CNC (computer numerical control) is a way of automating machine tool control by using software installed in a microcomputer connected to the tool. It’s often used to machine metal and plastic parts in the manufacturing industry.
The machine control unit (MCU), a microcontroller linked to the machine, stores and executes a bespoke computer program for each object to be made, which is commonly written in an international standard language called G-code.
The program specifies the instructions and parameters that will be followed by the machine tool, such as the material feed rate and the location and speed of the tool’s components.
A CNC machine can convert raw material into a final model in a variety of ways, including adding (additive) or subtracting (subtractive) material. The approaches that are available are determined by the machine type.
Additive CNC machines, such as 3D printers, and subtractive CNC machines, such as CNC milling machines, are excellent examples.
What Are The Benefits of CNC Machining?

Productivity
You can often step away from a CNC mill or other machine while it performs a complex set of activities because you can program it to do so.
In particular setups, this can incorporate out-of-hours automated machining, greatly enhancing your productivity and pace of output. This is especially true for precision engineers that run many CNC centers, like Oracle Precision.
Consistency
CNC machines are exceedingly consistent and accurate in the work they create, giving clients uniform and faultless results because they almost remove human mistakes.
This is why CNC machining is so important in areas where quality is key because the work produced has a considerably better level of reliability and quality.
Efficiency in terms of cost
With a high rate of output and a smaller number of errors in the final components, CNC machines more than makeup for their initial expenses.
Operators also require less training and can learn how to run a CNC machine in a virtual environment, reducing the requirement for training workpieces. The cost of these machines will continue to decrease as they become more popular and widely used.
Safety
Unlike conventional open guard machining, any hazardous safety issues, such as a jam or other machining error, are solely damaging to the machine and not a safety risk for the operator.
Versatility
CNC machines are great for short and long production runs since they can be reprogrammed in a short amount of time to generate a completely new product. You can alter programming without it taking too long or costing too much.
How Does CNC Machining Work?
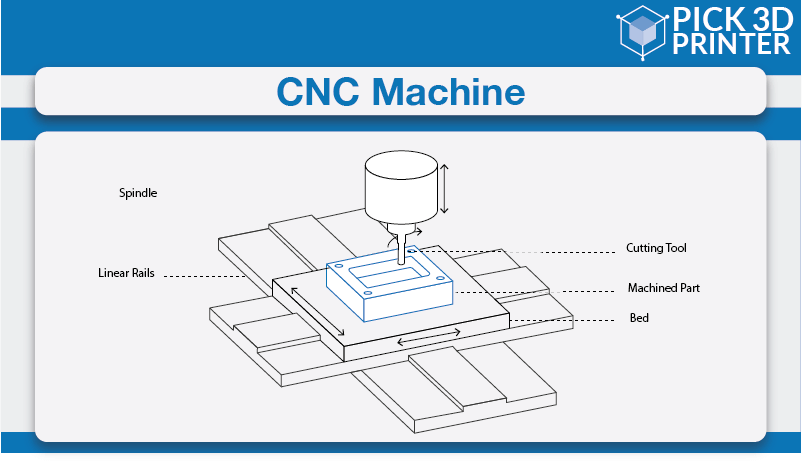
CNC machining is a subtractive manufacturing process, which means the ultimate product is created by eliminating extra material from the workpiece selectively. A four-step production procedure is followed by every end-to-end CNC machining operation.
These are the four stages of production:
Part designing
Computer-aided design (CAD) software is used to create the basic designs for CNC-machined parts. Engineers consider all aspects of the desired final product throughout the design phase, including criteria for optimal performance, operating conditions for the end part, and acceptable tolerance variation levels.
Design conversion
The CAD model must be transformed into a working CNC program using Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) software after the original design process is completed.
CAM software extracts the geometrical requirements from the CAD model’s origin file and converts them into a CNC-compatible programming language (such as G-code or M-code) that controls the machine’s mechanical operations.
Machine setup
The CNC machine must be prepared for operation before the operator may execute the CNC software. Attaching the needed tooling, such as drill bits and end mills, to the proper machine components, as well as affixing the workpiece directly into the machine, onto machinery spindles, or into machine vises or similar work holding devices, are examples of these preparations.
The operator can start the CNC program once the machine is properly set up.
Programmed operation execution
Finally, the CNC machine operator performs the mechanical processes that have been programmed. The CNC program precisely regulates the movements of the machine tooling during operation.
Types of CNC machines
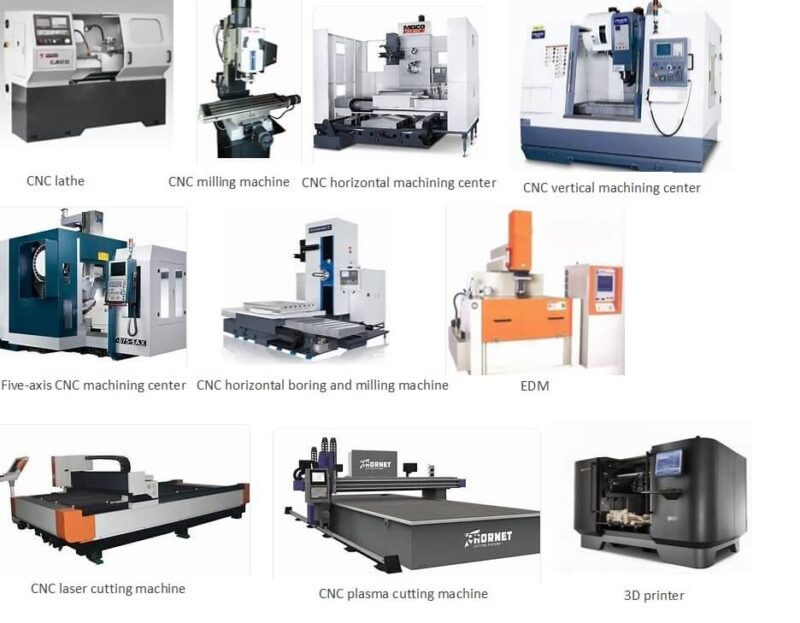

CNC machines come in a variety of shapes and sizes. All of these machines perform the same basic functions. It’s what distinguishes them from other computer numerical control systems.
Each machine works in a distinct way after that. The operation of a CNC machine is determined by the machine’s intended purpose. Some of the most common CNC machines are shown here.
CNC Milling Machines
These can be triggered by programs that use both numbers and letters as triggers. The programming directs the machine’s many components over diverse distances.
A three-axis system is used in the most basic mills. The complexity of newer models has increased. They have the ability to control up to a six-axis system.
CNC Lathes
A lath is a circular saw that cuts parts in a circular motion. This procedure is carried out using indexing tools. All cuts are carried out with extreme precision and speed.
CNC lathes are used to create designs that are too complicated for manually operated equipment. Lathes are often not sophisticated machines, despite the fact that they make intricate designs. The most popular system is a two-axis system.
Plasma Cutting Machines
Most of the time, we use plasma cutting CNC machines to cut metal products. Precision metal cutting necessitates a great deal of speed and heat. Compressed air gas is coupled with electrical arches to help achieve this.
Wires Electric Discharge Machines
Wire EDMs are another name for wire EDMs. Electrical sparks are used to mold objects into specified forms in these machines.
Spark erosion is a technique for removing parts of naturally conductive materials.
Sinker Electric Discharge Machines
Sinker EDMs are another name for sinker EDMs. These work similarly to wire EDMs. The difference is in how the pieces are removed using electricity.
Work materials are drenched in a dielectric fluid to conduct electricity in a sinker EDM. This is how specific forms are formed from components.
Water Jets Cutters
These machines use high-pressured water to cut hard materials. With granite and metal, we frequently employ water jet cutter CNC machines.
Sand or similar abrasive material is occasionally added to the water. This provides additional cutting and shaping power without the need for heat.
CNC Drilling Machines
To make circular holes in the workpiece, multi-point drill bits are used. To make vertical holes, we normally feed the drill bits perpendicular to the workpiece’s surface. The procedure can also be programmed to make angled holes.
CNC Machining Software

The CNC machining process uses software applications to ensure that the custom-designed item or product is optimized, precise, and accurate. Among the software applications utilized are:
CAD
CAD software is used to create 2D vector or 3D solid part and surface renderings, as well as the relevant technical documentation and specifications for the part.
A CAM program uses the plans and models created in a CAD application to develop the necessary machine program to make the item using a CNC machining method.
Additionally, CAD software may be used to find and define optimal part qualities, analyze and verify part designs, simulate products without a prototype, and deliver design data to manufacturers and job shops.
CAM
Computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) software extracts technical data from a CAD model and generates the machine program needed to run the CNC machine and manipulate the tooling to create the custom-designed product.
CAM software allows the CNC machine to run without the need for user intervention and can aid in the automated evaluation of produced products.
CAE
Computer-aided engineering (CAE) software is utilized by engineers during the development process’s pre-processing, analysis, and post-processing phases.
CAE software is used to aid in the evaluation and modification of product design in engineering analysis applications such as design, simulation, planning, production, diagnostics, and repair.
Finite element analysis (FEA), computational fluid dynamics (CFD), and multibody dynamics (MDB) software are all examples of CAE software.
Frequently asked questions (FAQs)
On a CNC machine, what are the 5 axes?
The number of directions in which the cutting tool can move is referred to as the “5-axis.” To approach the workpiece from any direction, the cutting tool on a 5-axis machining center moves across the X, Y, and Z linear axes as well as spins on the A and B axes.
What are CNC machinists responsible for?
CNC machinists set up and operate computer numeric controlled (CNC) heavy machinery to make components and tools out of metal, plastic, and other materials. Precision machinery that cuts, grinds, or drills into the material is known as computer numeric controlled equipment.
What is the language of CNC machines?
G-Code has become the industry’s standard set of CNC machine codes. G-Code is the most often used programming language for CNC machines.
What is a Part Program, and how does it work?
The part program is a set of instructions that define the work that has to be done on a part in the format required by a computer using computer numerical control (CNC) software. It is the process of converting a drawing sheet into a program sheet. A uniform format is used to feed all data into the CNC system.
Conclusion
The manufacturing industries have benefited greatly from computer numerical control technologies. This technology enables customer-friendly applications by allowing machines to be controlled.
Even on a conventional computer, you may simply handle it. The CNC machines are used for a variety of tasks, including grinding, milling, drilling, and routing of various materials. The devices can also be used for a variety of other projects that need precise mechanical motions.







