Among a number of different 3D printing processes, Binder Jetting 3D printing is a really interesting technology to uncover. Working with multiple material types such as ceramics, metals as well as polymers, Binder Jetting (BJ) has come a long way since it was first developed in 1993.
The technology was invented by MIT. However, soon realizing its perks, BJ was acquired by Z Corporation, an American company. And, later by 3D Systems. This sums up the popularity of this technology is nudging the giants in the additive manufacturing niche who all wanted a piece of it.
So, what is it that makes Binder Jetting such an amazing 3D printing process? How does it work? What materials does it utilize? There are so many questions that we must uncover to understand how BJ helps with a plethora of applications, not possible otherwise. So, let’s start and explore the ways Binder Jetting is useful and how does it work.
What is Binder Jetting 3D Printing?
Binder Jetting, as the name suggests, involves a liquid binder that helps bind the bed of powder. This binder when sprayed on the cross-section of the powder bed solidifies it and creates the model, layer by layer.
This 3D Printing process supports a variety of materials. Thanks to technology, you can work with gypsum, metals, ceramic, sands as well as polymers.
How Does BJ Technology Work?
Additive manufacturing technology is the house for many 3D Printing processes. And, all of them start with designing a CAD file.
Well, Binder Jetting 3D Printing is no different. Hence, to start working with a BJ 3D Printer, you must have a CAD design. This 3D model is then sliced and transferred to the 3D printer for further process.
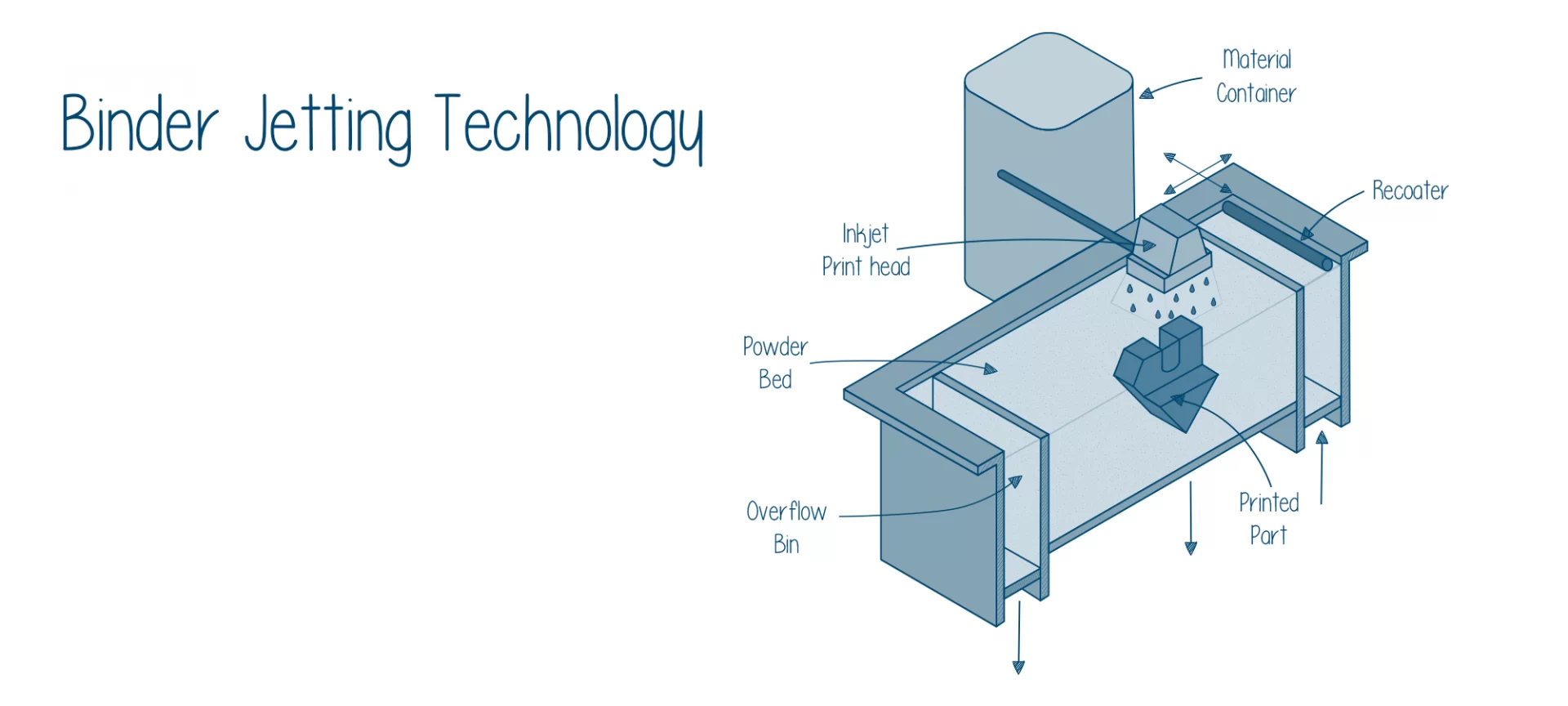
When modeled using a Binder Jetting technology, you must deal with two tanks along with a printing platform. When the printing starts, one of the two tanks is vacant.
However, the material for the creation of the 3D model is there in the other tank. Then, there is a leveling roller that helps spread each layer, starting from the first one over the build platform.
In BJ printers, the print head is for spraying binding agent, similar to the 2D printers. The binder agent drops over the material in the form of droplets.
This results in the unifying of the powdered material. This further creates the 3D part when repeated the process, forming one layer at a time.
What separates this technology from other 3D printing process is that BJ can create full-color models. Surprising? But very true. Users can play with different colors when printing with Binder Jetting 3D Printing.
For instance, if you wish to create a 3D model with ceramics, BJ can help make it look awesome. It allows you to add colors simultaneously with the binder. With binder and color added to different layers, the resultant model achieves a full-color effect.
After you have completed printing, there are post-processing steps you cannot ignore. For example, getting rid of the unsolidified powder surrounding your final object.
Also, these 3D models need curing for increased resistance. Moreover, this allows for retaining colors. The post-processing methods would differ depending on the material used.
BJ 3D Printing – Creating Models with Metals
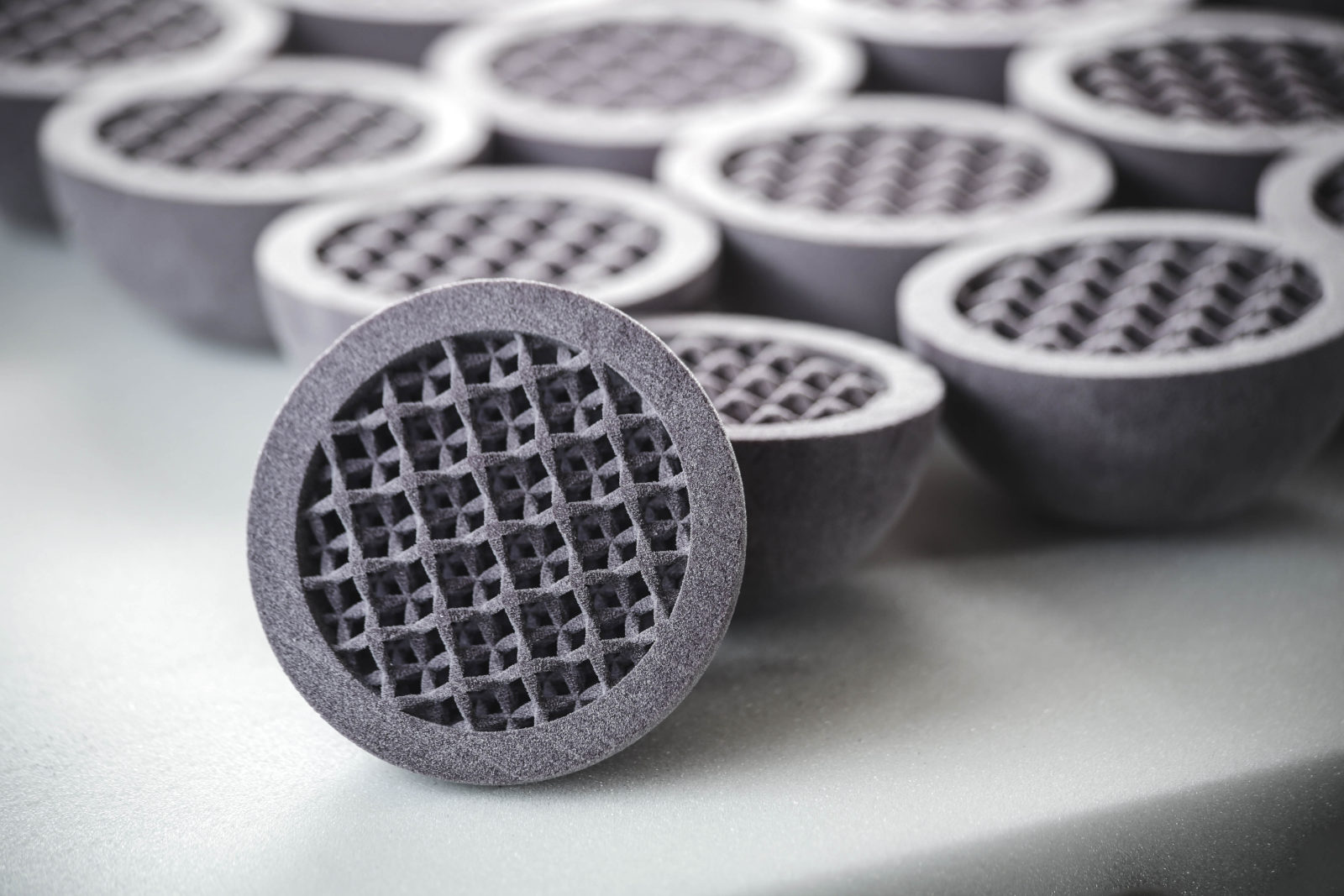
When using metal powder, the process involves a polymer binding agent to combine the granules together.
The technology lets users 3D print highly complex 3D parts with metal that is impossible using any other conventional manufacturing method.
Also, the 3D printing process supports various metals for part production. You can work with stainless steel, copper, Inconel, tungsten carbide, and titanium.
Once the printing completes, the parts are required to go through a secondary process to further strengthen the 3D models’ efficiency to be used as functional prototypes.
Typically, there are two different procedures: Sintering and Infiltration. The part must go through any of these two processes for further gaining strength and enhanced mechanical properties.
Sintering
Although infiltration is done more often, sintering is also preferred in some of the cases. To accomplish this task, the part after cured is sintered inside a furnace where it is kept till it reaches a density of 97 percent.
One problem with sintering is that it is susceptible to shrinkage. Also, it is not possible to predict the percentage of shrinkage and which dimension will have to experience it the most.
It is not even consistent throughout the design. Hence, the same needs to be considered while designing the CAD file for the 3D model planned for sintering later. But again, this is not the easiest part.
So, let us read about infiltration, the other option used as a secondary process after binder jetting 3D printing.
Infiltration
To carry infiltration, the cured 3D model is put inside a hot furnace. Inside this furnace, the 3D model fabricated using binder jetting is heated, resulting in a reduced density to around 60 percent.
The process leaves voids in the 3D model which is further filled using bronze to attain a density of 90 percent. In other words, the process helps in infiltrating the voids or gaps, making the models strong.
BJ 3D Printing – Creating Models with Sands
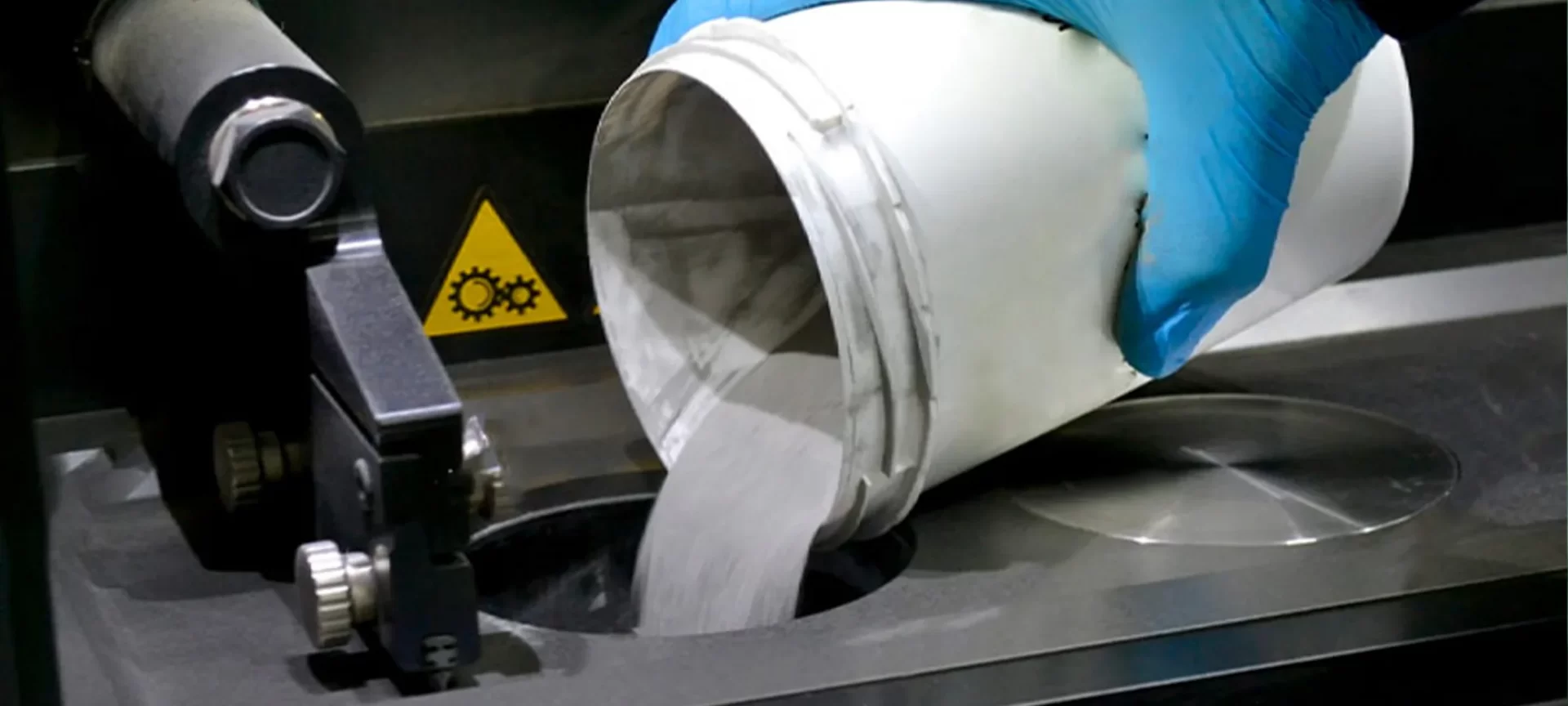

Working with sand is never been this easy and cheap. You may not expect this, but Binder Jetting 3D printing allows for low-cost sand modeling when compared to the traditional manufacturing processes.
Moreover, its capability to 3D print the full-color models definitely is a rare advantage that’s not available otherwise with any known 3D printing processes. And, to make that possible, the process involves combining plaster-based powders and liquid binding agent together.
In order to complete the 3D printing faster and efficiently, the machine makes use of two printhead jets, one for spraying the binding agent while the other for jetting color. Later, after the part is printed, it is cured.
To strengthen the mechanical strength of the model, it goes through sintering, explained earlier. What’s amazing is that the entire process does not require a lengthy post-processing method.
This is so because the 3D model is already in full color and it does not require much effort to get rid of the excess powder.
Another benefit of sand binder jetting is that one can create sand molds. The sand models can be created with either real sand or users can also make use of artificial silica.
The sand mold’s fabrication involves similar processing as it is with full-color sand printing. Starting with printing and then casting, almost every process is simple and easy to accomplish.
Hence, you can end up with finer geometries. Plus, these are low cost, adding more perks for the users.
Binder Jetting 3D Printing Materials
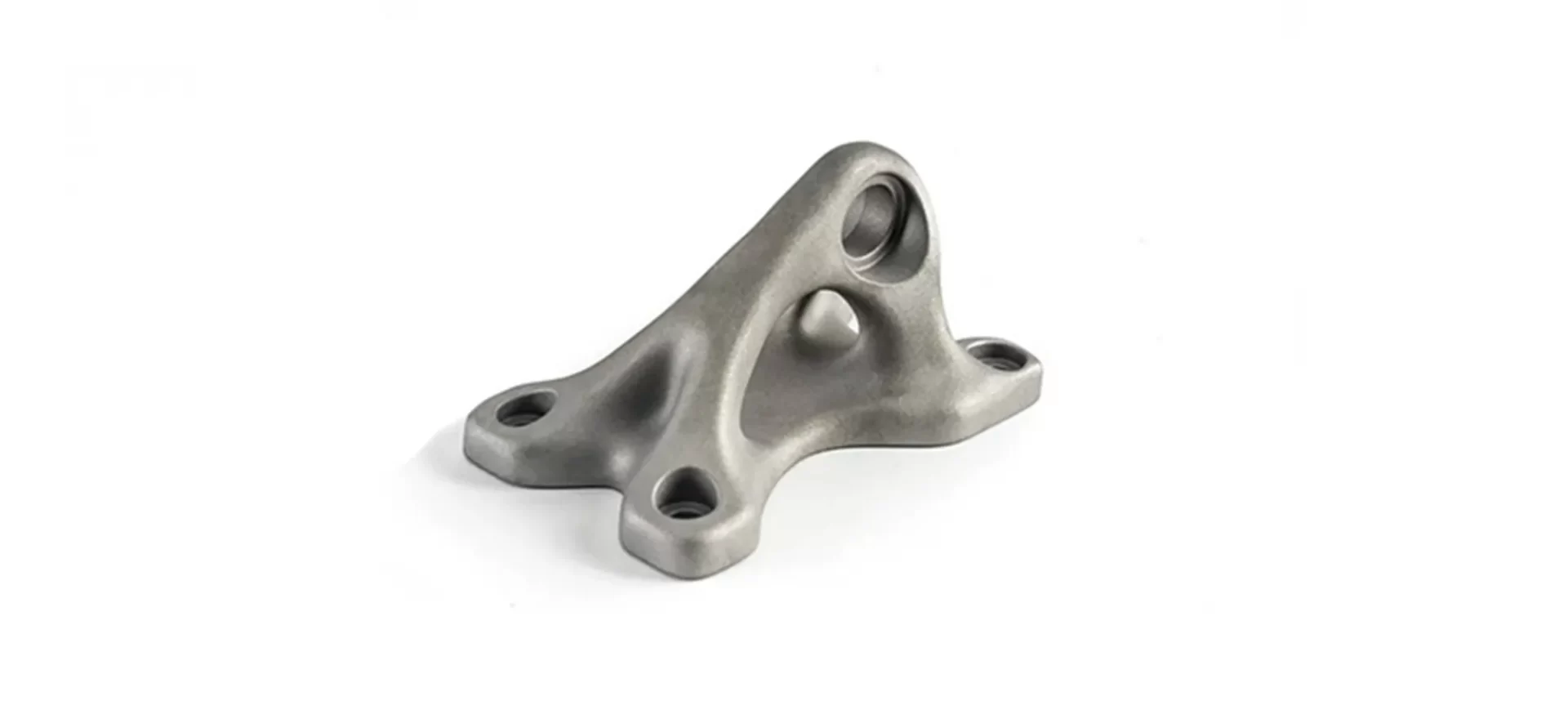

With time, more materials are being added to the family of binder jetting. However, there are a few common ones that are often use when working with BJ printers.
Silica Sand
If you are looking to create models that have high thermal resistance, this is what you must choose. Silica sand allows for amazing sand-casting results. Hence, it is used for a variety of applications where sand casting is involved.
Full-Color Sandstone
The parts created using this material are highly brittle. These models aren’t used as functional prototypes and are usually non-functional 3D models, available in full color.
Sintered Stainless Steel
As mentioned above, sintering does come with its downside, i.e. shrinkage. However, if you can get the estimate right during the designing of the 3D file, the results could be astonishing.
The finished models possess high strength and great mechanical properties.
Along with that, the models are highly resistant to corrosion. This makes these models suitable for important applications within an array of niches.
Infiltrated Stainless Steel
If you ignore the internal porosity up to 10 percent, the material can help attain great mechanical strength, making the models suitable for high-end applications.
Sintered Tungsten Carbide
Up for 3D printing some cutting tools? If you need a material with the ability to showcase high hardness, you must go with tungsten carbide.
And, using the Binder Jetting 3D printing with sintering, one can attain the best results without fail.
Sintered Inconel Alloy
Binder Jetting with Inconel alloy when combined with sintering could offer great results. Along with the excellent mechanical strength and properties, the models are resistant to chemicals and high temperature.
Binder Jetting – Pros and Cons
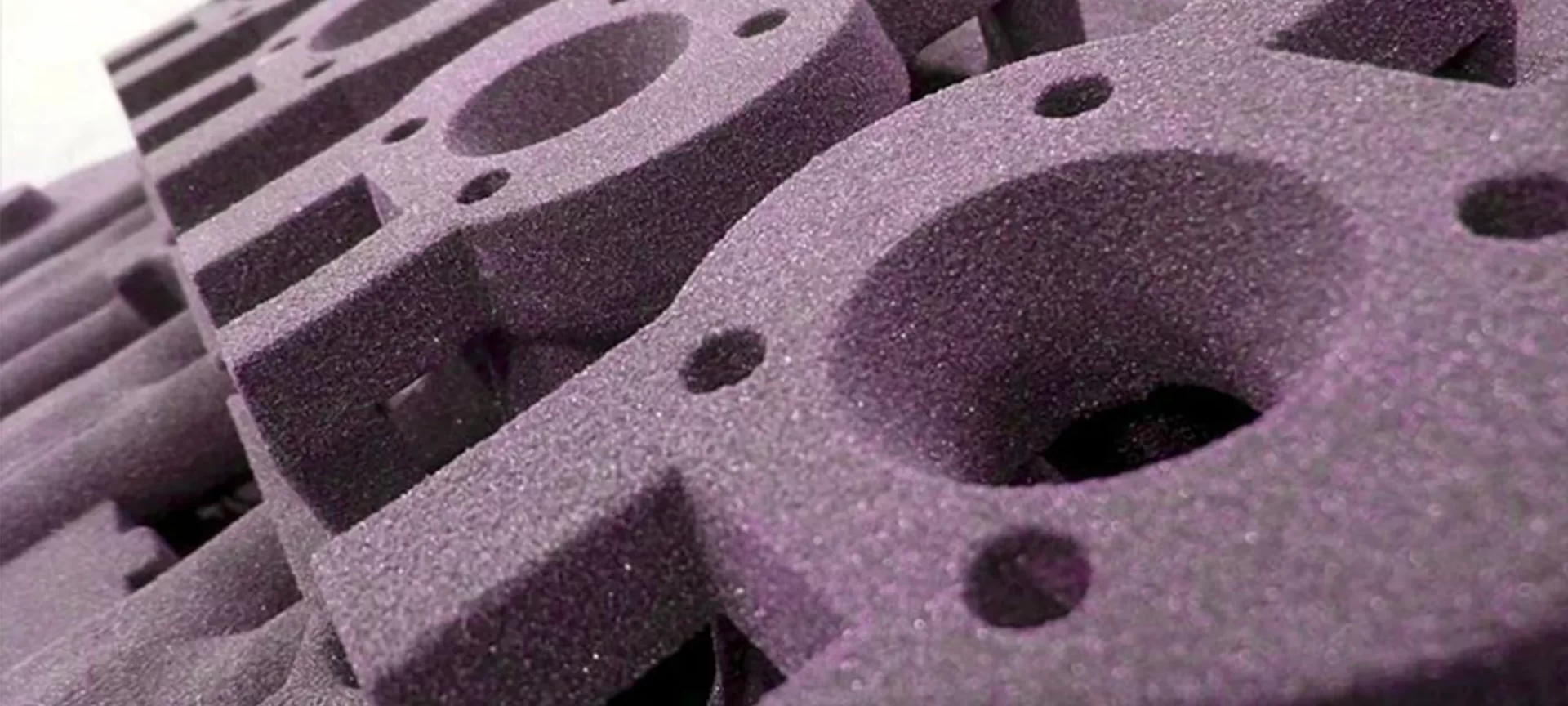

There are a lot of reasons for choosing Binder Jetting 3D printing. However, before you do that, you must have a clear idea of its perks and limitations.
Trying to summarize both the positive and negative sides of BJ technology, here is what you must expect.
Pros
Here are some of the advantages of fabricating parts using Binder Jetting 3D Printing.
Cheaper: Binder Jetting, when compared to the other 3D printing processes such as DMLS, SLM, or Material Jetting, is cheaper when producing full-color prototypes with metals. It actually can reduce the cost to a fraction of what is invested with other listed technologies.
Free of Warping: Apart from capable of creating larger components and models with complex geometries with metals, the process is not susceptible to warping or other thermal effects. Hence, it is easy to work with BJ as well.
Highly Capable: You can expect this choice very effective when producing low to medium batch production.
Cons
High Porosity: When compared to models produced using DMSL or SLM, the parts have higher porosity. This results in lower mechanical strengths than the parts created with SLM/DSLM.
Brittle: Before curing, the parts created using Binder Jetting are brittle and are easily prone to breakage during post-processing. This is the major reason why users can 3D print only rough details with Binder Jetting. This does limit the usage of this 3D printing process to some extent.
Limited Material: While the materials are constantly being added to the BJ family, there still aren’t many when compared with other 3D printing processes.
Binder Jetting 3D Printers
It’s time now to look at some of Binder Jetting 3D printers, before concluding this article.
DM P 2500
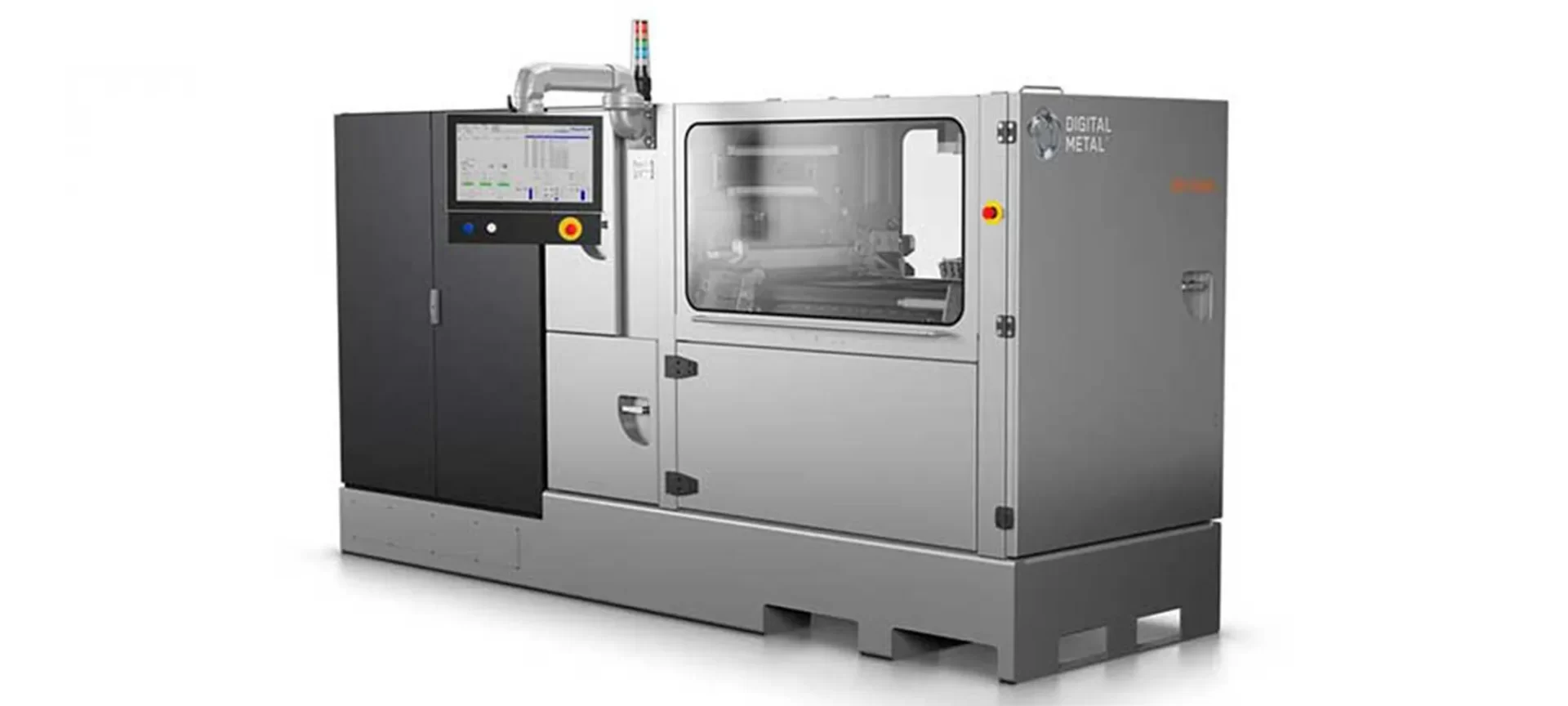

Manufactured by a company called Digital Metal, this 3D printer employs high-precision metal binder jetting technology for creating parts. The technology allows you to have greater accuracy and higher resolution.
The machine has a build volume of 203 mm * 180 mm * 69 mm which makes it possible to nest more than one part on a single build platform. All this, without any support structures! Isn’t that amazing?
M-Flex
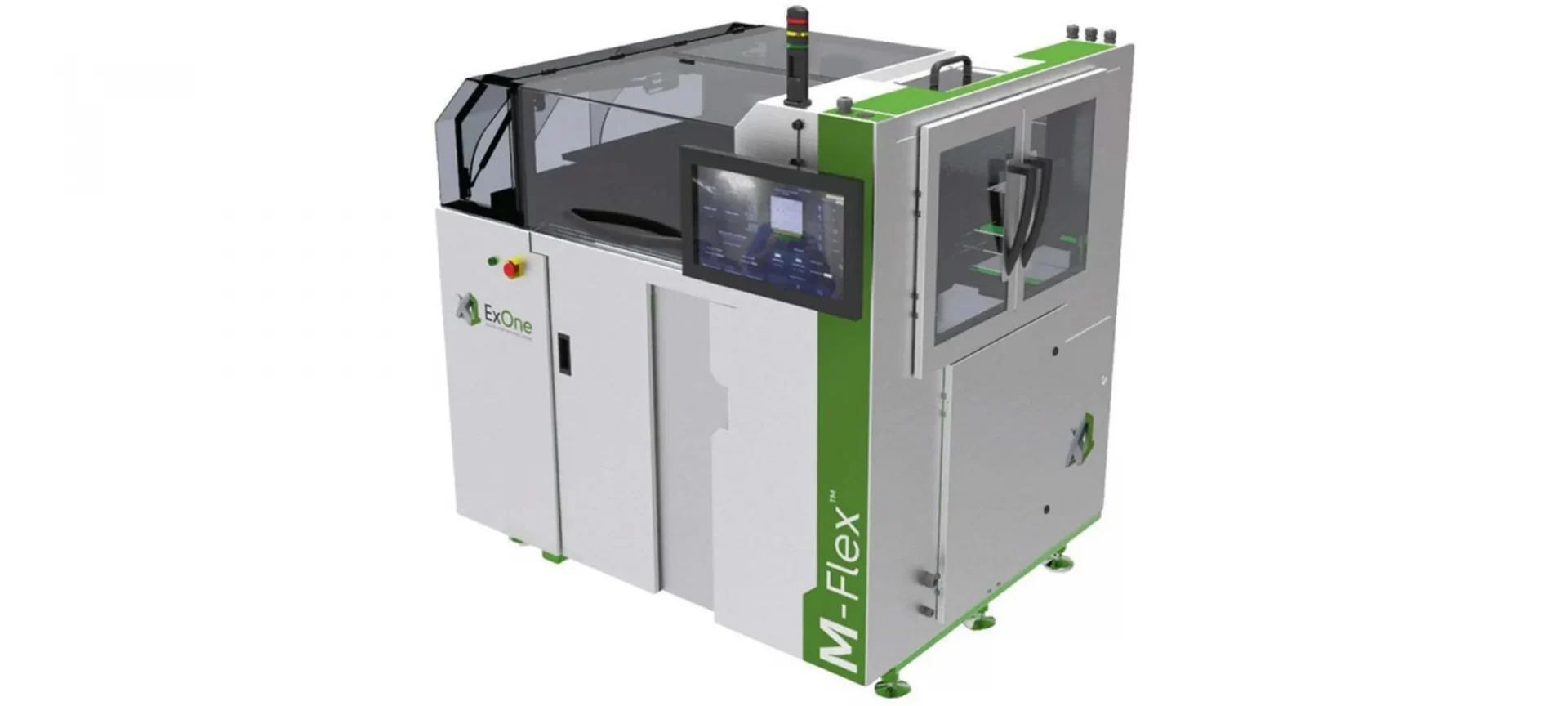

This industrial-grade 3D printer has an even larger build volume than DM P 2500. It also offers a wider range of 3D printing materials such as stainless steel, bronze, tungsten, Alloy IN 625, glass, silica, and ceramic sand.
The printer is compatible with creating customized metal parts in industry segments such as automotive, aerospace, heavy, gas, and oil industries, and also for consumer applications.
VX1000
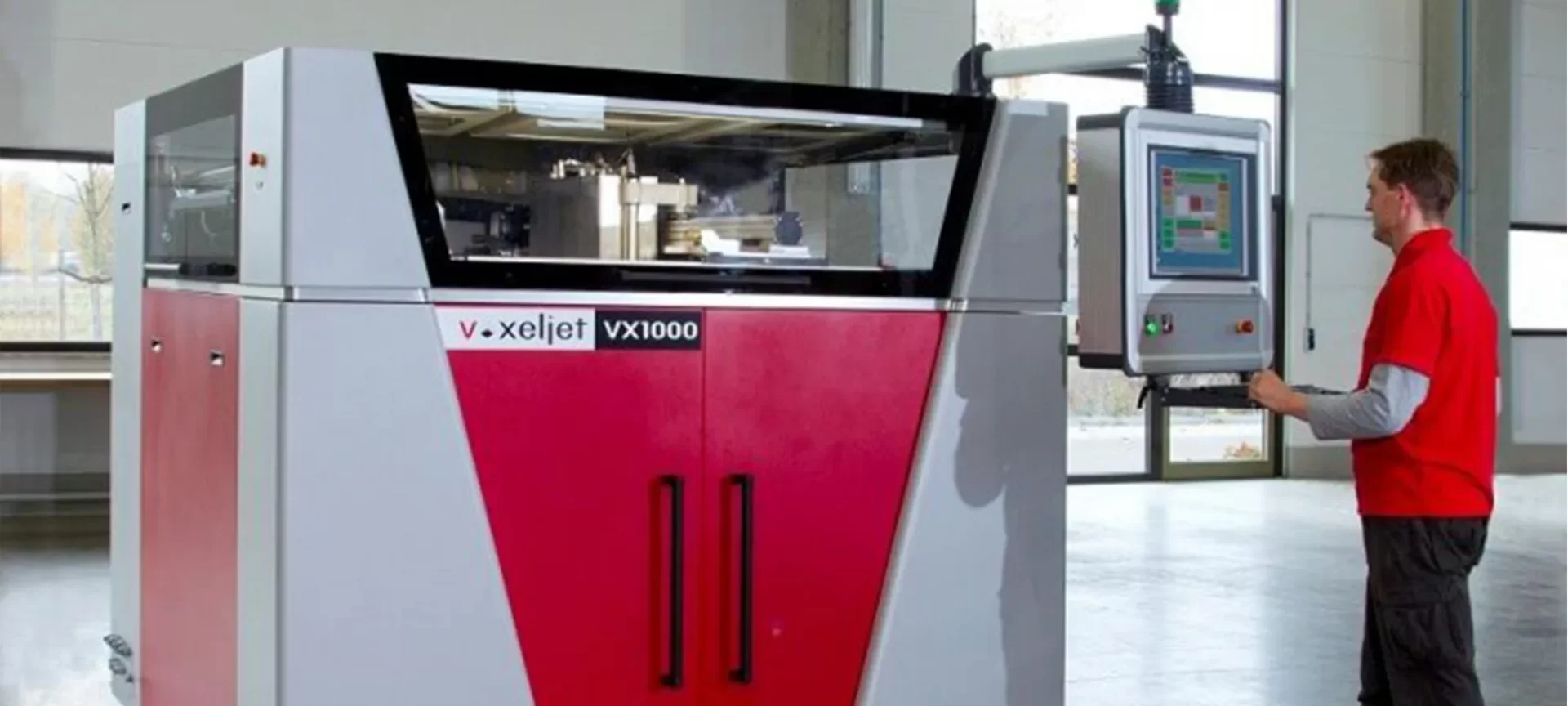

This one offers even more build volume than the previous two. The VX 1000 features a build space of 1000 mm * 600 mm * 500 mm and a resolution range of up to 600 dpi.
The 3D prints parts and functional prototypes with faster speed, lead time, and great quality. Although it offers fewer 3D printing materials than M-Flex, they are not considered low.
The machine is ideal for producing efficient sand cores, molds, and plastic parts. All of which will require post-processing, as is the case with any binder jetting 3D printer.
The Conclusion
Binder Jetting 3D printing is one of the most precise 3D printing technologies available in the market currently.
To associate with this technology is to secure your future. It is able to produce parts and functional prototypes of extremely high-quality.
Be it apart with a smaller build volume or with a larger. Be it a part with intricate design, or simple, binder jetting 3D printing technology is able to manufacture them all with dimensional level accuracy.
And the technology is still growing and linking itself to even more industries in which parts manufactured by it can be put into application.








