Due to the increase in its usage, the range of 3D printing technologies is on an all-time rise. What started with simple methods for manufacturing 3D printing parts such as SLA, FDM, SLS, expanded to more complex methods such as Binder Jetting, MJF, DLP, EBAM, DLS 3D printing, and a lot more.
Companies that can be termed as forerunners in the field of 3D printing are always working on a single task with their team i.e. to invent a 3D printing technology that can copy the quality of real products around us like no other. In one such quest, Carbon a venture-backed company headquartered in Redwood City ended up inventing DLS 3D printing.
The Carbon DLS process coordinates versatile printers, advanced software, and best-in-class materials for fabricating functional parts with end-use performance and aesthetics. The technique helps engineers and designers for creating products that outperform.
Starting from prototyping and low-volume production to production-at-scale global organizations like Adidas, Ford, and Beckton Dickinson, use the DLS 3D printing for creating a wide range of functional end-use parts and print them reliably. This; they also do via their own as well as a network of production.
In this article, we are going to lead you through this amazing technology by Carbon that has caught the attention of renowned global companies. It has amazing potential and is already believed to be one of those technologies that can make products closer to reality like no other.
DLS 3D Printing – Working, Applications, Material Options, and Advantages
Carbon DLS short form for digital light synthesis is an industrial 3D printing process that creates functional, end-use parts. Not simply like other 3D printing technologies do, but with mechanically isotropic properties and smooth surface finishes.
Coming to the materials that you are allowed, you can choose from both rigid and flexible polyurethane materials to meet your application needs for fabricating high-impact-resistance components.
For doing so, DLS 3D printing based printers use a breakthrough technology that uses:
- Digital light projection.
- Oxygen permeable optics.
- And programmable liquid resins
The result of these three is the production of parts with exceptional mechanical properties, resolution, and surface finish.
The Carbon DLS process is extremely beneficial to engineers and designers for iterating faster, delivering projects with less risk, and radically reimagining their products by introducing consolidated parts, impossible geometries, and programmable lattices.
How Does DLS 3D Printer Work?
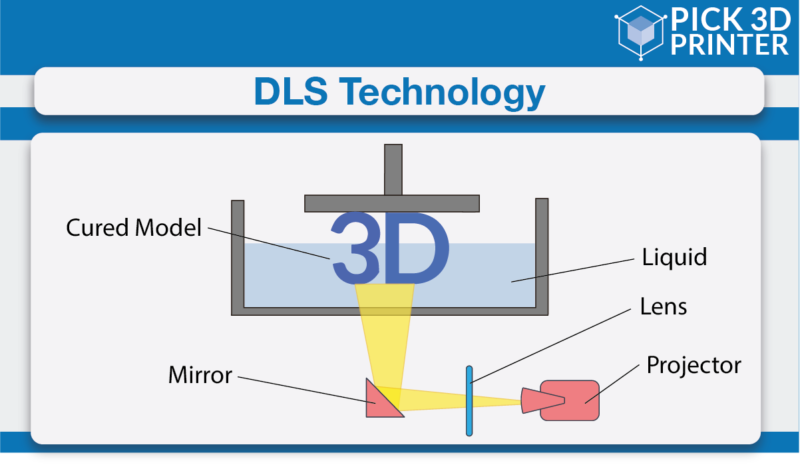
The Digital Light Synthesis process is driven by Carbon company’s groundbreaking Continuous Liquid Interface Production, more commonly known as CLIP, and programmable liquid resins.
What is CLIP?
CLIP, an abbreviation used for Continuous Liquid Interface Production, uses digital light projection with oxygen-permeable optics. This was first introduced on the cover of Science Magazine.
CLIP is actually a breakthrough photochemical process that, as the name suggests, continuously cures liquid resin into solid plastic parts using ultraviolet light rays.
It works by projecting light via an oxygen-permeable window into a pool of UV-curable resin. With the sequence of UV images getting projected, the complete part solidifies as the build platform continues to rise.
Traditional resin-based 3D printing processes such as SLA produce weak, brittle parts where DLS produces high-resolution parts with engineering-grade mechanical properties.
At the core of the CLIP, process lays a thin, liquid interface of uncured resin. It’s presently exactly between the window and the printing part.
Light passes through that area, and while this phenomenon occurs it cures the resin above it thereby forming a solid part.
Then the resin flows beneath the curing part as the printing progresses, this maintains the continuous liquid interface that powers the CLIP.
Following the build, the 3D-printed part is heated and gradually baked in a forced-circulation oven. There the heat sets off a secondary chemical reaction causing the materials to adapt and strengthen.
What is the Base Technology Behind DLS 3D Printing?
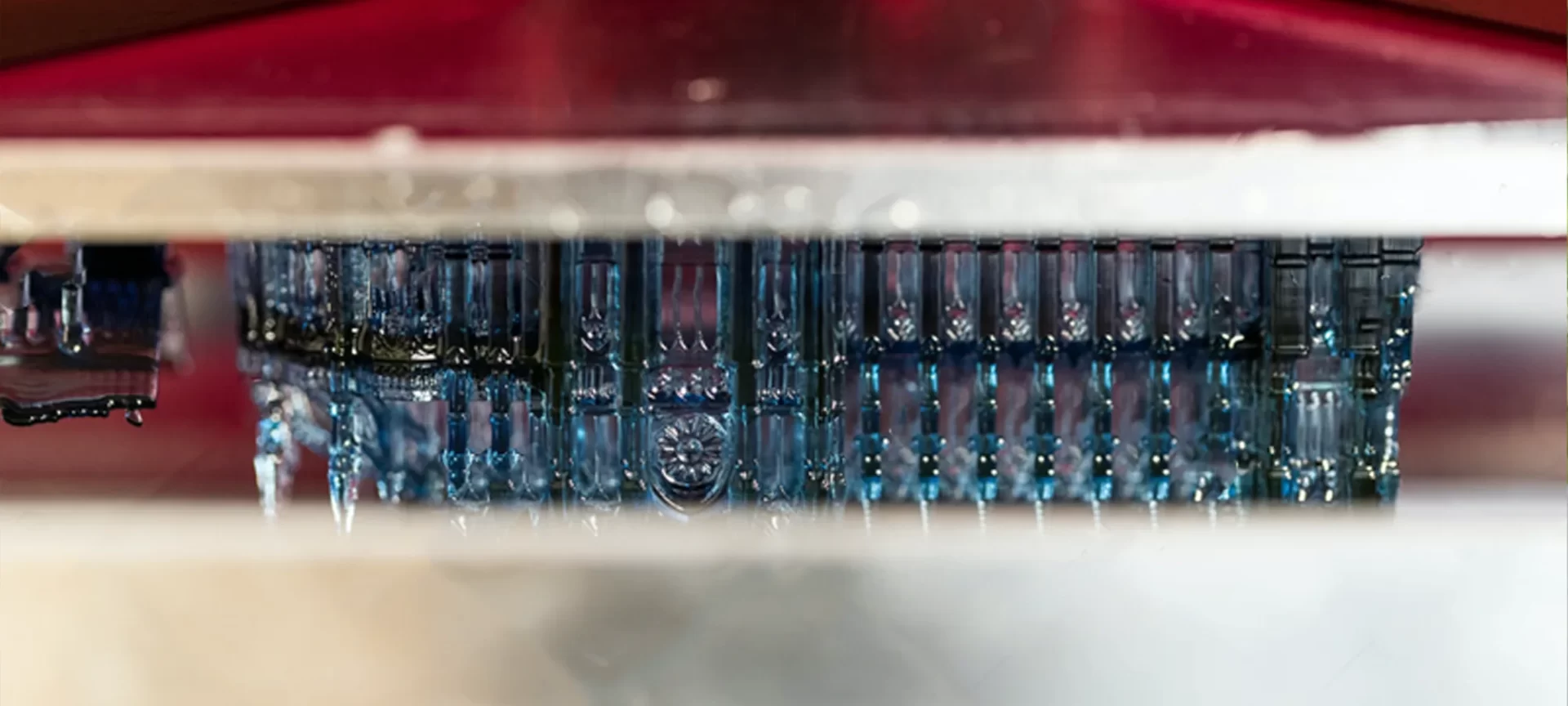

At the heart of Digital Light Synthesis is stereolithography. Both these 3D printing processes use UV light to cure the resin. But unlike the latter, the former doesn’t pause after each layer. Instead, the resin continuously flows through something that is called a “dead zone.”
The heart of the above-mentioned CLIP process is the “dead zone” — a thin, liquid interface of uncured resin between the window and the printing part. Light passes through this zone, cures the resin above it, and forms a solid part without curing the part onto the window.
In the meantime, the resin flows beneath the curing part, maintains the continuous liquid interface, and avoids the slow and forceful peeling process that is inherent to many other resin-based printers.
UV images of the same represent the cross-section of the part that is projected onto an oxygen-permeable window for solidifying the resin.
Parts are built upside-down, as the build platform rises from the vat of resin. Using DLS 3D printing parts are produced in two stages.
- Firstly, the 3D model is sent to the 3D printer wherein production of the parts happens using a liquid resin with digital light projections and oxygen-permeable optics used for solidifying the resin in the shape of your model, layer by layer.
- The second stage is also known as curing starts after the object is 3D printed. The object is then baked in a revolutionary CLIP process allowing not only for a chemical reaction but also for the particles of the resin to clip together. Thereby giving the object mechanical properties at an engineering grade.
What are DLS 3D Printing Applications?
As mentioned at the start of the article, DLS 3D printing has immense potentials. Adidas and Ford kind of leaders are already utilizing DLS 3D printing to their benefit.
But you can expect even more, as companies such as Lamborghini invest have also invested in the same. What are they doing with the technology? Well, let’s find out.
3D Printed Football Helmet
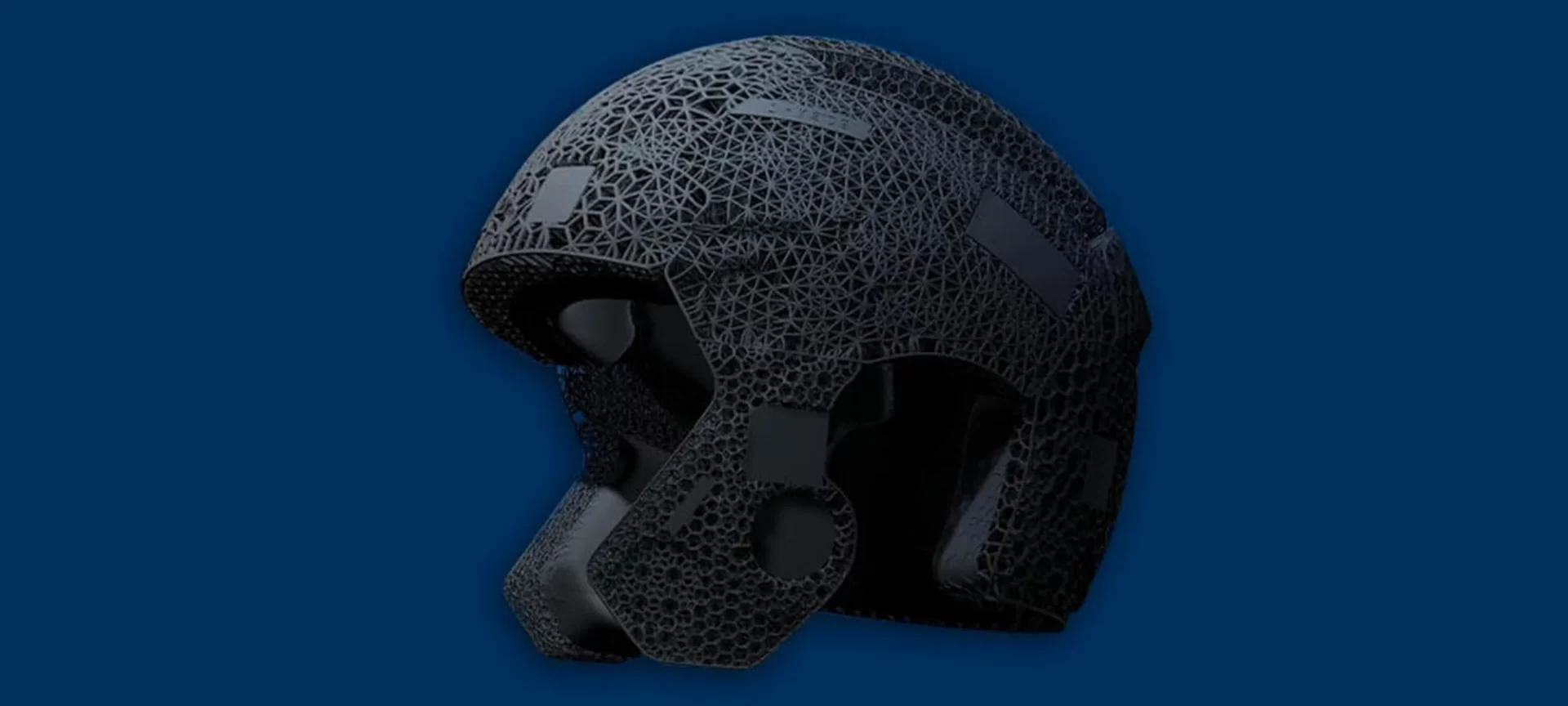

Riddell, a sports safety company that reaches for the latest innovations to provide their athletes with the highest protection and standards has partnered with Carbon.
The collaboration of these two innovation catering and innovation finding companies gave life to first the world’s first 3D printed football helmet.
All credits to additive manufacturing that Riddle was able to reach a level of customization that was previously impossible with traditional technologies.
Each helmet is designed in a way to perfectly fit the user’s head, giving him ultimate impact protection in addition to excellent comfort.
3D Printed Midsoles
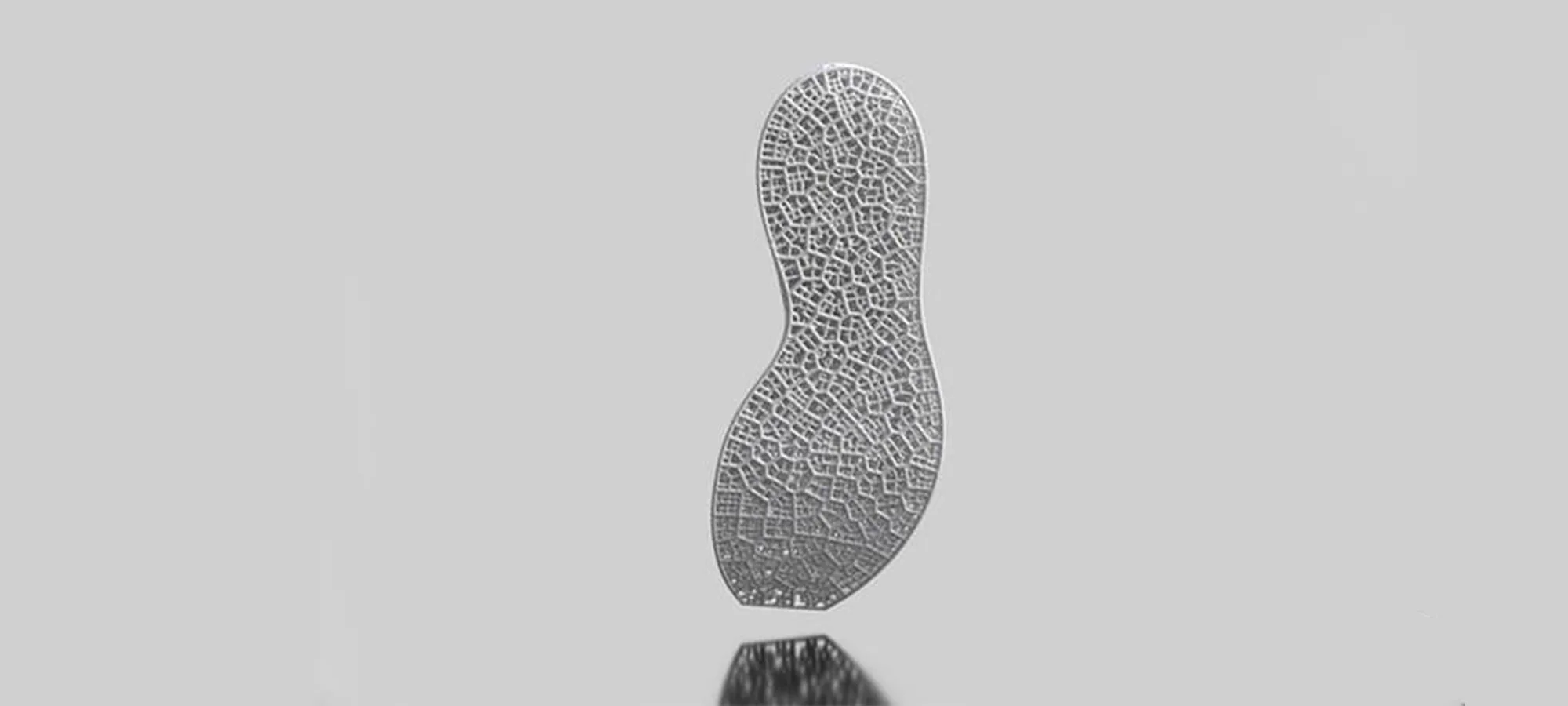

Being the frontrunner of shoemaking, Adidas started cooperated with Carbon in 2016 and not so time ago launched the first-ever partly 3D printed shoes that are out for commercial use.
With 3D printing, Adidas was able to enable customized midsoles even for mass production. In this case, additive manufacturing sped up the production process by three times thereby allowing Adidas’ designers to discover new design possibilities such as lattices.
These are substances that are widely used in the automotive and aerospace industry for reducing the weight of the 3D-printed parts and material waste. These aspects also affect the costs and bring them down.
3D Printed Automotive Parts

Seeing the potential of DLS 3D printing Lamborghini- the exclusive super sports car manufacturer employed it for developing 3D printed automotive parts that are light in weight and durable in a speedy manner.
Lamborghini wanted to reduce the number of components in their Super SUV, the Urus for which they collaborated with Carbon and redesigned the fuel cover and air duct split.
The 3D-printed automotive objects not only presented great impact strength but also high-pressure and temperature resistance.
Currently, the two companies are working to optimize a) interior components, b) mirror assembly parts, and c) other accessories with Additive Manufacturing.
What are the Materials used for DLS 3D printing?
You can choose to produce your parts using DLS 3D printing with 4 materials namely: EPU, FPU, RPU, and UMA90. All of these materials have a very smooth surface finish and will also provide you with great quality details.
Each material is somehow different from the other you can decide which one is the right one for you depending on your production needs.
EPU

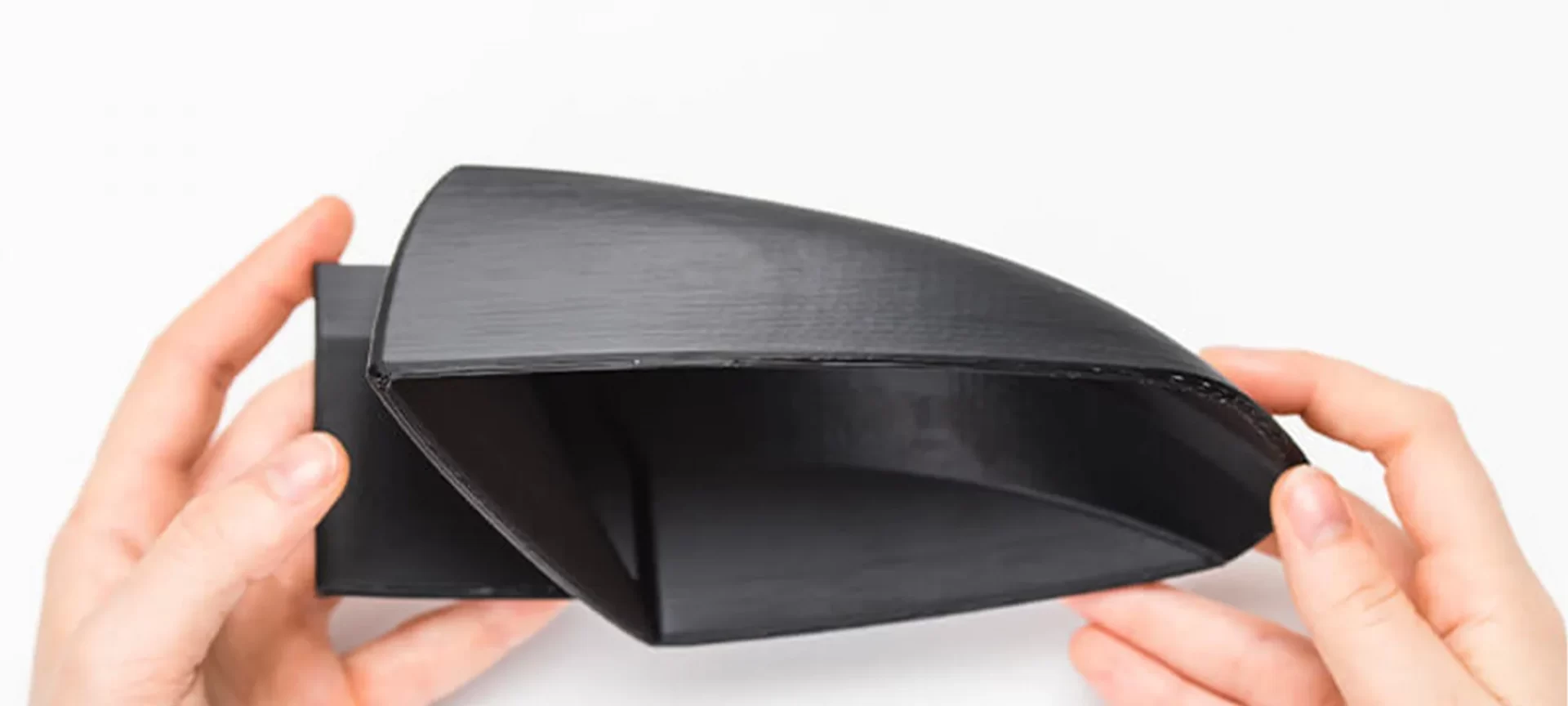
This material has one of the best mechanical properties out there in the market. It is not only flexible but also very strong and certainly shows high-performance material when used in applications demanding impact and tear resistance, as well as high elasticity.
It is perfect for functional prototyping as well as end-use products. Elastomeric Polyurethane is stretchy and rubbery, the material also able to maintain its elastic properties in a wide range of temperatures. Because of these properties, EPU can be easily used in grommets, gaskets, and flexible watertight seals.
FPU

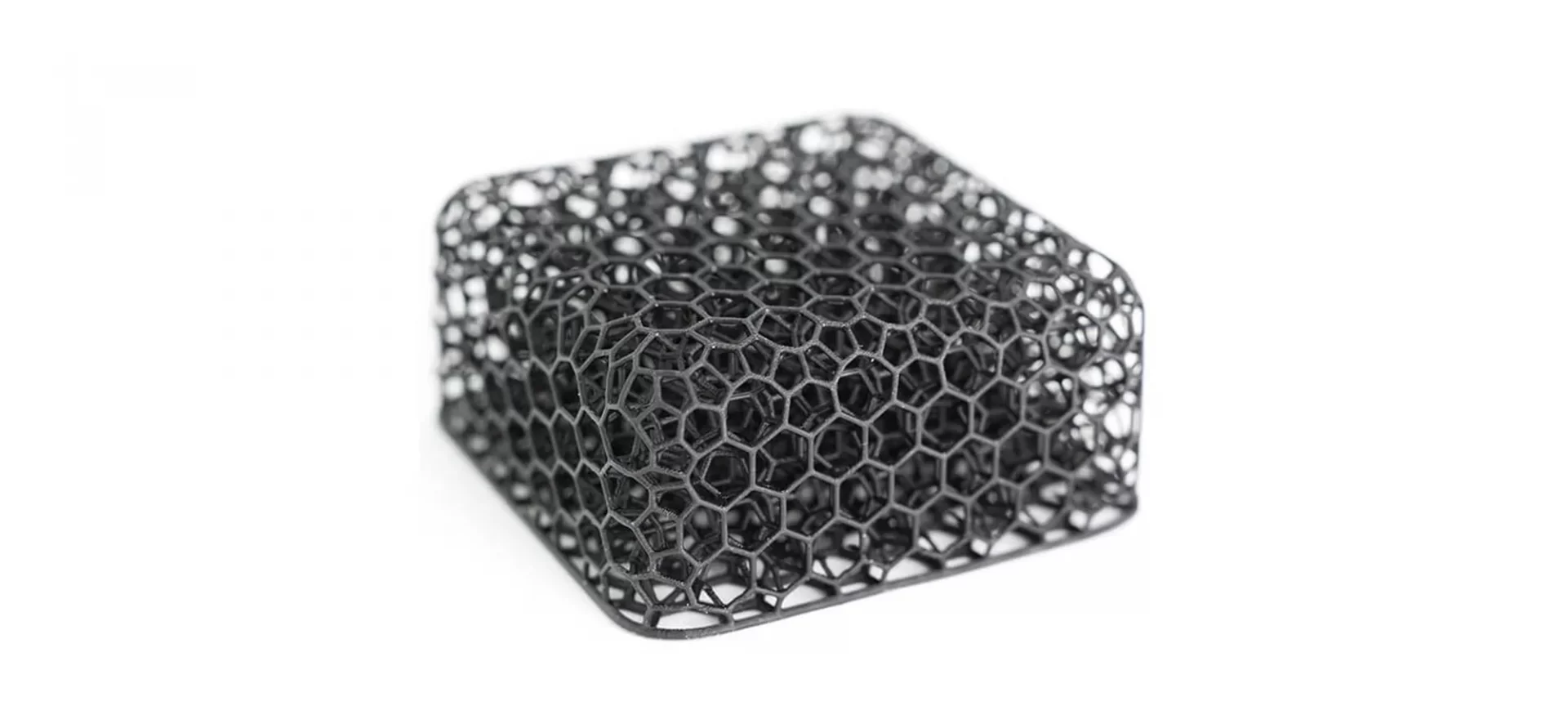
FPU is a semi-rigid 3D printing material that has a good impact, abrasion, and fatigue resistance. Its resin produces highly smooth parts and this is tested when it was used in printing a 3D printed bike.
FPU is a versatile material, in the sense that it can withstand repetitive stress, is tough and durable. These aspects make the material a perfect candidate for hinging mechanisms, friction fits, etc.
RPU

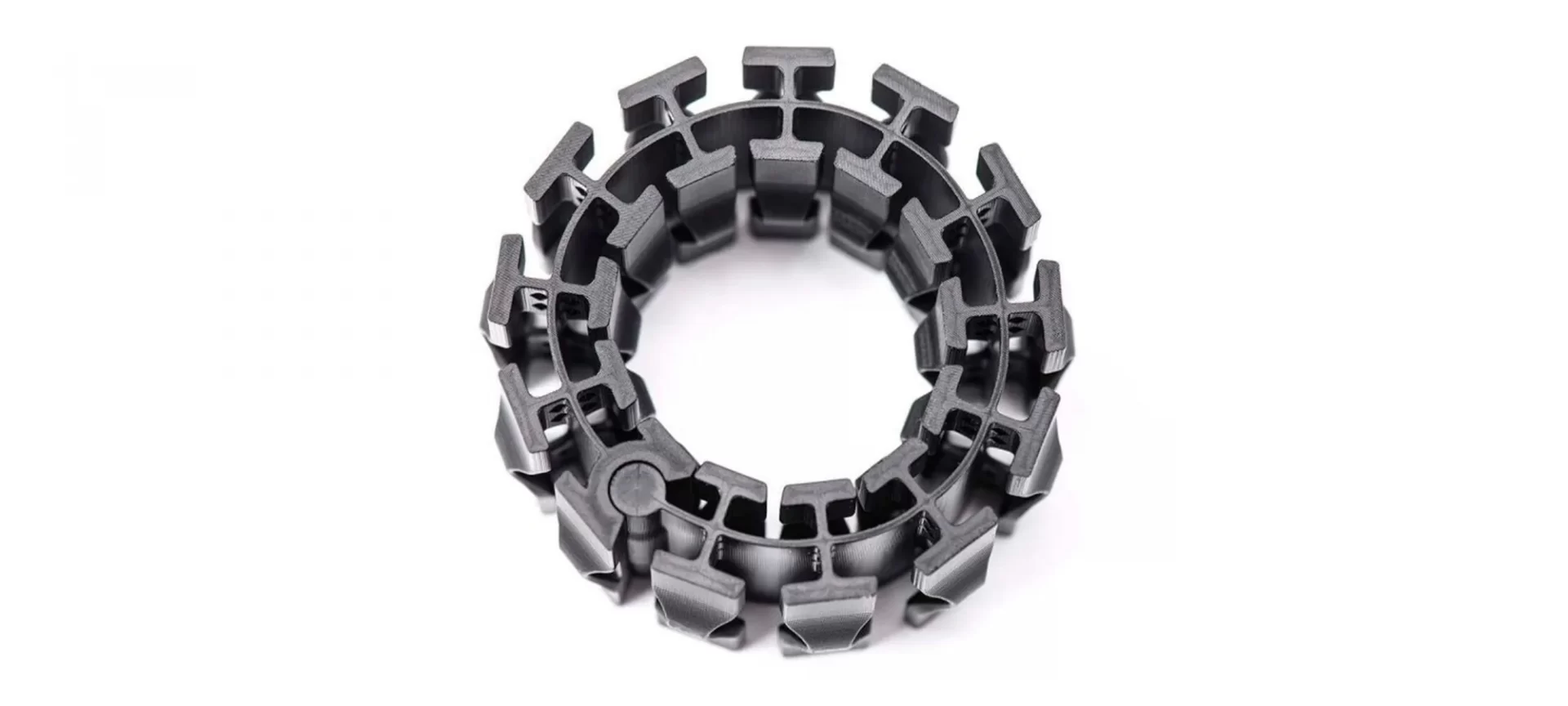
RPU stands out in the list of 3D printing materials for its strength to weight ratio as well as high-temperature resistance.
It is rather stiff and performs well against water absorption, also the material has excellent qualities to be a perfect one for consumer electronics such as computer mice, cell phones, and other electronic housings.
Apart from the electronics industry, RPU also easily meets the requirements of the automotive industry.
Urethane Methacrylate UMA 90

Launched in 2018, UMA 90 is the latest addition DLS materials family. It has an amazing surface finish and is strong; such a combination makes it a great material to produce prototypes and mechanical parts.
Additionally, Urethane Methacrylate also meets the requirements of toughness and abrasion resistance. A sum of these characteristics makes UMA 90 a high standard material, the ideal material for fixtures, jigs, and prototypes.
What Are The Advantages of DLS 3D Printing?

- Rapid Product Development, be it functional prototypes, iterates quickly, and produces with confidence. The Carbon DLS 3D printing process is proven for high-volume production in industries ranging anywhere from automotive to consumer products. This printing technology tests dozens of designs in the time it used to take to try one.
- You can easily make impossible geometries using this technology. Moldability constraints that are most critical for other technologies don’t apply here. You can easily enjoy the freedom of designing with undercuts and perfectly straight walls without sacrificing manufacturability.
- Unlike powder bed fusion 3D printing technologies, Carbon technology produces fully dense parts. This technology lets you streamline your production with reduced SKUs and less labor by consolidating assemblies.
- This completely innovative technology brings to parts as never before experienced a new aesthetic. Using it you can deliver designs that break new ground and let you deliver exactly what your customers need.
- With no tooling costs, DLS 3D printing lets you freely make every unit unique by offering personalized designs or build entire products around individuals. Moreover, Carbon’s factory management software enables you to track parts from design to delivery. Carbon DLS provides excellent surface finish and high detail. You can enhance your parts by applying textures to complex curved surfaces like grips and enclosures all by utilizing Carbon’s software.
The Conclusion
DLS 3D printing is the state-of-the-art technology innovated by Carbon and is extremely useful for making never-before-seen and experienced parts.
The applications remain the same automotive, consumer goods, sports, etc, what changes is the approach and strength of the manufactured parts.
An important point to know is DLS is completely different than SLA, SLS. Although it uses resins for 3D printing objects of different geometries, the technology differs in the core mechanism.
So, do not confuse it with them. Carbon is an exclusive manufacturer of DSL 3D printers and materials and you can visit its website to bring a machine to your workshop that lets you print objects of a quality that matches closest to reality.
Apart from producing world-class quality products, DLS 3D printing is also renowned for offering you speed like no other 3D printing technology. So, it’s not just quality, but quality in minimal time.







