While people are still to understand the various application and usage of 3D printing in day today life, introduction of different terms tend to make the matter worse.
For making things simpler, many individuals call 3D printing and rapid prototyping as one term. However, there is a very thin line that differentiates these two from each other.
3D printing is the process on which rapid prototyping works. It would be wrong to term these two terms together. In the beginning, when 3D printing was invented, the major focus was on creating prototypes for industrial test and trails.
With time, however, the applications grew and 3D printing was brought to use for different niches. It is no longer limited to creating prototypes but is also involved in manufacturing finished goods.
Because of this, there two terms are not just different but have completely different focus. On one hand, rapid prototyping refers to one task, 3D printing is a process which can be included in various task to accomplish different applications.
Before we delve deeper into the facts, let us define the two terms for a more precise outlook.
What is Rapid Prototyping?
Rapid prototyping is the term used for building a test prototype for something that would later be built using different materials with variable size.
This is why the strength or other mechanical properties of the prototype do not matter. What matters is the appearance and how the actual part will look after it is actually built?
The process helps engineers and experts understand the design better before it is manufactured in mass to avoid loss of money and time. Rapid prototyping can aid the speed of the entire process.
Even when developing software, engineers provide a sample application to the clients before it is developed completely. That is also known as rapid prototyping. So, looking at the literal meaning of the term, it means preparing a sample to understand the actual design before the production budget is involved.
The technology is around 40 years old. Rapid prototyping uses a 3D printing or additive manufacturing process to prepare prototypes. Stereolithography is the oldest process of all for building rapid prototypes.
The name clearly suggests that 3D printing has made the entire process fast and hence, the name, rapid prototyping.
There are many ways one can put the whole term together. Some may call it a visual prototype as the consideration is the assessment of the design of the prototype. But the fact remains the same. Rapid prototyping cannot be termed as 3D printing.
Rapid prototyping is only used for creating a three-dimensional model of the final product. One can test the 3-D visualization as well as can test the efficiency of a product’s design before manufacturing it is a larger quantity. During the process, 3D printing is used to create these prototypes.
What are the Different Types of Prototypes?
The prototypes can be further classified into two categories depending on their accuracy. Although prototypes must not be exactly the same as the final product, it does require to possess some level of accuracy to better assess the design and other properties.
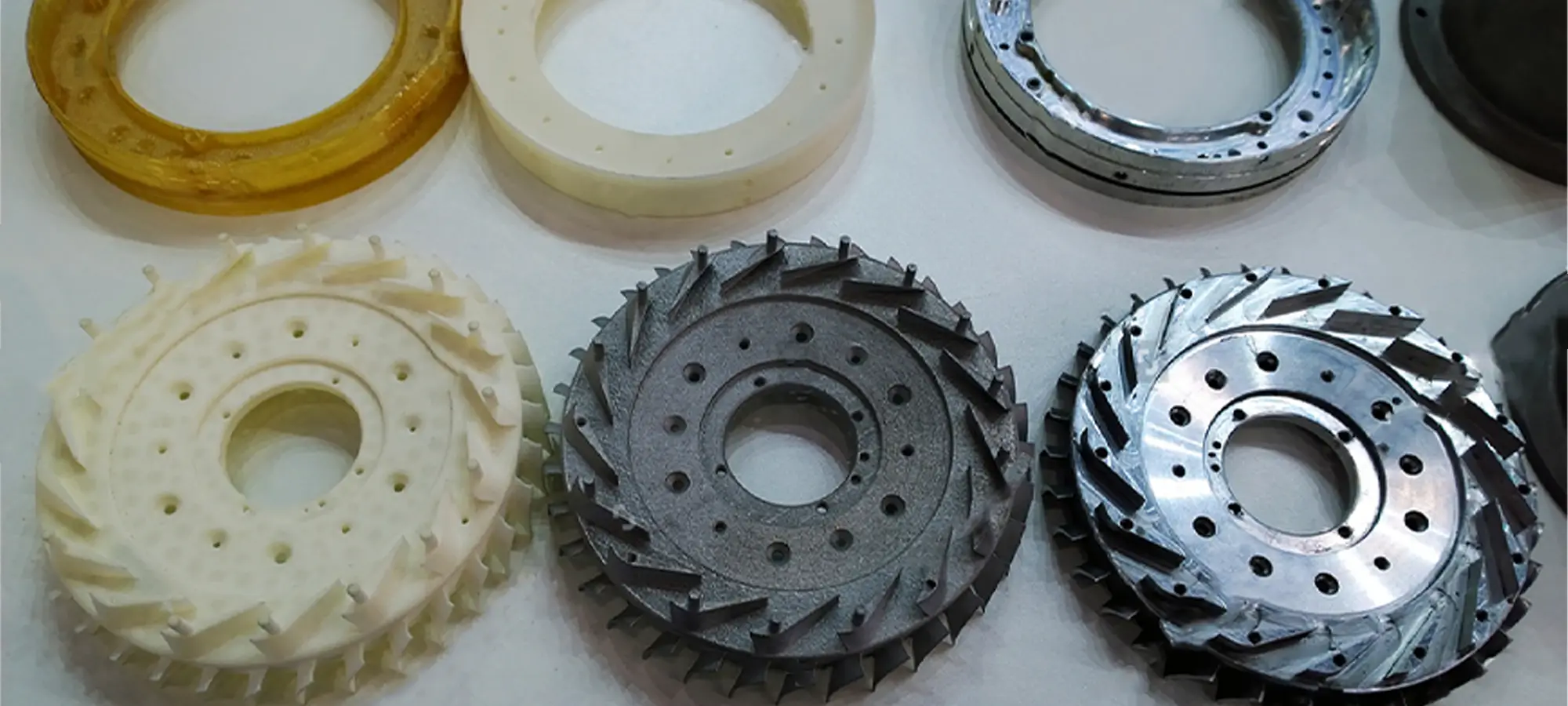

The accuracy can differ depending on appearance, size, interface with user and functionality.
Low Fidelity Prototype: These are very simple and do not require much time during preparation. These are used for checking broader concepts. For example, preparing mock-ups for cardboards.
High Fidelity Prototype: These are closer in appearance and functionality to the actual part. Hence, require greater build time and precision for printing. Such as motor part or design specific prototypes.
Benefits of Rapid Prototyping
Rapid prototyping helps in reducing design & development time as well as the overall product development cost. In addition, the risk for losing the entire budget and time after the failure of parts post mass production is reduced to null.
It also allows testing the functionality of parts to certain levels. Rapid prototyping also helps in evaluating human factors as well as ergonomics.
Disadvantages of rapid prototyping
Apart from all the benefits it provides, there is a certain limitation to rapid prototyping as well. Technology lacks accuracy many times. Moreover, the added initial costs increase the development budget. Many of the rapid prototyping processes are expensive and pretty uneconomical to utilize.
One cannot match the strength and the surface finish of the prototype as these are made of different materials. One requires skilled labor to complete the task in all the stages of rapid prototyping.
Material available for the process is limited and sometimes is incompatible and useless for building certain prototypes.
It sometimes does create confusion for the developers itself. Not able to match the properties of the prototype with the actual part raise more questions difficult to handle.
What is 3D Printing?
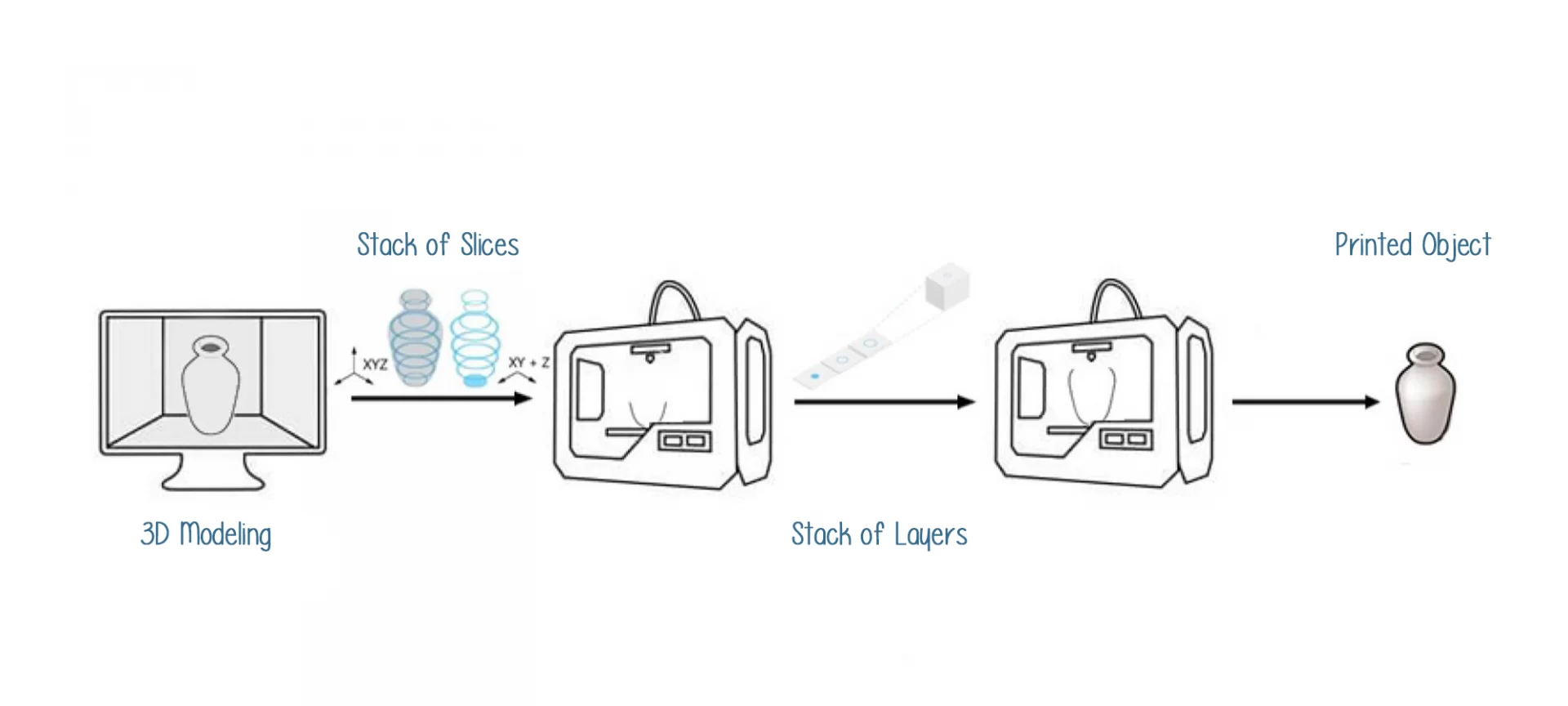
3D printing is a vast niche. With surging demand, the newer technologies for accomplishing additive manufacturing is been invested every now and then. While the start was slow, the growth has taken a steep slope upwards.
3D printing is now being used for various applications which were one sufficed for rapid prototyping.
The technology is being invested for bigger and important applications. For example, it is now easy to make prosthetics at a cheaper cost using 3D printing.
3D printing is even popular among aerospace applications for manufacturing lighter and stronger parts. Even fashion and jewelry designing are made simpler with the help of 3D printing.
These are just a few examples. There are many things that have been done using 3D printing and rapid prototyping is one of them. Can we consider jewelry 3D printing and 3D printing the same? It isn’t possible. Similarly, rapid prototyping uses 3D printing for creating prototypes and should not be termed as 3D printing.
3D printing involves creating each layer at a time and then adding the next layer over one another for completing the manufacturing. That is the reason why it is also known as additive manufacturing.
The different 3D printing processes part with different mechanical strength and visual finish. And, these processes work on different principles as well.
For example, fused deposition modeling uses filament material that is heated and melted and deposited layer by layer to form the three-dimensional object. Whereas, SLS works with powdered material which is melted by a laser beam selectively to produce parts. This also happens layer by layer.
The parts created by SLS are isotropic which is not possible with FDM and one can see visual layer differences. There are many other processes involved in 3D printing for printing different materials of varying strength and properties.
What is the Difference Between Prototyping and Rapid Prototyping?
Although the article lists a lot of reasons why consider rapid prototyping and 3D printing dissimilar, here are a few more to make the concept clearer. There are many components that make these two terms different. Let us see a few of the major ones making 3D printing and rapid prototyping completely different from each other.
Price Comparison
Rapid prototyping is costly when compared to 3D printing. These days, 3D printers are available in desktop-based versions. These are smaller and require less maintenance.
However, machines for rapid prototyping take larger space and are expensive to maintain. Moreover, the labor cost for many small 3D printers is close to null. An individual can operate these desktop-based 3D printers on his own without a need for a helping hand.
However, we cannot state the same thing for machines used to make prototypes.
In addition, the material used, the depreciation cost and many other factors tend to put rapid prototyping on an expensive side. It is more than double the cost of 3D printing. You may have to spend more than $10,000 yearly on your machine.
Printing Complexities
3D printing can be used for many complex tasks with minimum training and other’s support. Most of the 3D printers come packed with all the settings. All one needs to do is fit in the material and a few other parts and plug the system for starting the printing process.
However, this does not hold true for rapid prototyping. There are complexities in adjusting the parameters. The most common 3D printing process involved in 3D printing is SLA also known as Stereolithography.
In this process, the photosensitive resins are used as material. These resins are cured using a laser beam. Each layer solidifies and another layer is prepared over it. This goes on until the prototype is ready. The machines are mostly found in industries and are not easy to operate.
Application Areas
As mentioned earlier, the application of rapid prototyping is limited to industrial usage. It cannot be used for individual or small scale production. One can only build prototypes for assessing the design and appearance of the actual parts.
However, with 3D printing, the sky is the limit. Even when talking about the possibilities at this time, someone would be researching for finding more applications of the technology.
There are many ways scientists and researchers are utilizing technology to bring changes to the way manufacturing is carried on.
Companies are involved in producing printers with lower cost and higher efficiency. The technology is available to houses and for personal use. From learning institutions to mass production, 3D printing is being utilized for numerous tasks.
One can even buy a 3D printer for making toys for own kids. Or, one can build an entire business based on 3D printing.
While rapid prototyping is all about getting the trial part done, 3D printing keeps widening its hands towards better and efficient manufacturing needs.
Accuracy Levels
This is where rapid prototyping takes the lead. Using Rapid prototyping one can build parts with high precision and clarity and with better finish when compared to the 3D printers. It is also true that everything depends on the degree of geometry available and the technology used for 3D printing, rapid prototyping still is the showstopper. Using most advanced and accurate technology, rapid prototyping is considered to provide better accuracy levels than the desktop-based 3D printers.
It won’t be wrong to specify though that the newer technologies and better 3D printers are being designed continuously. Sooner, if not more, a similar level of accuracy may be introduced in the 3D printers as well. Who knows what the future entails? But the way 3D printing is progressing, nothing seems impossible.
Choices of Material
Material choices for 3D printing are not as much as for rapid prototyping. Although the newer materials are being introduced with time, rapid prototyping still works around a greater number of materials than 3D printing.
This may not bother those whose requirements are limited to the materials already available for 3D printing. What about others who are not able to enjoy the benefits of 3D printing because of the incompatibility of material they use for manufacturing.
Use of Technology
Rapid prototyping can be done using other technologies as well apart from 3D printing. For example, CNC Machining Prototyping, Vacuum casting, and Investment casting. However, 3D Printing can only be done through the additive manufacturing process.
The Conclusion
3D printing processes are very much useful in producing prototypes. But these are not the only option when it comes to creating test parts.
There are many other traditional methods that can be utilized for rapid prototyping. This may clear the confusion that makes it difficult to differentiate 3D printing and rapid prototyping.
Prototypes have been a huge help to industries for ages. These smaller yet similar designed parts have assisted manufacturers and businesses in eliminating the unknown and unseen factors many times. Because of this, there has always been a search for technologies that can better suffice rapid prototyping in terms of time consumption and price.
The major reason why additive printing was invested was to speed the rapid prototyping to ensure that the businesses do not have to wait for months and weeks to get the prototype done.
And, 3D printing succeeded in many ways. Some may confuse thinking the two terms the same, but these are completely different. One needs to see that fine line that clears the fog to see through the differences.







