The advent of additive manufacturing technology has given way for various other related development.
Working its way through the different niche, 3D printing has started impacting almost every sector. And, the medical industry isn’t an exception.
3D bioprinting is developed to provide the medical industry aid to fight against various problems that otherwise are difficult to solve.
We are talking about the additive manufacturing process which instead of using usual materials, involves biomaterials to imitate natural tissues. These could be cells along with growth factors that form structures similar to tissues.
In other words, you can create human organs with the help of 3D bioprinting. The process involves 3D printing and uses the technology to build biomedical parts while combining biomaterials.
The biomedical parts are created one layer at a time, as it happens in the additive manufacturing process. And, the steps continue until the final part is built.
It may sound very similar to working with an FDM 3D Printer. But it is not as easy as it seems, although the normal workflow does match the convention.
The researches are going at a high speed to explore the possibilities of the technology. By far, we do have made a lot of success in gaining benefits through 3D bioprinting solutions. However, a lot is still to be uncovered.
What is 3D Bioprinting?
You must have got a glimpse of what the technology entails and what it is like. But there is a lot more to the story.
3D bioprinting has brought a huge hope within the medical industry and researchers are making headways to find what relevancy it has with organ transplant and various other applications.
But what exactly is bioprinting? The technology works on additive manufacturing principles. Instead of standard materials, the 3D printers for bioprinting utilize bioink.
The bioink is used to create tissue-like structures. And, these structures are formed in a layer-by-layer manner.
The process has a huge impact on the fields of medical science and bioengineering. Talking about the recent advancements, bioprinting of cartilage tissue required for reconstruction and regeneration is already a reality now.
If you would look at the workflow, you would find it similar to any other 3D printer. You require a digital model to start 3D printing of the biomedical parts. And, this also happens layer by layer.
However, the process must be carried while maintaining proper sterile printing conditions. This is not only to ensures the accuracy of the complex tissues but also makes sure that the requisite cell-to-cell distances are perfectly fabricated to provide the desired output.
Processes Involved in 3D Bioprinting
The entire process can be categorized into three different steps as below.
Pre-Bioprinting
Pre-bioprinting is the pre-preparation process before the 3D printing of tissues starts. In this process, users create a 3D model as well as choose the 3D material for use in bioprinting.
To start the process, one first needs to acquire the biopsy of the organ. To accomplish the steps, the most common technologies available are computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
The technology initiates the tomographic reconstruction of the images. These images are created by isolating certain cells are then multiplying them as needed.
To ensure the proper availability of oxygen, the cells are mixed with a special liquefied material. This keeps the cells alive.
Bioprinting
In this stage, the actual printing happens. The 3D printer is introduced with the 3D image and the bioink to start the layer preparation.
The liquid mixture of cells, bioinks, and matrix goes into the printer cartridge for starting the deposition of each layer, at one time. This is done using the reference of the patients’ medical scans.
Post Bioprinting
The printer parts need to go through chemical and mechanical stimulation in order to form stable structures.
These structures are for biological materials. In case, the process isn’t well performed, the mechanical integrity along with the function of the 3D printed structure would stand at risk.
That is why the mechanical, as well as chemical stimulation, is the part of the post bioprinting process. Using these stimulations, signals reach the cells which direct the remodeling as well as the growth of these tissues.
How Does 3D Bioprinting Work?
There are several 3D printing processes in operation today. And, based on the specific technology, either extrusion, laser, inkjet, or acoustic, the bioprinting method also differs.
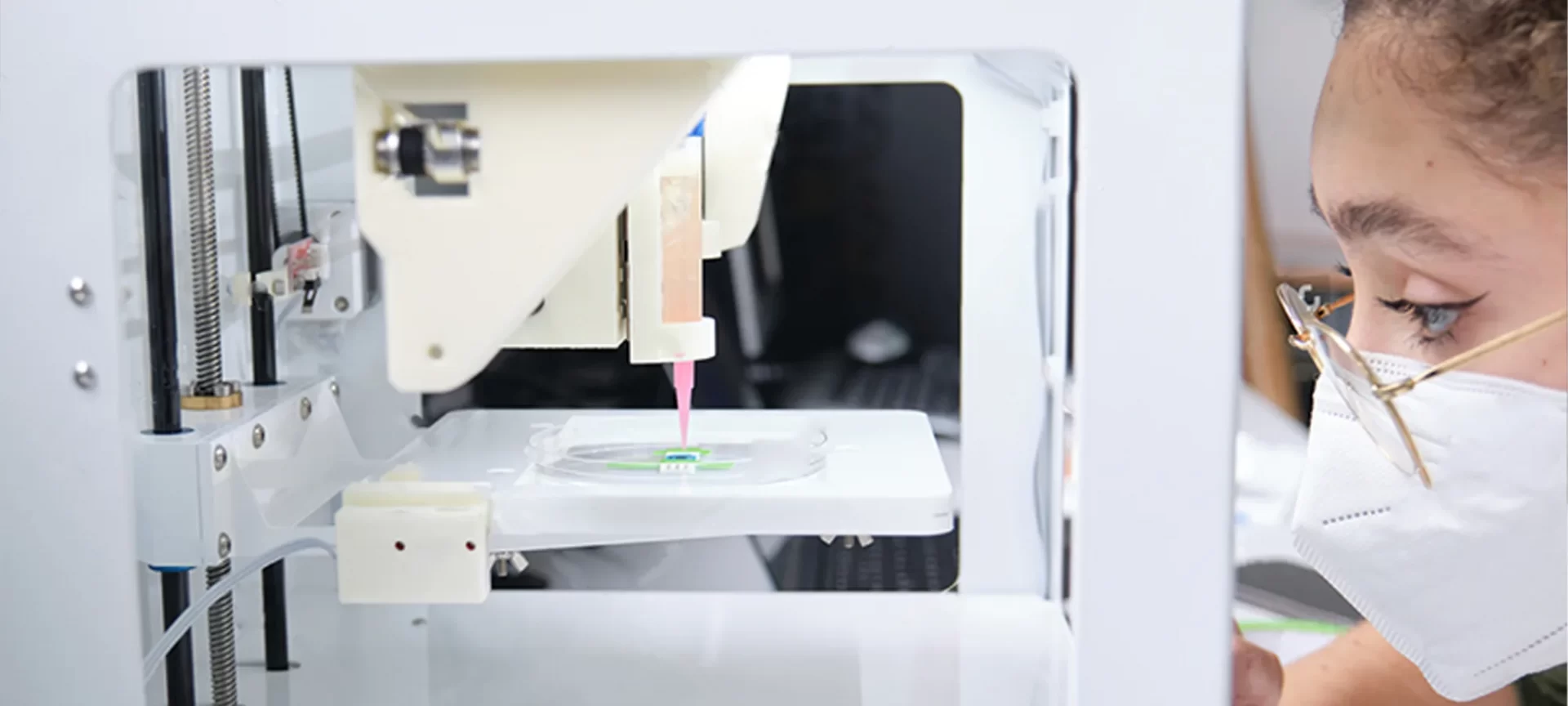

Among the differences that exist between these technologies, the basic workflow and typical process remain more or less similar. Hence, we can summarize the entire work in the following steps.
3D Imaging: 3D imaging is the process that helps acquire the exact dimensions of the patients’ tissue. To carry this, experts make use of a standard CT scan or MRI scan. To get the best results, the 3D imaging process must be carried with precision. It should help achieve the perfect fit for the tissue, needing no adjustment from the surgeons’ part.
3D Modeling: This is where the AutoCAD software pops in. It helps create the blueprint for the tissue. The blueprint even has the entire layer-by-layer instruction built-in high detail. If there are any little deviation, fine adjustments done on this stage would help avoid transfer to error yo the next stages.
Bioink Preparation: Bioink, as mentioned before is a very essential component in 3D bioprinting. It is a combination of a compatible base such as collagen, gelatin, silk, alginate, hyaluronan, or nanocellulose together with living cells. The base helps cells with a framework for growth and required nutriment for survival. The entire preparation of the substance is patient and function-specific.
Bioprinting: Now it is time for 3D printing with the prepared bioink. During this process, as it happens with the standard 3D printing machine, each layer deposits and hardens over the previous one, completing the tissue structure. The layer thickness of 0.5 mm or less is what we require to complete the process with precision. The amount of deposit of bioink would depend on the nozzle alongside the type of tissue used for printing. This mixture deposit is highly viscous.
Solidification: Although the layers that start with a viscous liquid solidifies to ensure the shape is perfect and not deformed in between of the printing process. The solidification carries on and becomes more prominent as more layers are deposited one by one. The entire process includes blending and solidification of layers. This is also referred to as crosslinking. Further the results are aided using specific chemicals, UV light, or even heat.
What id the Importance of Bioprinting?
The technology is impacting the medical field in various aspects. One of the greatest importance of bioprinting is that it can create tissue-like structures that are mostly similar to the actual human tissues and organs.
There are many advantages of the same. It can lead to better prospects in drug testing and clinical trials. Hence, probably reducing the dependence on animal trials.
If further pursued with success, bioprinting has huge potential to eliminate the organ donation and transplantation problems. Instead of waiting for years, one can easily print the organs of patients for transplants.
The matter of fact is that 3D bioprinting organs are the primary aim that the researchers are trying to accomplish as soon as possible. Along with that tissue repair is also possible with bioprinting. The technology helps sort out problems related to patient-specific.
What Are The Applications of Bioprinting?
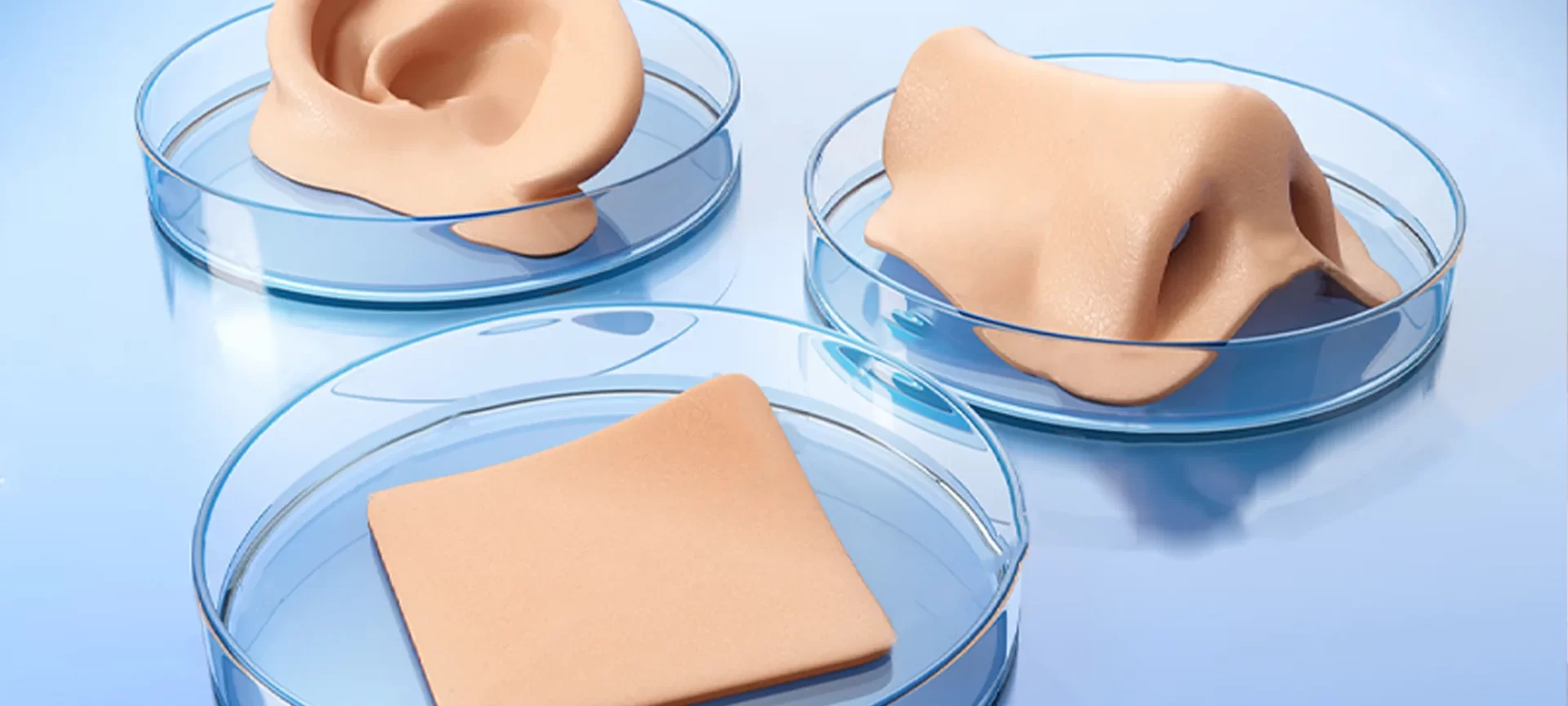

It is true that realizing the real potential of 3D bioprinting is far-fetched. However, there are a lot of developments already underway.
With some, we have already made a huge success and with others, we are still fighting to find the right solution. Here are a few applications that are possible with bioprinting:
As we know that the problem with organ failure is increasing at a higher rate, a need for a comprehensive solution is much needed.
In such a scenario, artificial organs could change the face of medical science for good. Being able to 3D bioprint organs could solve all the issues pertaining to the lack of availability of organs.
Hence, resulting in a faster solution to the patients. This would be a revolution for the entire healthcare system.
3D printing of tissues for pharmaceutical testing would erase the need for animal testing, providing researchers and scientists with a more ethical way to proceed.
One can also identify the several side effects of new drugs. Hence, allowing for better administration of correct dosage and proper precautions related to the medicines for humans.
Cosmetic surgery is another great application that would let patients avail of the perks of 3D printing to the core.
Skin grafting and plastic surgery is now a difficult process, involving the use of skin and tissues from another location on the patient’s body to cover the burn.
With bioprinting, these cells could be generated through 3D printing. Hence, eliminating the need for skin extraction from the patient’s body.
The other applications include bone tissue regeneration, prosthetics along with dental aids.
List of 3D Bioprinting Companies on Demand
With an increase in demand, the number of 3D bioprinting companies is rising. Although the number is yet limited, future prospects are very high.
Here are a few of the major players within the niche that could help accomplish your projects related to bioprinting.
CellInk

The company is based out of the USA. CellInk is engaged in the development of both bioprinters as well as bioprinting materials.
The company works for providing use models in order to help researchers as well as healthcare providers. You can count on CellLink for carrying personalized medicine research, 3D cell culture, and enhanced therapeutics.
Using technology, you can 3D print tissues. For instance, skin, liver, cartilage, and a lot more. Not just that, the company can help print fully functional cancer tumors. This can enable the development of better and newer cancer treatments.
Digilab

Digilab is a very well-established company in the bioprinting niche. It has been working since long now for creating technologies and 3D bioprinting solutions for clinical diagnostics and various other areas of life science.
The company has come up with its innovative CellJet 3D printer. The machine can 3D print cells with 95 percent viability.
By far, no 3D printer has been able to reach that benchmark. With its unique offerings, the company has been able to help with a lot of causes.
The printer can 3D-print cells which then be utilized for cancer biology, stem cell research, automated cell arrays, tissue engineering, regenerative medicine, or even cell-cell or cell-drug interaction studies.
Organovo
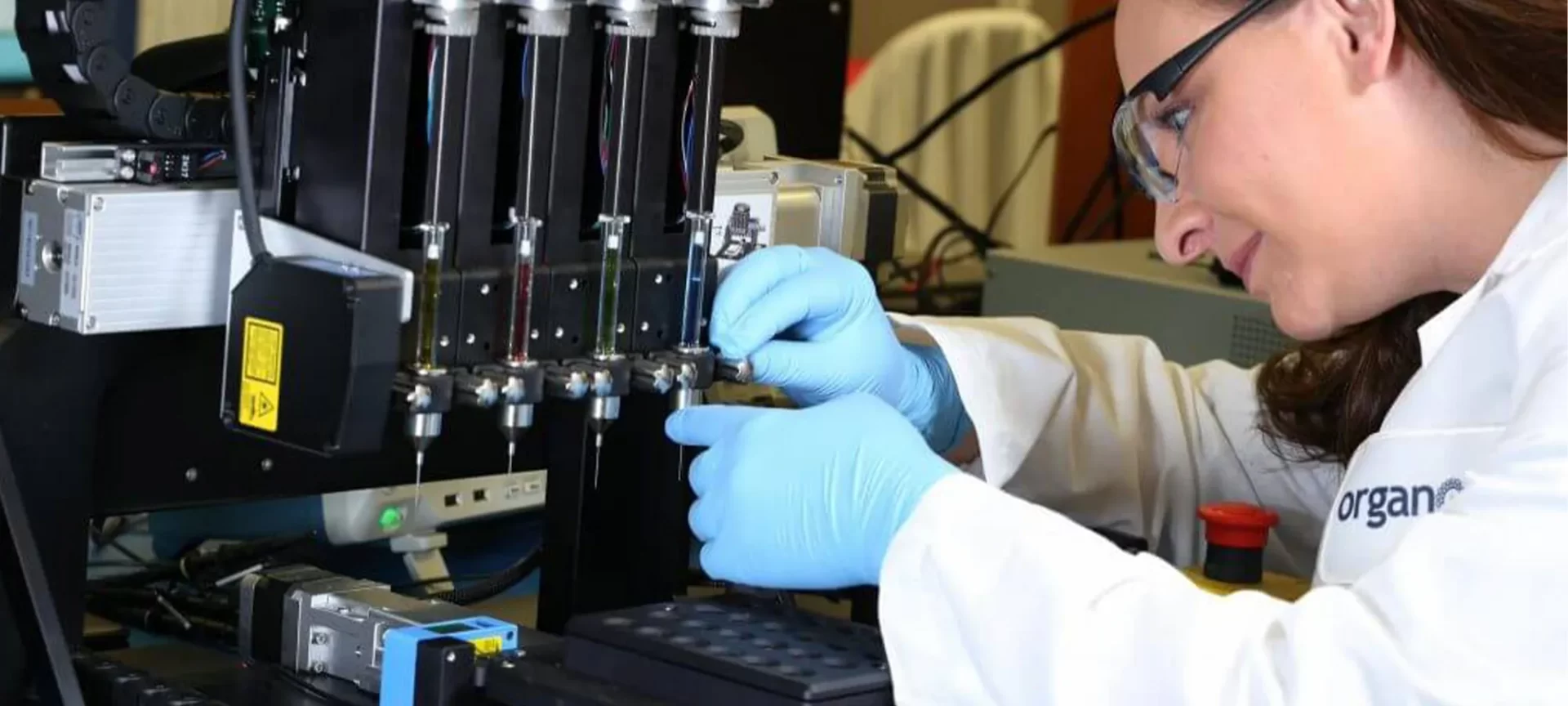

No way, we are going to leave this from the list. The company operates from San Diego and is very popular among the tissue engineering companies.
Organovo has been actively working rigorously to develop a line of human tissues that could enable medical research.
They are very precise with their aim and wish to profit industries working for drug discovery. They are capable of creating normal tissues as well as specially designed disease models.
The company’s goals are very progressive and they do think out of the box. Organovo, together with L’Oreal is working for the development of synthetic skin.
The Conclusion
From what you have learned from this article and on the basis of various possible applications of bioprinting, you may have realized how crucial is the technology for future developments.
And, you can also make out that the technology would keep growing with time. All the developed nations are already investing a huge amount to explore the possible potential of the technology.
Not only 3D printing is able to bring justice from an ethical perspective, but it would also become one of the most necessary technologies in the coming future.
It has been able to provide hope for better medical facilities. If given proper time and effort, the field of bioprinting would become an example for everyone.
3D bioprinting is definitely helping us through a lot of medical challenges currently. This does not limit its potential though.
There is more to it. And, with advancing time, the importance of the technology would be firmer and obvious.







