Aluminum is one of the various materials that 3D printing is tying its knots with. We all are familiar with Aluminum as one of the most useful metals for manufacturing things that we use in our daily lives.
Aluminum is used for making varied products like cans, foils, kitchen utensils, window frames, beer kegs, and airplane parts.
And, there is no doubt that 3D printing Aluminum will offer more room for innovation when compared to manufacturing using traditional methods.
And this is because of the inherent benefits of 3D printing technology like mass customization, lightweight manufacturing, dimensional level accuracy, more efficiency, and a lot more.
In this article, we will primarily target exploring the various tips associated with 3D printing Aluminum. But first, we would like to establish the fact that it is possible to 3D print parts made of Aluminum.
And if you do not believe us, simply visit the website of 3D printing service providers such as Sculpteo, i.materialise, or 3D Hubs and order 3D printed Aluminum parts straightway.
So, the question is: Which 3D printing technology can help create parts made of Aluminum? And are there some tips with which closest to desired quality Aluminum parts can be made? You’ll get answers to such questions in our article. Excited? Let’s get started.
Which 3D Printing Technology Can Create Aluminum Parts?
For manufacturing Aluminum 3D parts, you need to majorly make use of DMLS 3D printing technology which is a short form of Direct Metal Laser Sintering.
It is a 3D printing technology that was developed by EOS firm manufacturing 3D printers based in Munich, Germany. The first EOS 3D printer EOSINT M250 came into the 3D printing market in the year 1995.
The other technology is commonly called SLM, the abbreviation holds for Selective Laser Melting. The credit for developing SLM 3D printing technology is given to Fraunhofer Institute ILT in Aachen, Germany.
Often these two technologies are misconstrued as one single 3D printing technology which is not true. And you will know it in a while, how?
What is DMLS 3D Printing Technology?
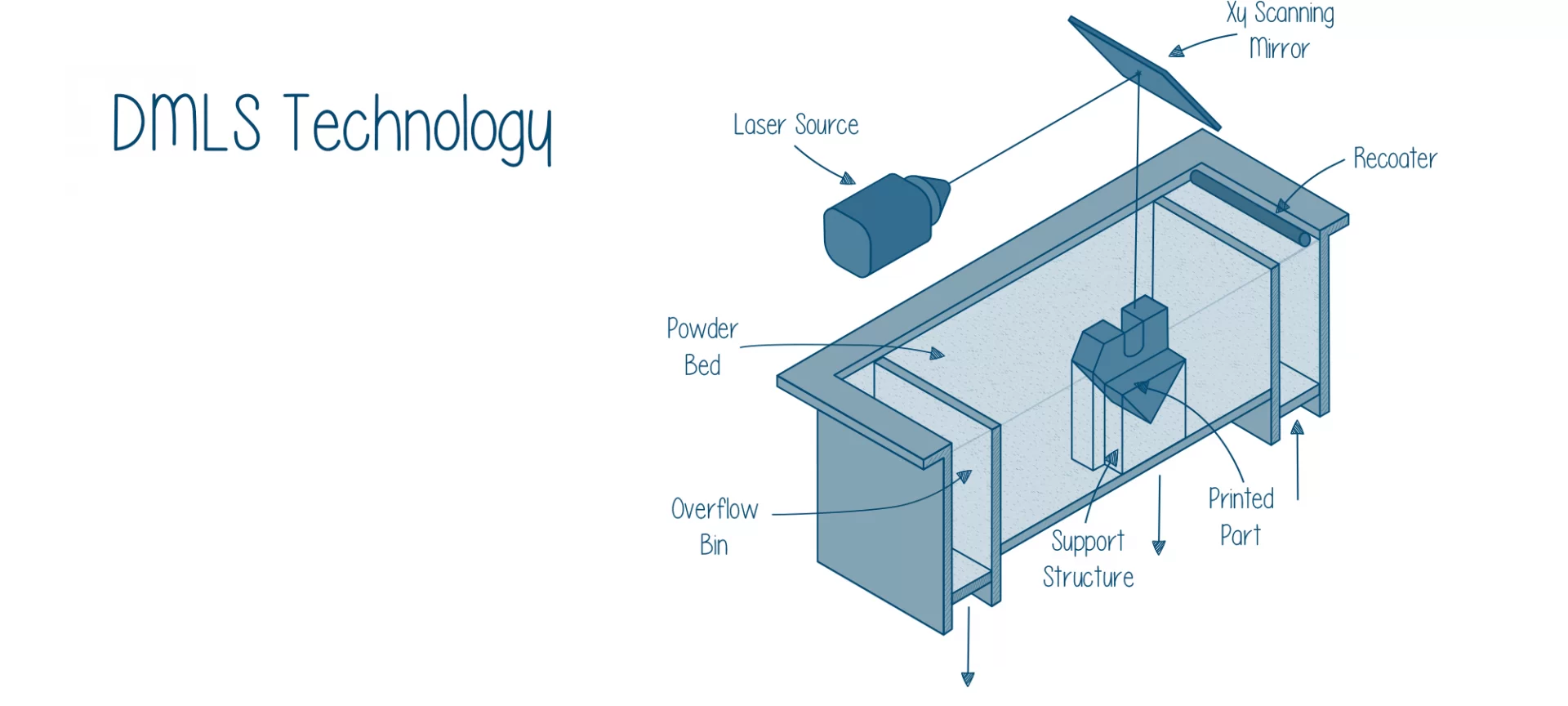
After the 3D model of the object that you wish to manufacture is sliced and fed to the 3D printer, like every other 3D printing process, DMLS too begins.
- Step 1: The process commences with the DMLS printer hopper being filled with the desired metal powder, which while 3D printing Aluminum would of course be Aluminum. The heaters fixed inside the printer will do their work of bringing the Aluminum powder near the sintering range. Additionally, by doing this work, DMLS printers will make use of inert gas. This would protect the heated powder during the process of part building.
- Step 2: The building of an object begins with the spread of a thin layer of Aluminum metal powder onto the build platform of your DMLS 3D printer. Now is the time for the laser to do its duty of selectively sintering the Aluminum powder into a solid. The spreading of powder as well as sintering continues to happen layer-wise until the complete part is built.
- Step 3: After the part is completely built it is left to be cooled and then the loose material surrounding the Aluminum metal powder is removed from the printer. The last step involves support material removal and does the remaining post-processing work.
This is a basic way in which 3D printing Aluminum happens via Direct Metal Laser Sintering method. Now, let’s go through the basics about Selective Laser Melting to know how Aluminum parts are made through it.
What is SLM 3D Printing Technology?
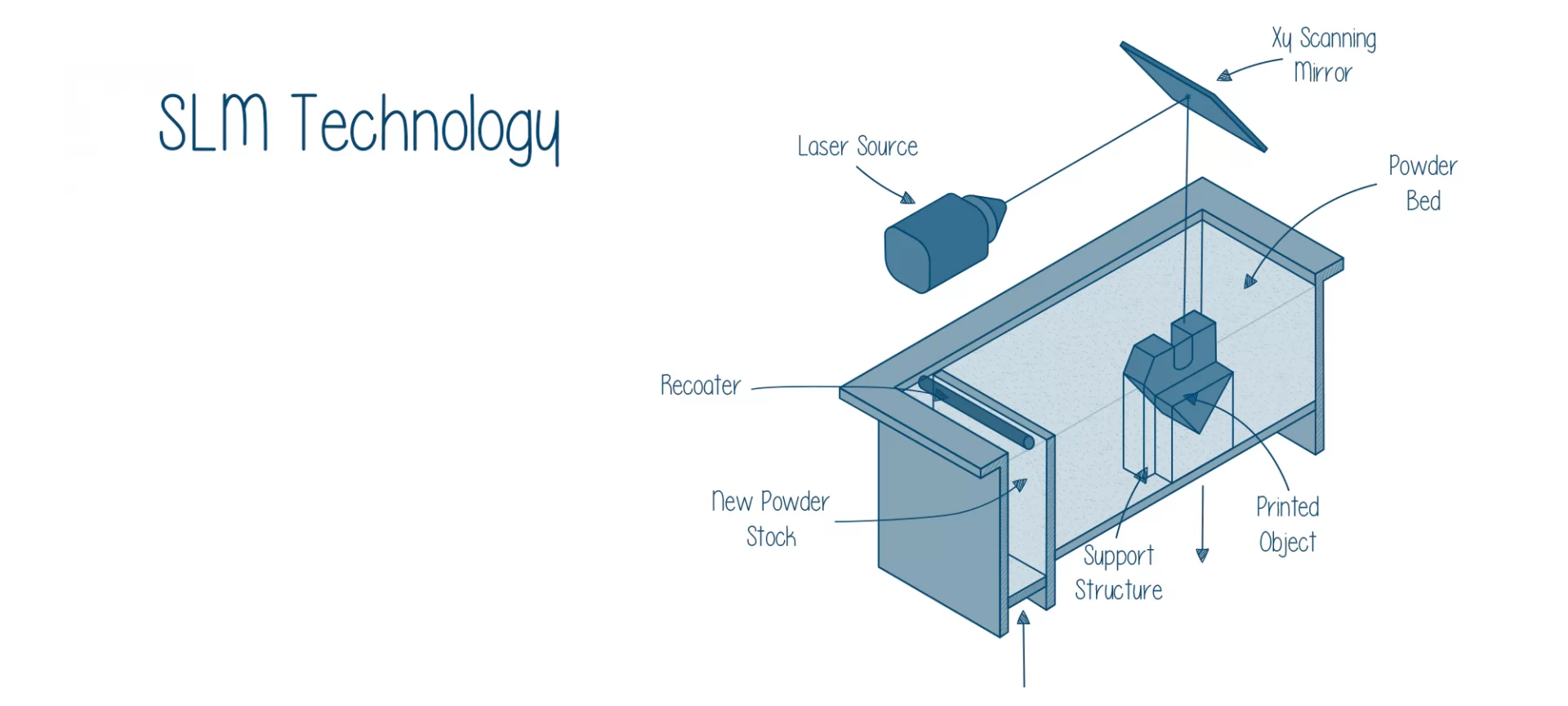
Both, DMLS as well as SLM fall under the powder bed fusion 3D printing category, but are different than each other.
- Step 1: The chamber filled with Aluminum metal powder is spread across the substrate or build plate of an SLM 3D printer in very thin layers by a coater blade.
- Step 2: A high-power laser source starts fusing a 2D slice of the model by particularly melting the Aluminum material. The build plate of the printer then starts to drop down by the height of one layer while the coater spreads another layer of fresh powder finely across its surface. The same process is repeated until you have the finished part.
- Step 3: This complete process is performed in a controlled atmosphere inside the SLM 3D printer. Once the part is completely built, it can be removed from your SLM 3D printer. The manufactured parts need to be removed from the build plate which is often done with the help of the bandsaw. After which you need to remove the support structures that are used in this process. At times when the support material is made from the part material, the removal process can be difficult and time-consuming.
- Step 4: Sintered parts are often known to have a rough finish because of which you need to do some post-processing. It is commonly known to machine parts for achieving fine tolerances as well as finish fine features, surfaces, and holes.
This is the other method with which you can 3D print Aluminum parts. And the difference between it and DMLS is that SLM melts Aluminum while DMLS fuses or sinters it.
Now let’s go through one of the common materials used for making Aluminum related parts or functional prototypes.
What is AlSiMg0.6?
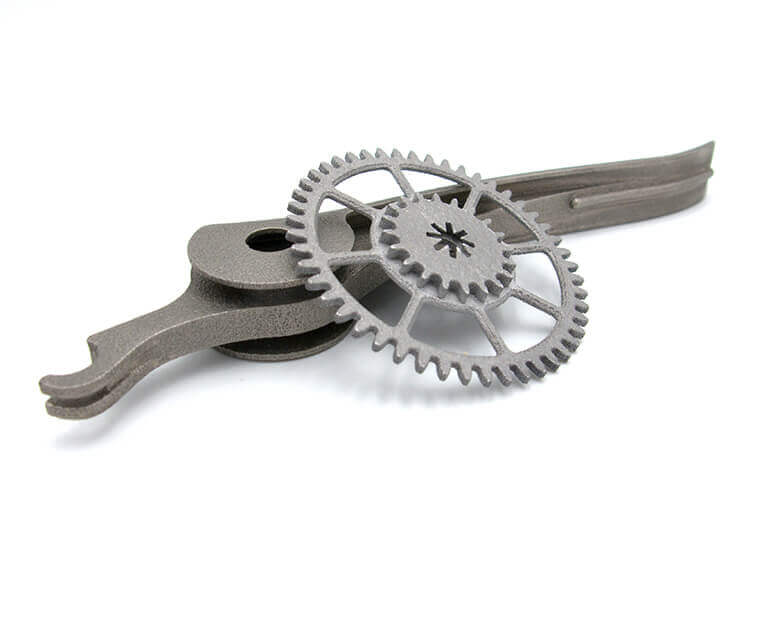

This alloy of Aluminum is used by the 3D printing service provider Sculpteo for 3D printing Aluminum. Objects 3D printed by this material are 90 percent composed of Aluminum, 7 percent from Silicon, and 0.6 percent from Magnesium.
The material has good mechanical properties that can be used for making parts that are subjected to high voltages. It is durable and light in weight and has a composition that makes it very suitable for molding. AlSiMg0.6 is commonly used in foundries for fine objects and complex geometries.
Aluminum is a material that’s fused at a very high temperature, and metal additive manufacturing requires great technical expertise for the pre-study of the thermal and mechanical effects before the 3D print.
In addition, it requires excellent knowledge of the finishing techniques for the completion of the object. By 3D printing Aluminum, you can print parts that are often most successful in projects where 3D printing is fully justified because it is the best production method, compared to other manufacturing techniques.
Especially note that 3D printing Aluminum is often advantageous for manufacturing:
- Complex designs/wired geometries/non-demountable mechanisms
- Increasing speed of production and reducing assembly time
- While doing short runs
- Topology optimization/weight reduction
- Mass customization
- Remote production
What are the Applications of 3D Printing Aluminum?
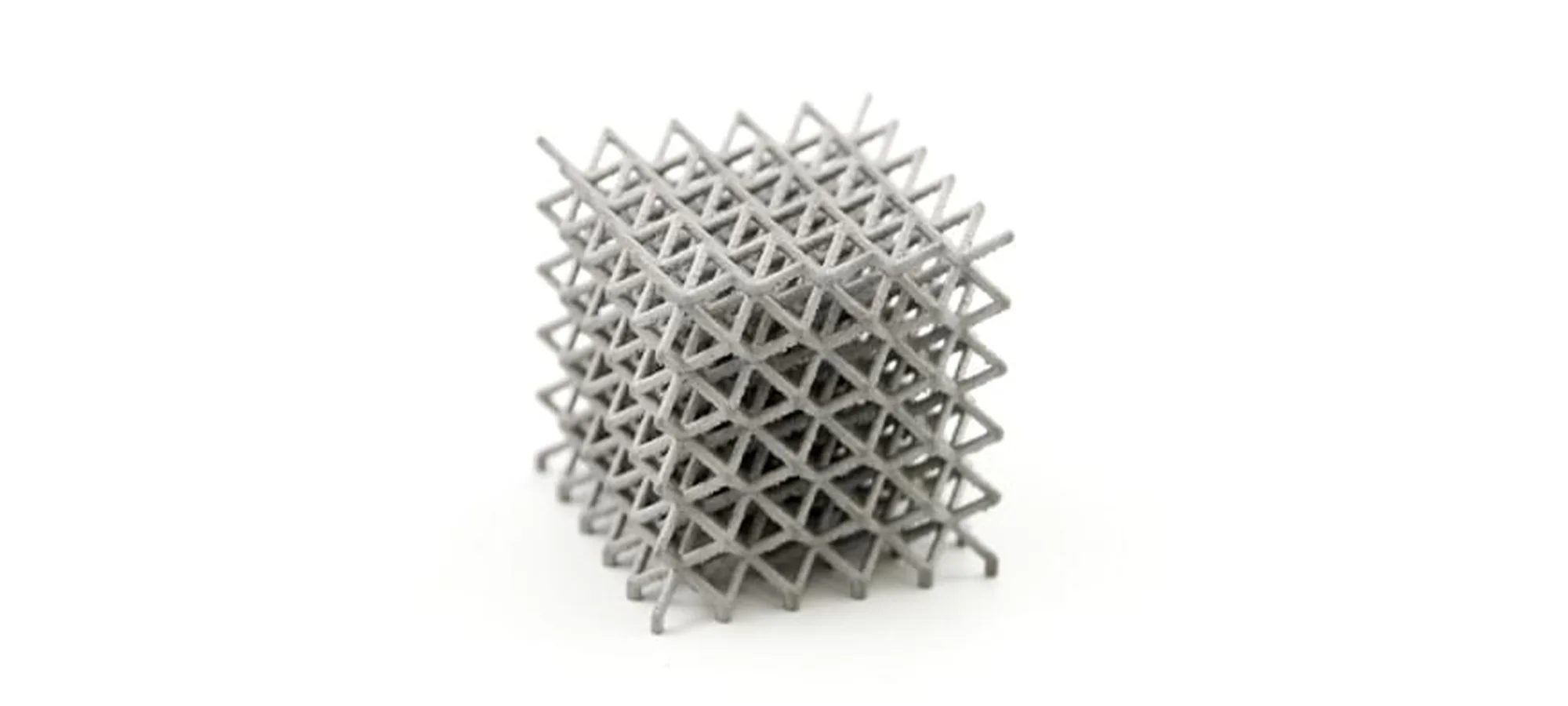

The base used in Aluminum 3D printing is an Aluminum powder that’s sintered together using a high-powered laser source.
Models printed in Aluminum are known to have characteristics such as being very strong, precise, and handling details of 0.25mm.
3D-printed Aluminum is often used for fully functional parts as well as spare parts and is also suitable for printing jewelry.
Moreover, some Aluminum as such as the one from i.materialise comes in a natural gray finish which looks a little different from the traditional, shiny, milled aluminum – it’s slightly grayer and more matte.
How to Design a Great Aluminum 3D Print?
When designing a 3D model with Aluminum, there are some basic rules, tips, and tricks which if take into account would be extremely beneficial to you.
The minimum wall thickness of the part or functional prototype that you manufacture with Aluminum should stick to is 1 mm wall-thickness-3d-print.
In scenarios wherein you would like to have small details on your print, Aluminum is a good material to do so. Also, DMLS and SLM technology allow a very fine level of detail, even as small as 0.25 mm.
But additionally, note that, if your details consist of engraved or embossed text, your letters will need a minimum line thickness in the order of 0.4 mm, a minimum height of 0.4 mm, and a minimum depth of 0.15 mm 3d-printed-details.
While designing your 3D model with Aluminum, you should take a second to think about the geometry of your design whether it has angular shapes, right angles, and straight lines or not? If yes, it can look a bit less attractive compared to freeform or organic shapes!
So, in such scenarios, it is better to have steep angles of more than 35°. This is because they are likely to have better, smoother surfaces.
Also, note that angles measuring less than 35° and overhanging structures are known to have poorer surface quality. The ideal shape when using DMLS and SLM is that of a mesh, such shapes are easy to design and deliver the best results.
If you are using DMLS technology, a high-powered laser sinters Aluminum powder together for forming your print. However, support structures are a must as they keep your model rigid during printing and also prevent internal stress and deformations.
In case you would not use support structures, try for walls or overhangs with angles above 40° Lower than 40 would mean that they are in danger of collapsing during the printing process.
Such structures are automatically generated and 3D printed in Aluminum. After they are printed, they are removed manually and, finally, the part will be sandblasted for achieving a smooth finish 3d-printed-support.
If you do not mind having design holes in your model, you should take into account a minimum diameter of 1 mm. Otherwise, the Aluminum powder will get stuck inside the print and we won’t be able to remove it.
Finally, always remember that nested objects i.e., objects floating within another object, hinged, and interlinking parts, for example, chains, cannot be made using the technology of DMLS because support structures are must while printing these structures.
It’s also advised to learn more about 3D-printed Aluminum, and the complete information concerning a) the material, b) colors and finishes, c) design guides and d) technical specifications.
If you already have a 3D model and would like to print it in Aluminum there are many finishes available on Sculpteo, i.materialise as well as 3D Hubs.
For availing of their services, all you need to do is:
- Simply upload your file.
- Choose Aluminum and see the price in seconds.
The Conclusion
Apart from the Aluminum alloy mentioned in the article AlSi10Mg is also a material with good strength, high flexibility, and outstanding thermal properties which can be 3D printed.
Both these materials have remarkable mechanical properties, serve multiple industries, including biomedical, automotive, and aerospace.
They can be easily molded and used for functional parts requiring stiffness, low weight, high strength, and high accuracy. They are also corrosion-resistant and are ideal for outdoor applications.
Recently, researchers from HRL Laboratories developed a new method, apart from DMLS and SLM for 3D Aluminum 3D printing called neofunctionalization. This is particularly for 3D printing high-strength aluminum alloys, including Al6061 and Al7075.
This process involves feeding a printer nano-functionalized Alumina powder, which is then heated until it forms an object. Futurism reports that the printed structures maintain their alloy strength and do not crack, owing to the nanoparticles acting as nucleation sites.
The research is published in the September 2017 issue of Nature and is a testimony that aluminum 3D printing is making significant progress.
Apart from the 3D printing services mentioned in the article, Shapeways, Desktop Metal and Markforged also offer the service of 3D printing Aluminum.
It is important to note that there is a huge difference in the quality of 3D printing Aluminum than manufacturing it with other manufacturing processes.
With 3D printing Aluminum, you can avail yourself facilities of mass customization, achieve dimensional level accuracy, and turn all your dream ideas about various parts and functional prototypes into reality.
While that is not possible with traditional manufacturing technologies! And this is the reason that this domain reports a scope of a good future with this material. Because more and more industries dependent on Aluminum parts are turning to 3D printing and the trend is increasing.







