Stereolithography. Or often referred to as SLA, is a very popular 3D printing technology around the world.
The Stereolithography process is utilized for various applications around the world. Apart from prototypes, the technique does have nuances of other importance.
The technology is very widespread and is used for most professional setups, based on the accuracy and precision it provides.
SLA makes use of a high-powered laser which harden the photosensitive liquid resin to create the final 3D model, one layer at a time.
The process is very basic but is capable of producing amazing results. SLA is among those primary 3D printing technologies that are used in abundance.
Apart from SLA, two more processes are commonly utilized: FDM and SLS. However, let our focus be on SLA for the time being.
To start with, the Stereolithography process has gained a lot of recognition in the commercial world after the introduction of desktop SLA 3D printers.
Before this, the technology was limited to industrial use. And, the 3D printers weren’t easy to afford. With time and changing demand though, a lot of developments took place around Stereolithography 3D Printer.
The results are very obvious. You can find a lot of amazing SLA 3D printers with low cost and better results.
Companies are trying out their hands and progressing towards a better future with 3D printing. Many businesses have already.
So, let us check out a more detailed overview of the Stereolithography process and how is it changing the face of rapid prototyping as well as traditional manufacturing.
A Brief History of Stereolithography Process
Because of the cheaper cost and easier workflow, FDM 3D printers are more popular than SLA among end-users. But SLA is the oldest of all. Among all the 3D Printing processes, the Stereolithography process is the first invented additive manufacturing technique.
You may have heard about 3D Systems, a 3D printing company founded by Chuck Hull. The SLA technology was created by the founder of 3D systems, Chuck Hull.
The name was also termed by Chuck Hull and the story dates back to 1986. If you listen to the creator, SLA is a process in which the 3D model is created by printing layers one over another using a photosensitive material and the laser source to harden it.
Later in 1992, 3D Systems came up with the first-ever SLA apparatus. Because of this, it became possible to create complex parts using the same SLA process to fabricate the model, layer by layer. The entire process would take a fraction of the time of the conventional method.
Since then, we have come a long way. Today, 3D printers are easy to handle and are affordable as well. Plus, the desktop variants can be used at homes or individually as well.
How Does Stereolithography Process Work?
The SLA was the beginning of the additive manufacturing niche. It did take some time to get into the mainstream, however, not no going back. The SLA 3D printers are capable of a lot of wonderful things.
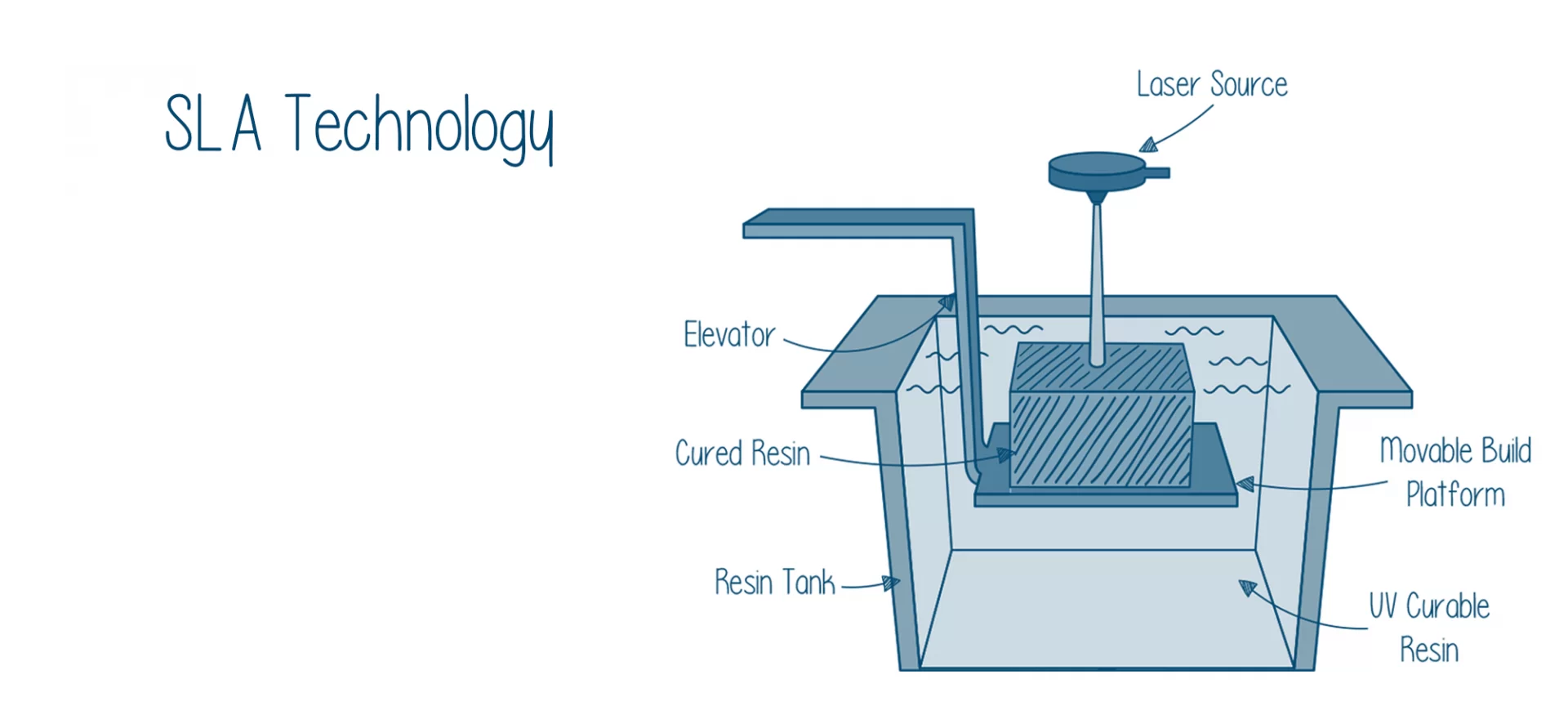
When talking about the components of the SLA 3D printers, you must know about the four primary ones that are usually present in all the machines.
First, is the resin stored in a tank? The resin is the liquid photopolymer which usually looks like a clear plastic in its liquid form.
Then comes the perforated platform which is immersed inside the tank containing resin. The platform is moved up and down as per the printing needs.
This is where the material hardens and turns into the final 3D model. And, how could you forget the energy source?
The 3D Printers have a high-powered source of ultraviolet laser to treat the photosensitive polymer.
Last but not the least, the user interface. This helps in controlling the platform along with the laser movements to get you the desired results.
The working of the SLA 3D printers is divided mostly into three sections:
Designing of 3D Models

This is the first step for every 3D printing process, either SLA or any other for that matter. You cannot think of creating a 3D model without having a blueprint for the same.
And, the 3D designs provide these machines with an idea of what needs to be done. The 3D designs are created with the help of CAD software.
These CAD files aren’t processed in the format they are available for 2D designing. On the contrary, if your CAD software does not allow you to save the file in STL extension, you must convert it first. STL is the standard triangle language representation which was developed by the Abert Consulting Group in 1987.
An STL file illustrates the surface geometry of the designed models. Moreover, it neglects the unimportant attributes such as color or texture and a few others.
These files are then processed through the 3D slicer software. During this step, the STL format converts into G-Code. This G-Code is the native language of 3D printers.
3D Printing Using SLA 3D Printers
 3D Printer: Form 3 by Formlabs
3D Printer: Form 3 by Formlabs
This is where the printing of 3D objects takes place. The G-Code fed to the printer provides it with the instructions. 3D printing takes place with one layer at a time.
The mirror, controlled with the help of a computer is used for directing the laser at the desired cross-section of each layer. As soon as the laser hits the liquid resin, that specific cross-section solidifies.
Once the layer is completed, the build platform increments and another cross-section is exposed to the laser for treatment.
The movement of the build platform depends on the layer height set for the Stereolithography process.
The entire process keeps repeating until the final object is created.
Post Processing
After finishing the 3D model, the build platform rises out of the tank. The excess resin can be spilled away. You can now remove the model out of the platform and get rid of any excess resin attached to it.
The final step is to cure the object inside a UV oven. This helps in increasing the maximum possible strength of these 3D models. Hence, the post-processing is a must requirement in case of every SLA 3D Printing process.
Why SLA Process?
There are many good reasons why so many professionals choose SLA over any other 3D printing process. A lot depends on the physical and mechanical properties of these models.
The way they look, their precision, and many other parameters make SLA one of the most popular processes of additive manufacturing.
Precision
We have already talked about accuracy and precision a few times in the article. And, it is something that we cannot ignore.
This property has made SLA one of the best suited 3D printers for professional applications. It can build models with minimum possible layer height. Plus, you can create complex geometries that are impossible to fabricate otherwise.
The finest of details can be carved most subtly. All thanks to the Stereolithography process which made everything so easy for all of us.
Isotropy
This is one of the most crucial features of SLA 3D models. That is why the range for many important applications. In 3D printing, the parts are created with layer bonding.
One layer is attached to the previous one and so on. When such attachment happens, the layer difference is very obvious. For example, FDM 3D printers create anisotropic parts.
However, this is not the case with SLA 3D printers. During the Stereolithography process, the bond between layers is strong and happens at the molecular level. This creates high strength and the parts are isotropic.
Watertightness
The objects created by SLA 3D printers are flowing and continuous. You can either create complex geometries featuring solid parts or with internal channels, you get to see feel the water tightness.
The feature is very crucial for certain applications, including engineering and manufacturing applications. It is suitable for those jobs where air or fluid needs to flow in a controlled manner. More like in a predictable state.
Designers have come up with SLA printers in order to solve air and fluid flow challenges. It is applicable for automotive uses, validation of parts design as well as biomedical research.
Smoother Surface Finish
Have you ever worked with FDM 3D Printer before? If yes, and now you are shifting to SLA 3D printers, you would notice a huge difference in the surface quality.
SLA 3D printers are capable of producing the finest surface finish similar to the ones created with injection modeling and other conventional methods. Or, you can even call it better than most of the other processes.
From accuracy to finer details, all are represented in the most beautiful way. You can make out how SLA printers are capable enough when it comes to creating the most stunning appearances of models.
Either its smoother finish or the smaller details, everything is taken care of in the most perfect way possible.
Stereolithography Materials Versatility
SLA resins have always been able to impress a lot of audiences because of its versatility. It is available in a wide array of formulation configurations.
You can work with a soft resin and at the same time, the hard resin is also available. You can find a heavily filled resin stuffed with secondary materials such as ceramic. And, you can also select the material range invented especially for industrial use.
The different resins are available for different purposes. The resins are configured in a variety of ways to provide users with varying sets of mechanical and physical properties.
Stereolithography Advantages and Disadvantages
There are many good things about SLA 3D printing. However, there are few limitations as well which makes this process unsuitable for a few applications.
Advantages
- With SLA 3D printers, one can create highly precise 3D models, impossible with any other 3D printing process.
- The 3D models created are isotropic in nature, hence, providing greater molecular bonding between layers of the 3D parts.
- Resins are available in different configurations for achieving varying properties suitable for different tasks.
- SLA is the best option for rapid Prototyping. The models are of high quality and exhibit fine details. One can also 3D print the most complex geometries with ease. By using the layer thicknesses as low as 25 μm, one can achieve high precision.
- It creates smoother print surfaces.
- One can go for higher build volumes without thinking of compromising on precision.
Disadvantages
- The print time is longer than the other printing processes.
- If you are printing steep slopes or overhangs, you will require to create support structures. However, if not handled well, these can collapse during the building process. Or, they also tend to break apart when ensuring the final curing.
- Because of the fragile nature. Also, these can lose their shape and structure when exposed to sunlight for long. That is why these models cannot be used for outdoor applications or creating lamps. Moreover, these cannot be engaged in mechanical testing for the same reasons.
- The Stereolithography materials come in limited color choices. You can choose between black, white, grey, and clear resins. On top of that, resins are usually based on proprietary usage. Hence, these cannot be used interchangeably for different 3D printers’ make and brands.
- The cost of 3D printing with SLA machines is higher when compared to FDM.
The Conclusion
Additive manufacturing has given us a lot of new ways to accomplish a manufacturing task. We have got so many different 3D printing processes, including the Stereolithography process.
And, SLA is one of the best of all the techniques available. Also, being the oldest one is highly favored by experts. The technology has come very far.
Started as an alternative to additive manufacturing, it has become the one-stop solution for various needs. It can create highly detailed designs, thanks to the laser power.
Plus, it can help make complex geometries a reality. Though, it is coupled with post-processing methods and is a bit difficult to accomplish with success. It is worth every try.







