3D printers are becoming popular with time. Some prefer to buy the fully assembled machines while few like to explore a little more with DIY 3D printers.
While working with DIY machines, the most exciting part is exploring the different 3D printer parts that make it such a powerful technology. Though it is difficult at times to complete the assembly in few hours, the experience does provide a lot of know-how about the 3D printer anatomy.
By learning about the parts, one gets better understanding of the working of 3D printers. Hence, can utilize the knowledge later when actually printing with the machine.
One can even solve minor to major problems such a nozzle jam and many others, when familiar with the inside out of these 3D printers.
In short, if users are looking forward to a strong career in 3D printing, the right way would be start with the different parts that make up for the most revolutionary technology.
List of Major 3D Printer Parts
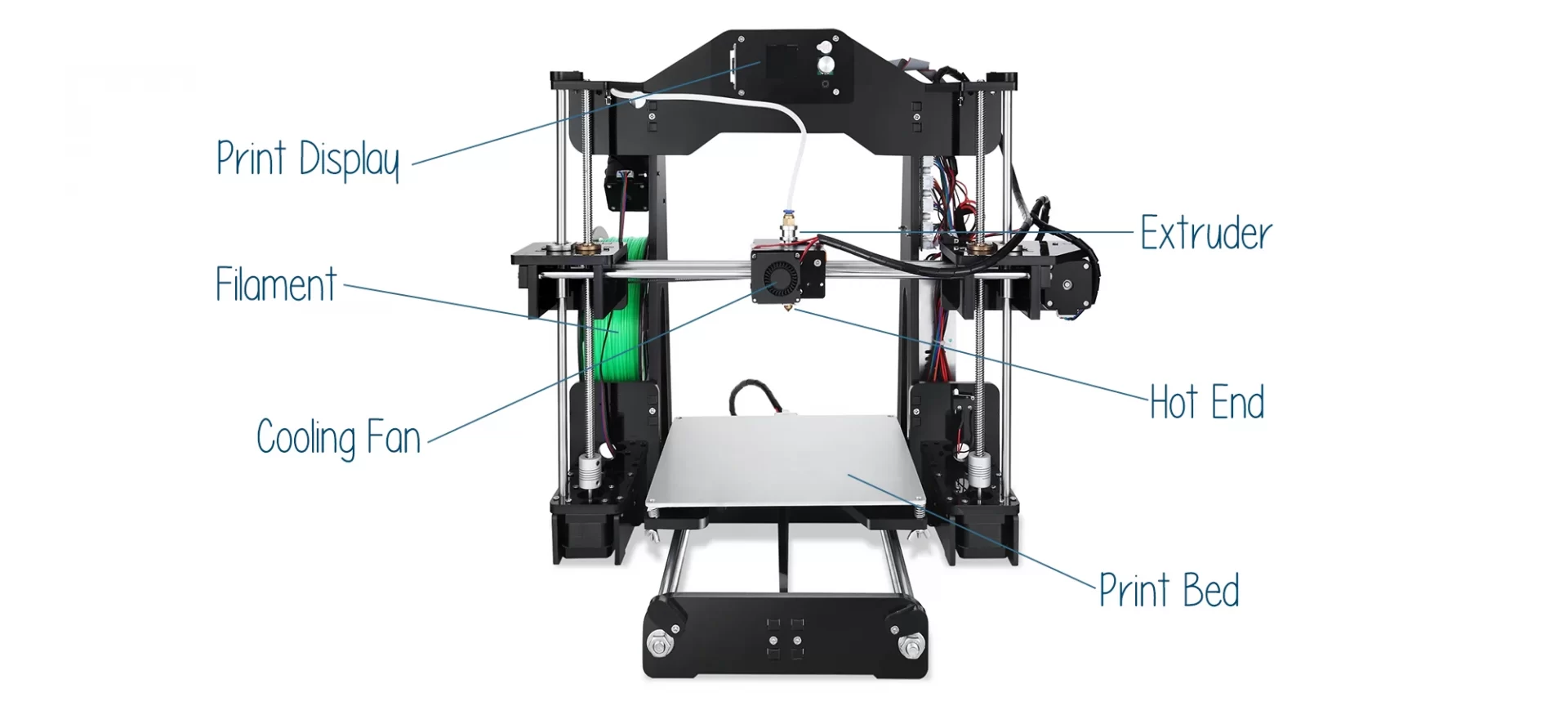
3D printers are complex, however, when examined closely, they can be made super easy to understand and work with. The first step must be to check out the 3D printer parts list.
These components of 3D printers help accomplish tasks from printing smaller to larger parts with ease. The list here contains the component of cartesian printers which are recommended for beginners.
MotherBoard or Controller Board
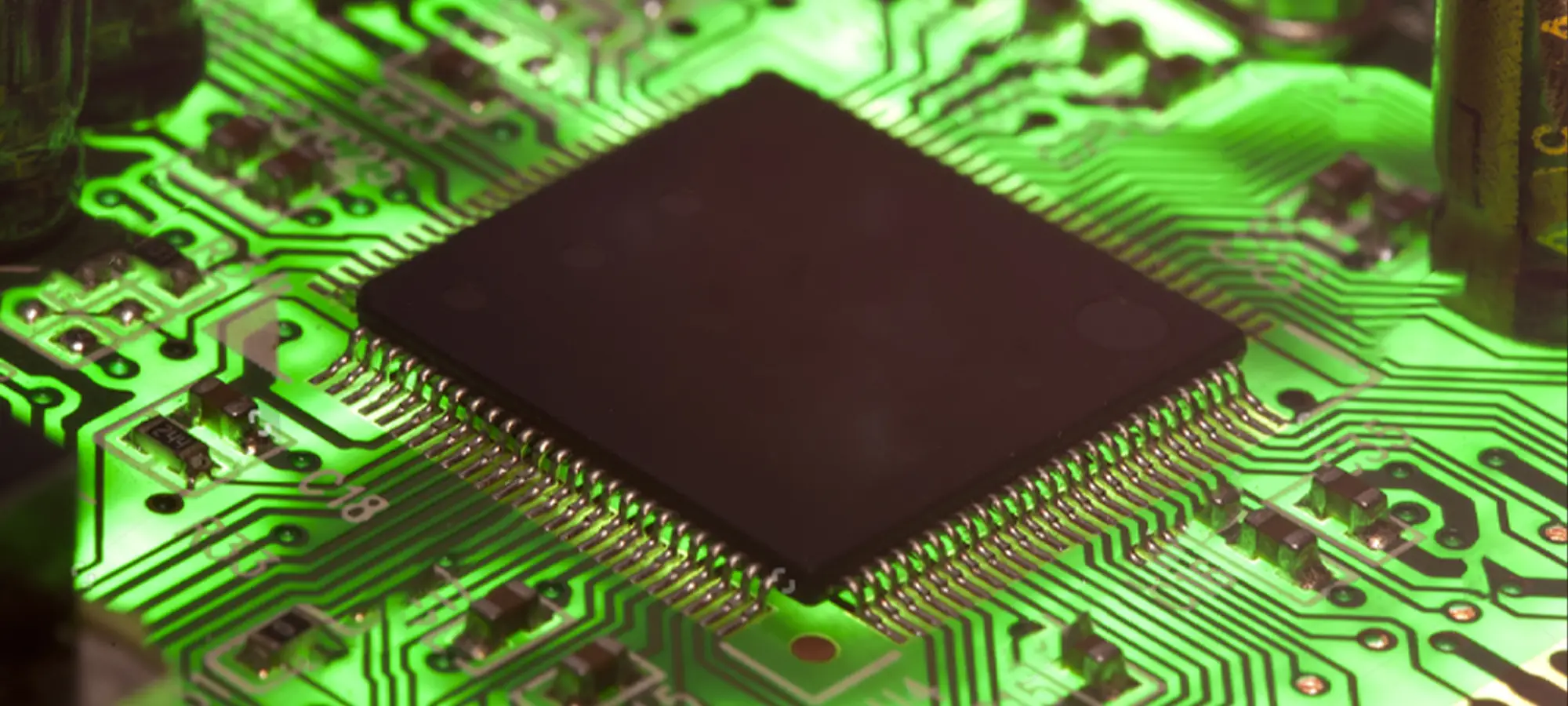
The motherboard which is also known as mainboard or control board. As the name suggests, this component is responsible for maintaining the smooth processing of the machine.
Being responsible for all the fundamental operations, motherboard works as the brain of the 3D printers. It directs the motion components as per the instructions sent from a computer and at the same time, interprets signals from the sensors.
You must have guessed how crucial it is to have a great quality controller board for achieving high performance from a 3D printer. Even if you put every best part in your machine, while ignoring the controller board, your 3D printer would be worthless.
Frame
Frame helps keep all the other components of your 3D printer together at one place. It also maintains the stability of the entire machine. If your frame is robust, you will have a more durable 3D printer.
Companies use different materials and the most common ones are the metal and acrylic. In old days, wood was used for the frame of the consumer 3D printers.
However, to maintain the highest stability, one must choose the metal body. These printers aren’t always expensive as well.
For example, Monoprice offers budget 3D printers under $300 with aluminium frame. Yes, you heard it right. With limited budget, you can still own a metal frame 3D printer.
When talking about frames, the open and closed frame designs also make a difference. A closed frame offers better results by maintaining consistent temperature around the print space. There are few printers that also offer semi-enclosed frames.
Print Material
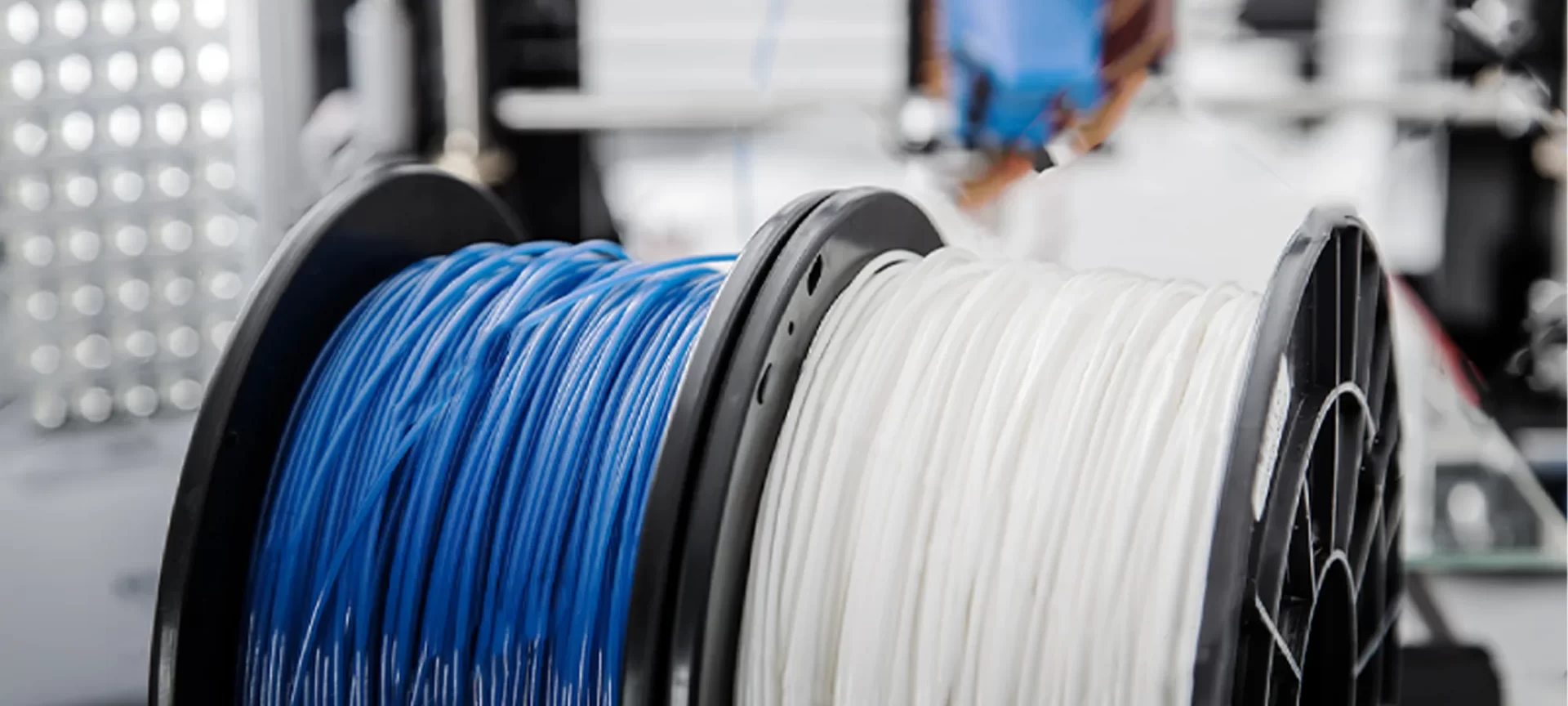

Filament is used for the FDM 3D printers. Filaments are available in spools. These are heated to certain temperature and are liquified to be deposited on the print bed.
This happens in layers. The objects created by 3D printers are made of these filaments. There are many types of filaments used for 3D printing. And, each one of them have different properties. They have their own advantages and limitations.
When getting a printer, one must take care of the compatibility with different filaments. Not all printers allow multiple filament compatibility.
Some can process only one kind of filaments, mostly PLA. And, others can work with multiple choices of filaments including PLA, ABS and many others.
There are other 3D printers that only accept the proprietary filaments. Hence, you must be aware of your 3D printing needs before opting for a 3D Printer and the filaments it supports.
Motion Controllers
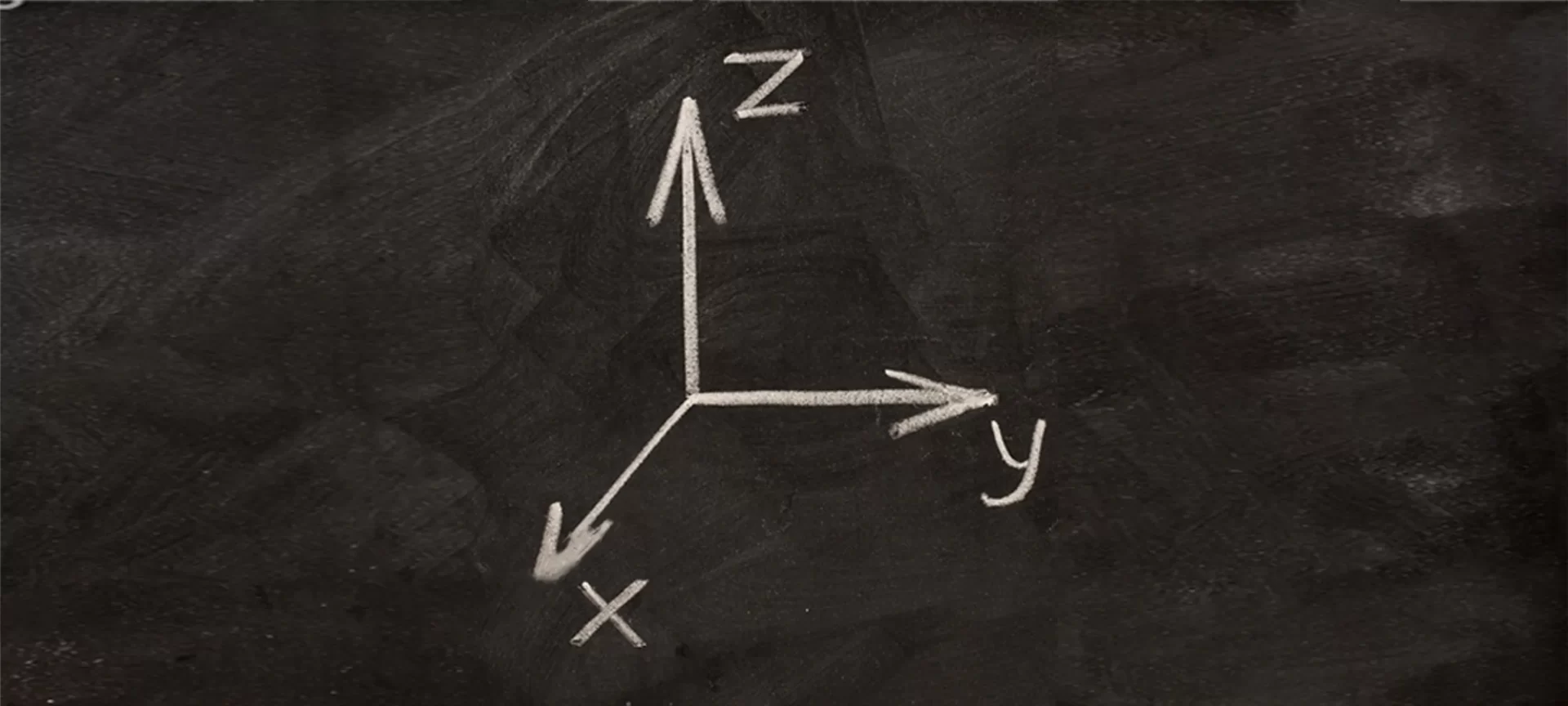
You must know that the 3D printers, as the name suggests works along the three axes. Motion controllers receive instructions from the mother board about the movement they must make, while they are the ones who perform the actual movements.
- Belts: The belts connected to motors are responsible for moving X-axis and Y-axis. The movement happens from side to side. This movement does affect the print speed and precision, hence are very crucial for the attaining best results. One must ensure that the belts aren’t loose or the print may ruin. For this, one can use tensioners.
- Stepper Motors: These are responsible for the mechanical movement of the device and are controlled by Stepper driver. These motors connect with X, Y as well as Z axis. These motors help in driving the print head, print bed, along with the leadscrews. Because the rotations are made in steps, they are called Stepper motors.
- Threaded rods: Threaded rods are connected to the stepper motors. With the movement of threaded rods, the print head moves in upward and downward directions. In few 3D printers, the print bed movement also relies on threaded rods. So, the Z axis movement is dependent on Threaded rods. Although these could be used for the movement along the X and Y axis, being expensive, majority of the printers use belts. Belts are faster and lighter alongside being cheap.
- End Stops: End stops ensure that the end points are marked along the three axes when the movement of components take place. It identifies the range of movement of each component.
PSU
PSU, abbreviated as Power Supply Unit helps in supplying power for a smooth operation of 3D printer. You can find the PSU mounted on the frame. Or, it can also be available separately along with another controller box. However, mounted one provides compact look and occupies less space.
PSU strength would decide what temperature your 3D printer is capable of working with. For advanced materials, one must choose the one with higher temperature range allowance.
Print Bed
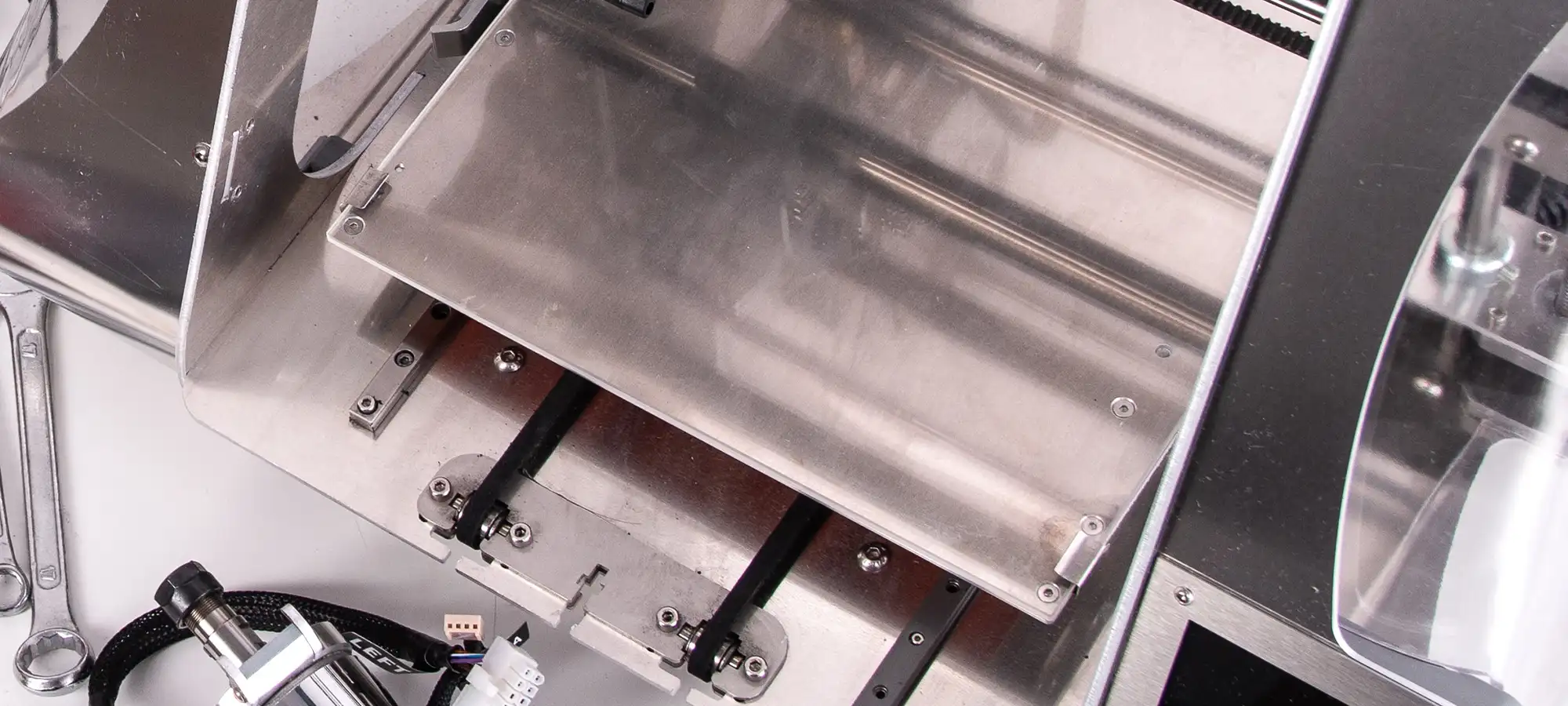
Mostly, anyone who has worked with 3D printer would know what a print bed is. This is the component where the models are created.
The filaments are deposited on the print bed, one layer at a time for building the entire object. One of the major 3D printer parts that does decide the quality and surface finish of the printed object.
Different 3D Printers boasts different kinds of print bed. You can find heated as well as non-heated print beds. A non heated print bed may be enough for PLA, however, for advanced filaments, heated beds are recommended. These helps in enhancing adhesion and stability for first layer of the print.
Also, the print beds are designed using different materials. For example, aluminium and glass print beds. Both have its own benefits and limitations. Aluminium print beds heat up faster and glass print beds, being flatter, provides better finish and are easy to maintain as well.
Some 3D printers offer automatic calibration of print beds. However, users need to level the bed manually in some.
Extruder
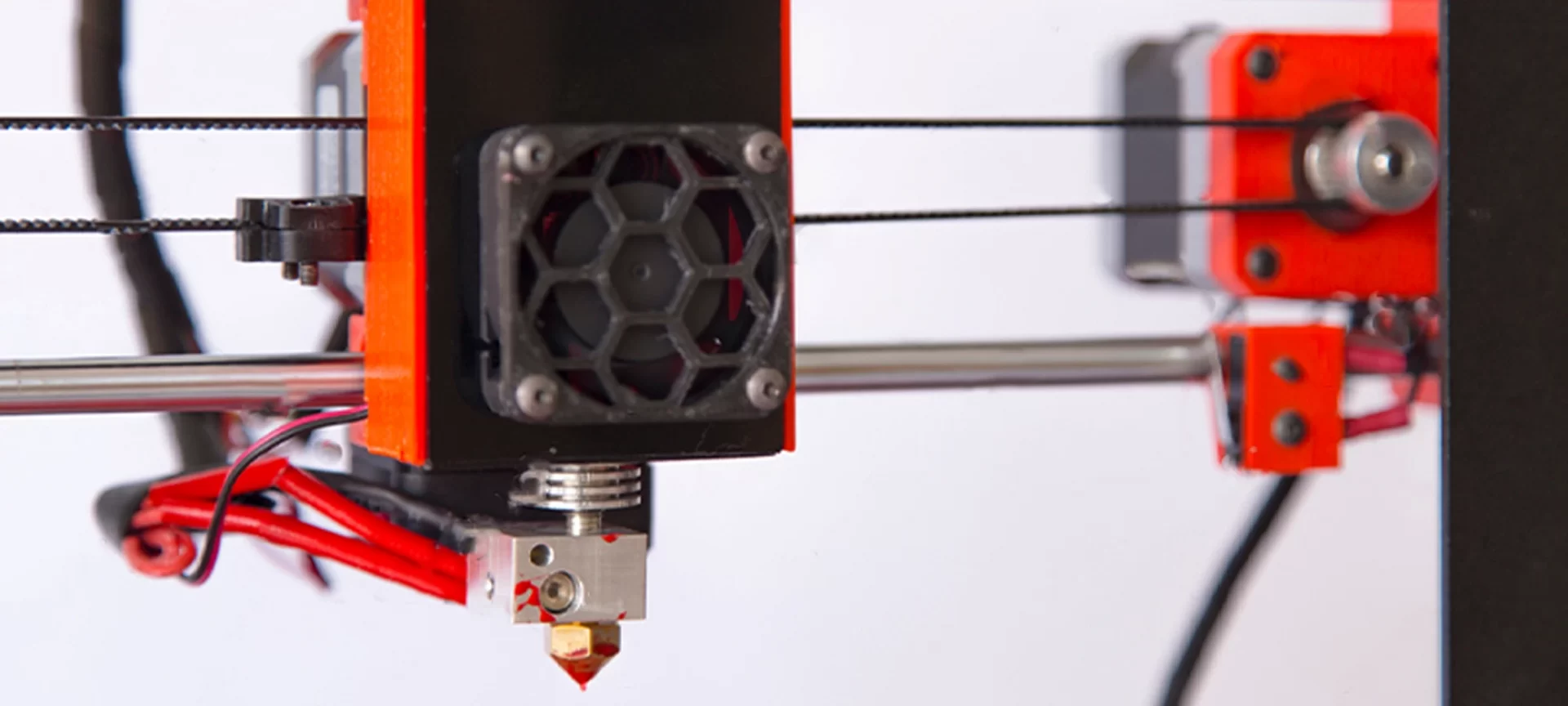
The extruder, also known as print head extrudes the filament and deposit it on the print bed. The extruder can be categorized in two sections. One is called the cold end while the other is known as the hot end.
The job of the cold end is to lock the filament while pushing it gradually downwards to the hot end.
The hot end that has a nozzle attached to it at the end, maintains a high temperature greater than the melting point of the filament. The hot end melts the filament which is further deposited on the print bed.
The extruder itself is made of different parts.
- The Filament Drive Gear: Also known as extruder drive gear is responsible for pushing the filament into the hot end.
- The Heat Sink: The heat sink along with the heat Sink Fan ensures that the material is still in solid state until it reaches the nozzle.
- The Heater Cartridge: This is the component that works to heat up the filament.
- The Thermocouple: To maintain the right temperature, the extruder uses a temperature sensor. This is used for the hot end.
- The Cooling Fan: Once the melted filament is deposited, it must be cooled down for setting before the next layer gets deposited. The job of the cooling fan is to ensure the same.
- Nozzle: This forms the tip of the extruder. The filament is melted and it comes out of the nozzle for deposition. There are different sizes of nozzles that the printers use. 0.4 mm is the most common one. By keeping the smaller diameter of nozzle, one can achieve finer details with greater accuracy. And, larger nozzle helps in printing at a higher speed.
Some 3D printers are equipped with dual extruders as well. With a dual extruder, one can print simultaneously with two different filaments. Dual extruders have two kinds of setup. Either both the nozzles are included in one print head or connected with two different print heads.
Feeder System
There are two most common feeder system used in 3D printers: Bowden feeder system and Direct feeder system. In a Bowden setup, there are different locations for cold and hot ends.
While a filament tube is used to direct the filament towards the hot end. This setup can dramatically increase the print speed as the extruder becomes lighter.
When talking about the direct setup, the cold end and the hot end are directly connected. The direct feeder system is most common among the users who work with flexible filaments.
Connectivity
When it comes to connectivity with other device, 3D printers differ a lot. Some provide only the ethernet or USB port for connection. However, many new 3D printers are now available with Wi-Fi setup as well.
The interface can also help connect the mobile phone or laptop through Wi-Fi connection to your 3D printer. The file transfer can also be done using any of the three options.
For a standalone experience, many 3D printers also come with SD card slots. These slots are used for file transfer while the printer works without a need for any other device.
User Interface

These days, most of the 3D printers, even the budget ones, comes with an LCD user interface. With the help of this interface, one can control the printer settings without a need for computer.
Hence, these machines can work as standalone machines. The majority of the 3D printer has a mounted interface. However, you may find some models with separate controller box including the LCD interface.
This interface can help check and set the machine parameters. You can also use this interface to initiate the loading or unloading of filament. Moreover, an auto-leveling system can be initialized with the help of this small screen on the 3D printer.
The Conclusion
The 3D printing technology is growing with leaps and bounds. Doesn’t matter if are from a technical background or a non-technical one. Users can definitely learn to operate 3D printers because of all the help available online.
And, to know a little more than what others know, would certainly put you in a better place. So, why not start with the components of 3D printers?
3D printers are housed with many smaller and larger parts. Every part has their own role to play. Some tackles the movement while some work for accuracy various other important jobs.
These parts work in conjugation to provide a stable and uniform precision. The objects printed with a 3D printer bear varying properties and quality, depending on the difference in these parts and components.
However, all of these components have equal share when it comes to the operation of the 3D printers. Knowing about these 3D printer parts is a great way to start the journey towards 3D printing.
Who knows, you can someday, be able to create your own 3D printer. Possibilities are endless and when basics are strong, one can dream for higher goals.







