with varying characteristics.
PLA is the major filament used with different materials to create composites. For example, it is combined with wood or metal to showcase the respective properties of the other materials.
Conductive:
Conductive material was founded much later after the development of 3D printing. As the name suggests, the material exhibit conductive properties and is widely used for interesting applications.
These are used for printing touch sensors in gaming pads. The material is also useful in providing desired results when used for printing conductive traces in wearable electronic devices.
The material is usually created with PLA or ABS. And, as the respective properties of these two filaments go, the conductive ABS is durable than its PLA variant, however, it does encompass the fume issues when melted.
The average cost of PLA or ABS filament is $25, talking about the standard ones. The specialty filaments can range up to four times of this cost.
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
SLS works on the powder bed fusion technology sintering different layers of polymer powder to create the final part. To start the process, a container of polymer powder is subjected to a temperature just below the melting point of the polymer.
Using a recoating blade, a layer of the powdered 3D filament is deposited onto a build platform. To sinter the powdered particles together, a laser beam is utilized.
After the layer is formed when heating the desired cross-section of the layer, the build platform is moved down equals to the thickness of one layer.
Another layer of powdered polymer is deposited on the printed layer and the process continues until the part is completely printed.
The interesting part is that the un-sintered powder acts as the support structure. Hence, the parts printed with SLS do not need one.
SLS Material
Most of the filaments used for FDM 3D printers work with SLS 3D printers as well. For example, PLA, Nylon, PEEK, and ULTEM. Apart from this, there is one more material that is used in SLS 3D printers.
Alumide
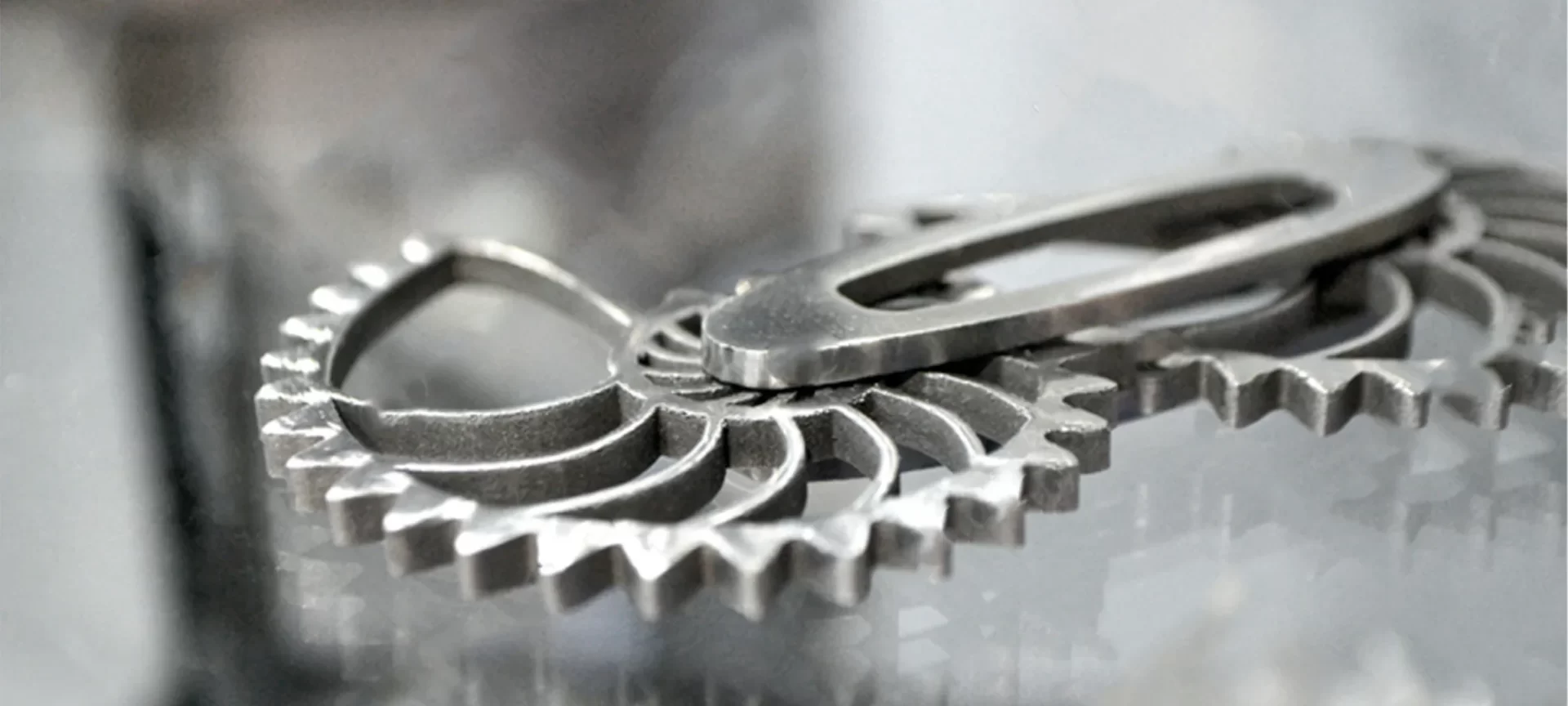

Alumide is from the family of nylon. It is formed when nylon is combined with aluminum particles. Hence, the material exhibits similar properties to that of nylon. It is durable.
However, there are few differences too. Unlike nylon, aluminide results in the shiny, and porous surface finish. Moreover, the parts created with this material showcases excellent size accuracy. These are tough and can be used for long term applications.
Nylon 12 is the most used SLS Material and costs around $50 – $60 per kg. The cost of other advanced materials would be much higher than this.
Stereolithography (SLA)
This was the first 3D printing process developed by Chuck Hull in 1986. The SLA 3D printers use liquid photosensitive materials that are exposed to the laser beam through the galvanometers positioned on the X-axis as well as the Y-axis.
This helps in selectively curing the cross-section of the liquid resin, which further solidifies the layer in the process.
SLA Material
As mentioned before, the SLA 3D printers work on liquid resins. SLA resins were developed to simulate or copy the various properties found in the existing 3D printer materials listed above.
For example, you can use the SLA thermoplastic similar to PLA if you wish to create a biodegradable part. You can even use SLA plastics resembling the properties of ABS as well as HIPS.

Resins can be used for creating highly detailed parts utilized as functional models. The major benefit of the material comes into the picture when printing a larger model.
This can be done in relatively less time. There are other advantages too. The SLA resins are speedier and accurate. However, these are costs that most of the FDM filaments.
Standard resins cost approximately $50 per liter. However, the most expensive ones can even go up to $500 per liter.
Direct Metal Laser Sintering
Direct Metal Laser Sintering, abbreviated as DMLS is a similar fashion to SLS. The major difference that sets the two technologies apart is that DMLS is used specifically for printing metal parts.
Instead of melting the powder as it is with SLS, it heats the material so that the powder particles fuse together, that too on a molecular level. DMLS produces parts from metal alloys. Like SLS, DMLS also does not require a support structure.
DMLS Material
Here are a few of the most common materials used with DMLS 3D Printers.
Inconel

This 3D printer material is a superalloy that is created as a composition of nickel and chrome. It is highly resistant to stress and temperature and can withstand extreme conditions as well.
Plus, it can bear huge pressure without any hassle. The material is used for high-performance tasks such as airplane black boxes. It is even used for printing components of rocket engines. These have a huge demand in chemical industries as well.
Cobalt-Chromium
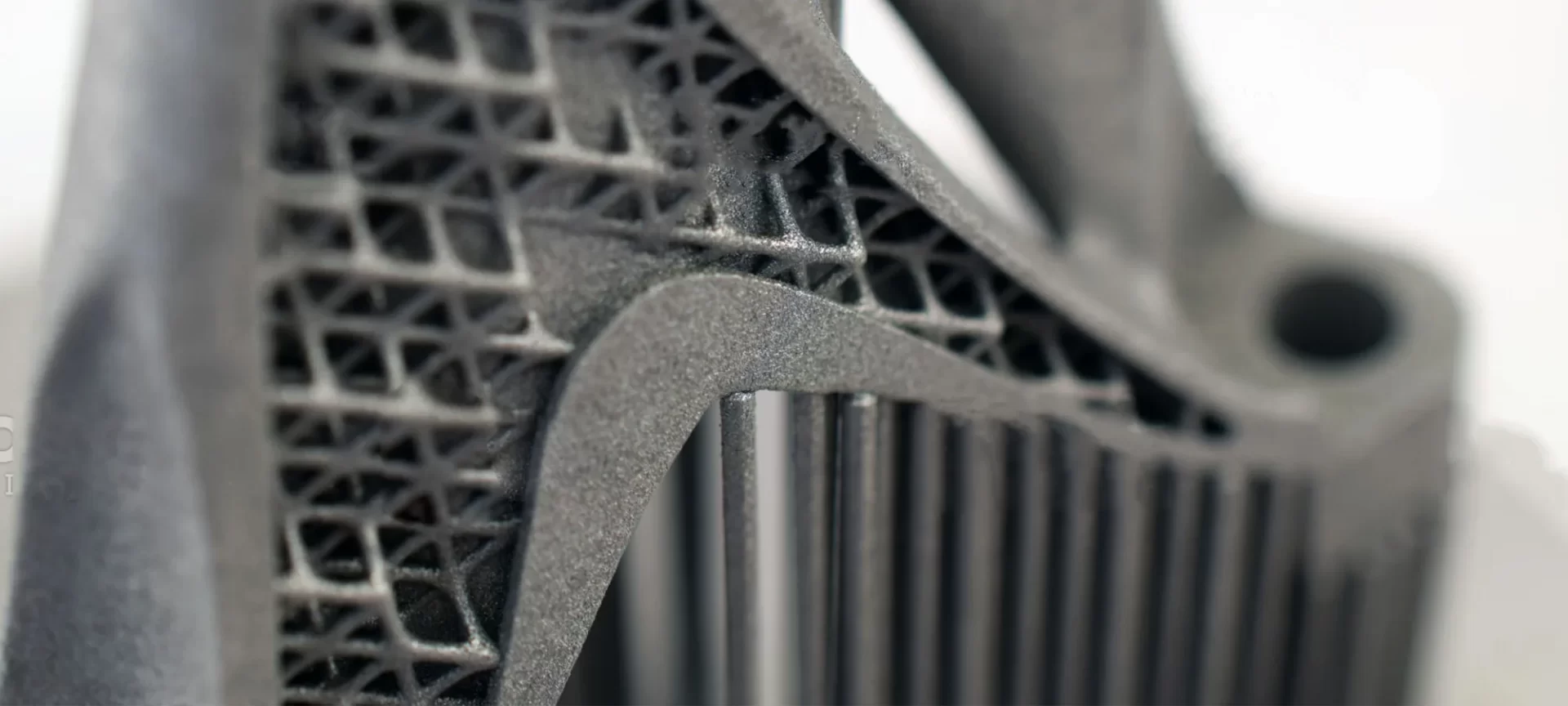
This again is referred to as the “superalloy”. Because of its strength and resistance to heat and pressure, the material is utilized for high-performance applications.
Among the different applications, it is majorly used for medical fields, designing parts for the aerospace industry and others. Moreover, the material is also resistant to corrosion.
The metal powder prices can start from $300 per kg and can go much higher than that depending on your choice.
The Conclusion
There are many other 3D printing processes and applications. And, the number is increasing at a fast pace. With an increase in demand from different industries, the choice of materials is also surging.
With time, manufacturers are coming up with their proprietary filaments and materials that are unique and offer distinguished characteristics. Even the same material from different brands could showcase different results.
With that said, it is important to understand how to choose a material based on its properties and price. The selection of 3D printer materials can make or break the entire project. It is very crucial to have depth knowledge of materials that fit your application.







