With FDM 3D printing’s failure in not letting people achieve the kind of quality they wish to, there has been a search for a 3D printing technology that is not only able to provide a satisfactory volume of part or functional prototype, but also quality.
And this search has led people to opt for Stereolithography, Powder Bed fusion techniques, and even Electron Beam Additive manufacturing, and maybe a lot more.
DMLS 3D printing stands for Direct Metal Laser Sintering technology. As the name suggests, those who know even the bits and pieces of 3D printing technology would understand that it has something to do with Laser Sintering techniques.
In this article, we are going to take you to four important aspects of this technology. Starting with the overview of this technology, its history, how does it work inside a 3D printer that you purchase, its advantages and limitations. So, let’s get started.
What is DMLS 3D Printing?
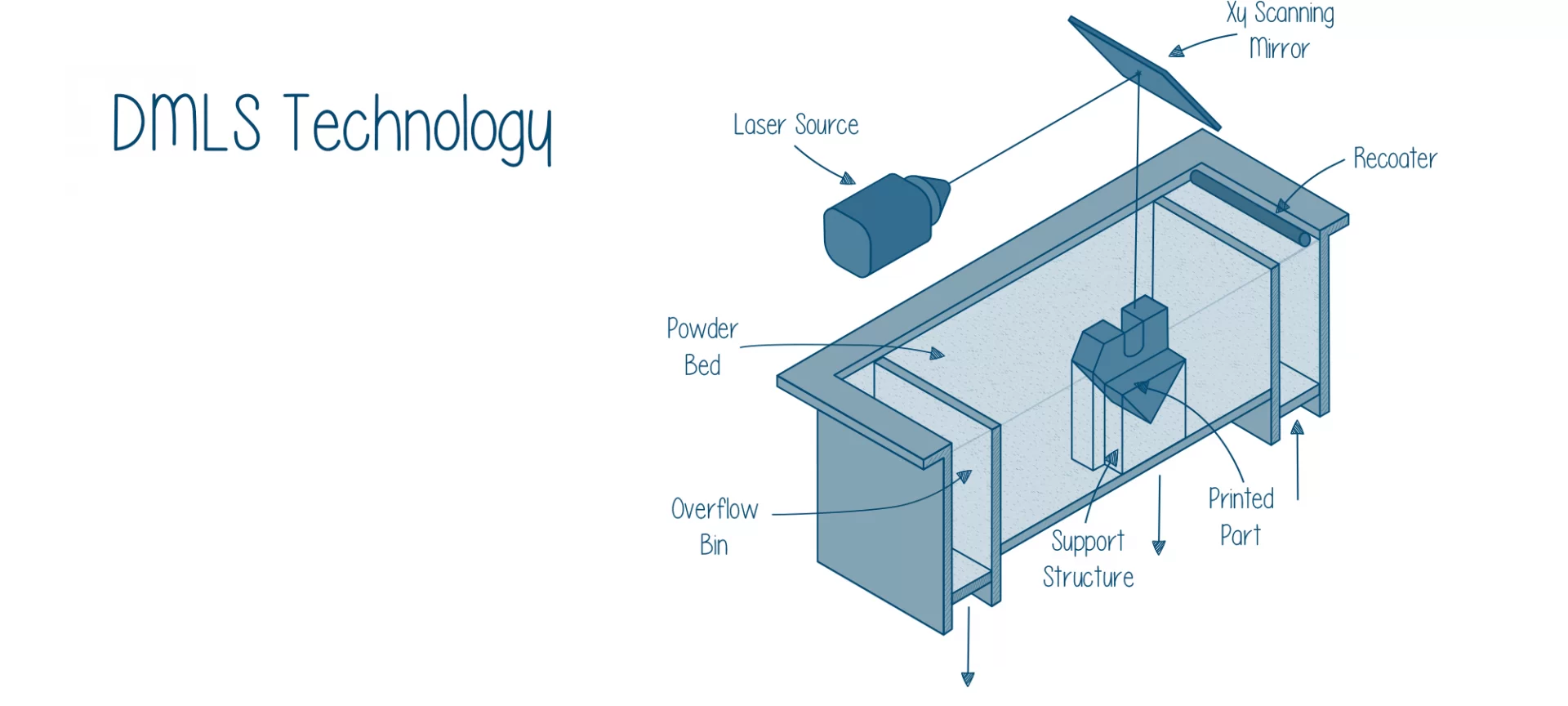
This process of 3D printing is often referred to as the modern powder metallurgy process of manufacturing parts and functional prototypes.
It is a much more mature process of metal molding technology that uses heat and pressure for forming metal parts and functional prototypes that finds its applications in various fields.
So one thing you get to know for now is that you are dealing with metal powders, instead of filaments and resins as in the case of the two most popular techniques for 3D printing i.e. FDM and SLA.
Typically the metal particle size is in the order of 20 to 40 micrometers.
This particle size is important when seen from the layer resolution of the final part or functional prototype.
The smaller the particle size, the finer the order of layer resolution in the manufactured part or functional prototype.
Factors such as layer height and laser spot put resolution limits to DMLS 3D printing technology.
There is always an ongoing competition between companies that manufacture printers based on this technique versus the companies that make 3D printers based on SLM 3D printing.
However, there is a basic point of difference between the two technologies.
Point of Difference Between DMLS 3D Printing and SLM 3D Printing
Fusing the metal powder and the temperature range used for the same is where the difference comes between DMLS 3D printers and the SLM 3D printers.
SLM 3D printers will heat the powder that is spread on their print beds until the powder completely melts into a liquid. But DMLS 3D printers do not go to that extent.
So, a lesser amount of energy is needed for operating DMLS 3D printers compared to SLM 3D printers.
For this reason, DMLS is more famous with metal alloys whereas SLM works best with pure metals.
History of DMLS 3D Printing
The story of this 3D printing technology started with the invention of Selective Laser Sintering technology.
EOS, a company based in Munich Germany is known to have developed additive manufacturing technologies for laser sintering of metals and plastics.
Till the time the company gained worldwide rights of SLS 3D printing technology, the advances in the development of even more efficient technology.
And that quest of developing the technology more and more, the company led to finding DMLS 3D printing technology for manufacturing of parts and functional prototypes.
The first lot of DMLS 3D printers were produced in the year 1995 and since then, EOS has been a leader in this technology to date.
A little bit of controversy lies in the legal part of issuing a license for SLM 3D printing technology which was developed around the same time when DMLS 3D printing technology was developed.
The only change being SLM was developed at Fraunhofer Institute of Laser Technology.
SLM has also advanced over these years, with the court issuing multiple licenses and cases in the matter.
Each of the issues was however not related to the technology, but for breaking the licensing agreements, EOS emphasizes DMLS and also holds an interest in the SLM 3D printing technology through their licensing agreements which it shares with Trumph Gmbh.
How Does DMLS Printing Work?
The model, slicing, and printing layer by layer is one pattern that DMLS shares with other 3D printing technologies.
The change comes in the mechanism once a model is created and sliced with the suitable software.
However, once the code needed for making the part or functional prototype is supplied to the printer, the process of 3D printing can begin.
For starting the desired DMLS 3D printer, the hopper of the printer is filled with metal powder that you wish to print the part or functional prototype with.
Once the process is started, the heaters of this printer start heating the metal powder to a temperature that is in the sintering range of the corresponding alloy.
For the execution of this complete process an inert gas is used. The use of inert gas is for protecting the heated powder as well as the part as it is built via the 3D printing process.
The building of layer after layer begins with a thin layer deposition on the build platform of the 3D printer.
Once this process is completed then the laser’s participation in the process of 3D printing begins. Selective laser sintering of the powder into a solid part is done hereafter.
Whereas the sequence of dispensing a layer of 3D printing material and its sintering continues till the production of part is completed.
What remains, here onwards is the cooling of the solidified part or functional prototype.
When the part is exposed to cool down, the surrounding loose metal powder is removed from the printer as a part of the post-processing and other essentials are done.
The parts or functional prototypes manufactured from the DMLS process can then be sent for higher finishing using machining, heat treatment, or surface finishing.
All of the steps that we have stated in this process remain the same for SLM 3D printing as well, but instead of sintering the metal powder, it is melted, and then the process continues.
Pros and Cons of DMLS 3D Printing
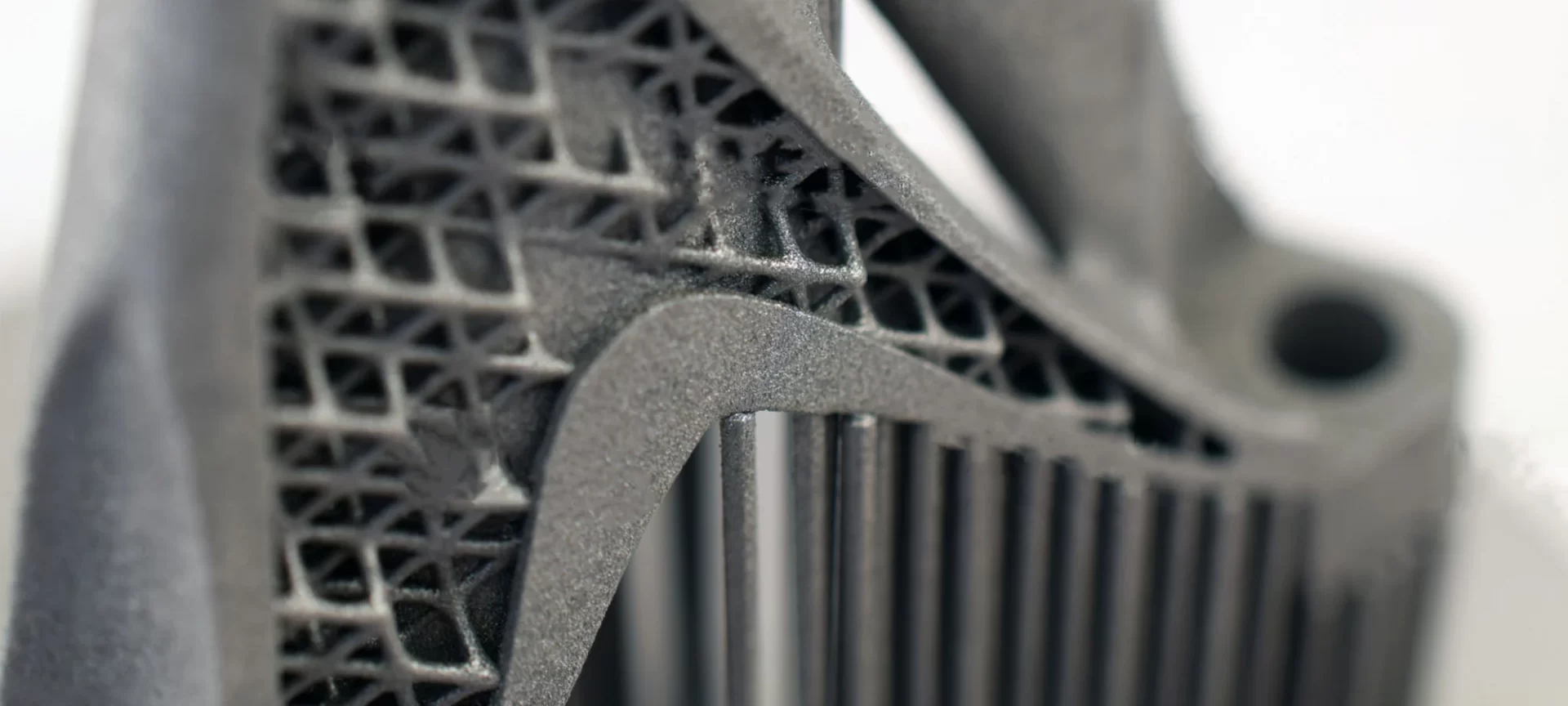
Every 3D printing technology that is used for making parts and functional prototypes has its own lists of pros and cons and so is the case for this 3D printing process as well.
Because DMLS and SLM are fundamentally the same procedure they share a lot of these pros and cons that we care about you have exposure to.
As far as the pros of this technology are concerned they are similar to most other 3D printing technologies.
The 3D printing technology in general offers an inherent benefit over all the traditional manufacturing technologies and that is: it builds part or functional prototype layer by layer and hence offers a very high quality of accuracy in all its parts and functional prototypes.
Because such a quality of a part or functional prototype cannot be made using any subtractive idea of manufacturing.
Having said that let’s look at the Pros of this method.
- Parts or functional prototypes can be manufactured directly using metal alloys or even pure metals. The properties of the raw material are not changed. Apart from printing directly from a metal or its alloys, mixtures of the metal powders can also be used for printing parts and functional prototypes that find their application in various fields.
- The variety of 3D printing materials used in this technology exceeds other 3D printing technologies because they are available in many forms such as steels, stainless steels, aluminum, titanium, nickel alloy, cobalt chrome, and a lot of other precious metals.
- When the finished part or functional prototype is compared with finished parts or functional prototypes made from other technologies, they stand out and impress the observer with their strength. DMLS is known to manufacture some of the strongest parts and functional prototypes because of which it is also considered as the method which can produce parts that can easily replace metals. SLM is also known to produce a stronger part, but in that technology, the printing material is melted.
- Lastly, the benefit of this 3D printing technology is that metal powder that is not used in the process can be reused so there is practically no waste that is produced in this additive manufacturing process.
- If you look at the cost of the 3D printers based on DMLS 3D printing and compare it using the build volume that they offer, you might find a huge difference in the price. And this is for a simple reason that, when you compare the layer resolution provided by other 3D printing technologies and compare it with the layer resolution offered by this 3D printing technology you would find a huge difference. The process yields a very good result but one has to wait for it as it is a slow process and the 3D printing materials are also expensive. Because of which small businesses are yet not able to prefer this 3D printing technology.
- When compared with a melted metal part, DMLS is known to produce relatively more porous parts. The porosity can be controlled when you are printing using DMLS 3D printing technology, but it can be completely eliminated neither during the process nor the post-processing.
- The kind of build volumes which can see an FDM 3D printer produce is not what DMLS 3D printers can. They have a relatively very small build volume. Because of which often people think the value of parts and functional prototypes produced using this technology cannot be equivalent to FDM or SLA 3D printing technology.
After having seen through various areas related to DMLS 3D printing technology, let’s look at the application that parts and functional prototypes produced by it are used for.
Application of the Process
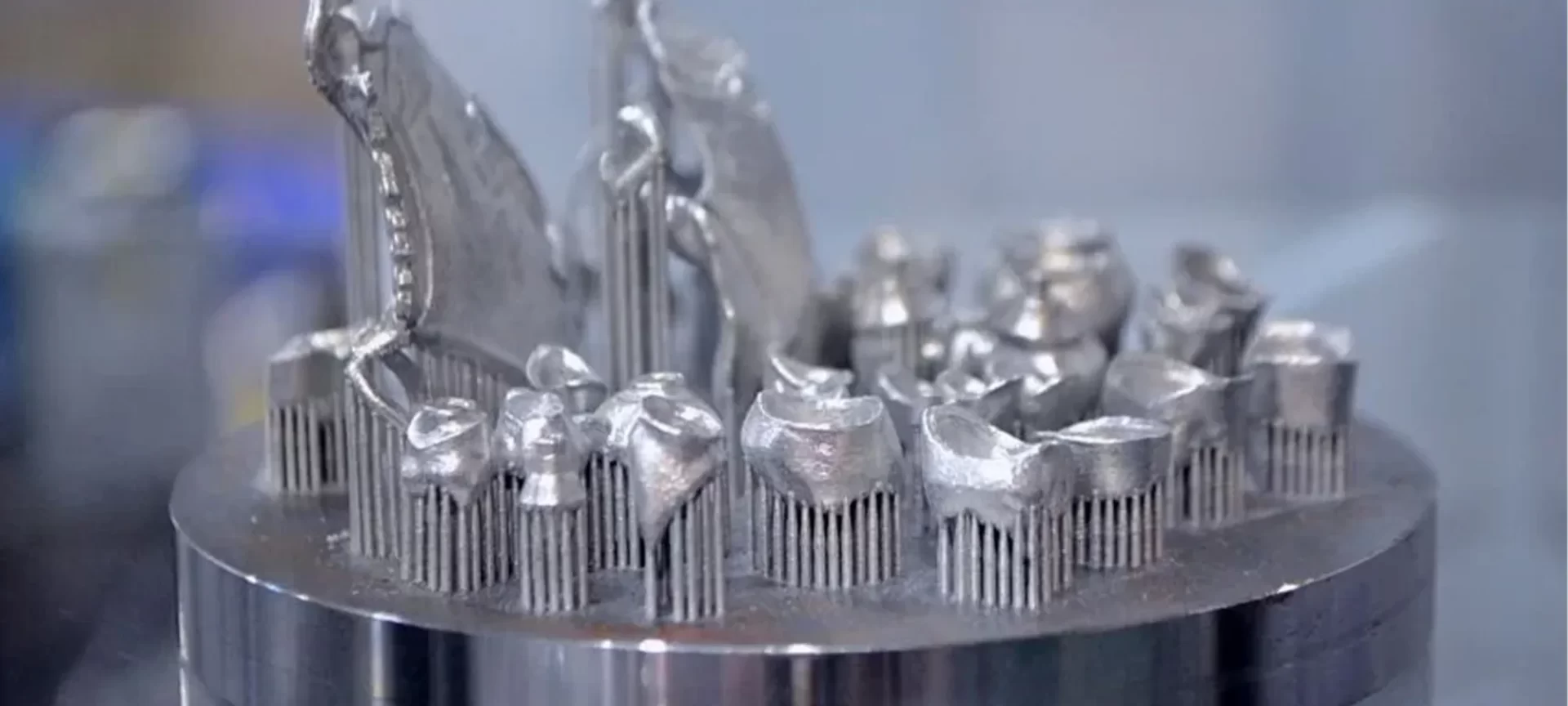

The process has found applications in the field of Medicine, Dentistry as well as Aerospace.
Starting with Medicines you would be able to see custom prosthetics modeled and printed using titanium alloy for replacing portions of bones that are lost in an accident or any other diseases.
Not only do they have the strength needed, but they are also resistant to attack by the body.
And the porosity of these parts and functional prototypes help bones grow into a prosthetic structure. These prosthetics can be customized according to the problem of the patient.
In dentistry, DMLS 3D printing is used for making bridges, crowns as well as partial dentures which can be easily modeled for the patient.
Even using high-strength materials such as Cobalt-Chrome. In the field of aerospace, DMLS is able to create complex geometries that other 3D printing technologies cannot.
Weight reduction which is the most important concern in the field of aerospace is accurately taken care of by this 3D printing technology.
As well as increasing the strength and durability of the parts and functional prototypes used in the industry is also some area where this technology is proven to be greatly beneficial.
Not only simple brackets and complex turbines can be produced using the technology, but also complete rocket exhausts can be a thing.
The Conclusion
People generally tend to have biased when it comes to 3D printing technologies. They tend to think that this technology is only applicable to plastics. But that isn’t the matter.
And technologies such as DMLS 3D printing proves so. Complex parts made from precious metals can also be manufactured using this 3D printing technology.
Although the technology is not yet able to produce parts and functional prototypes of the same volume SLA and FDM is able to, it is growing.
And with the growth of the complete 3D printing technology, who knows someday one will be able to produce the parts of the same build volume as SLA and FDM 3D printing technologies do, using DMLS 3D printing.
Because the research is on and the teams are working towards this agenda and making the technology more and more accessible and flexible and hence beneficial.







