The casting process is one of the oldest metal manufacturing methods. Although the process at its core has essentially remained the same with passing time, it has evolved to become more precise and automated.
The different types of methods of fabrication using casting nowadays are: a) Sand Casting b) Investment Casting c) Plaster Casting and d) Die Casting.
The most popular among these is Sand casting. It utilizes expendable sand molds to form complex metal parts that can be made of almost any alloy.
One of the many innovations in this process is the possibility of sand-casting 3D printing. By doing so, we can benefit the production in many ways.
Before looking at how 3D printing can benefit sand casting, we’d like to take you through the general process of Sand Casting.
So, that while listing the benefits that sand casting 3D printing has, you get the exact idea about the areas in which the benefits are. So without wasting any further time, let’s get started.
What is The General Process of Casting?
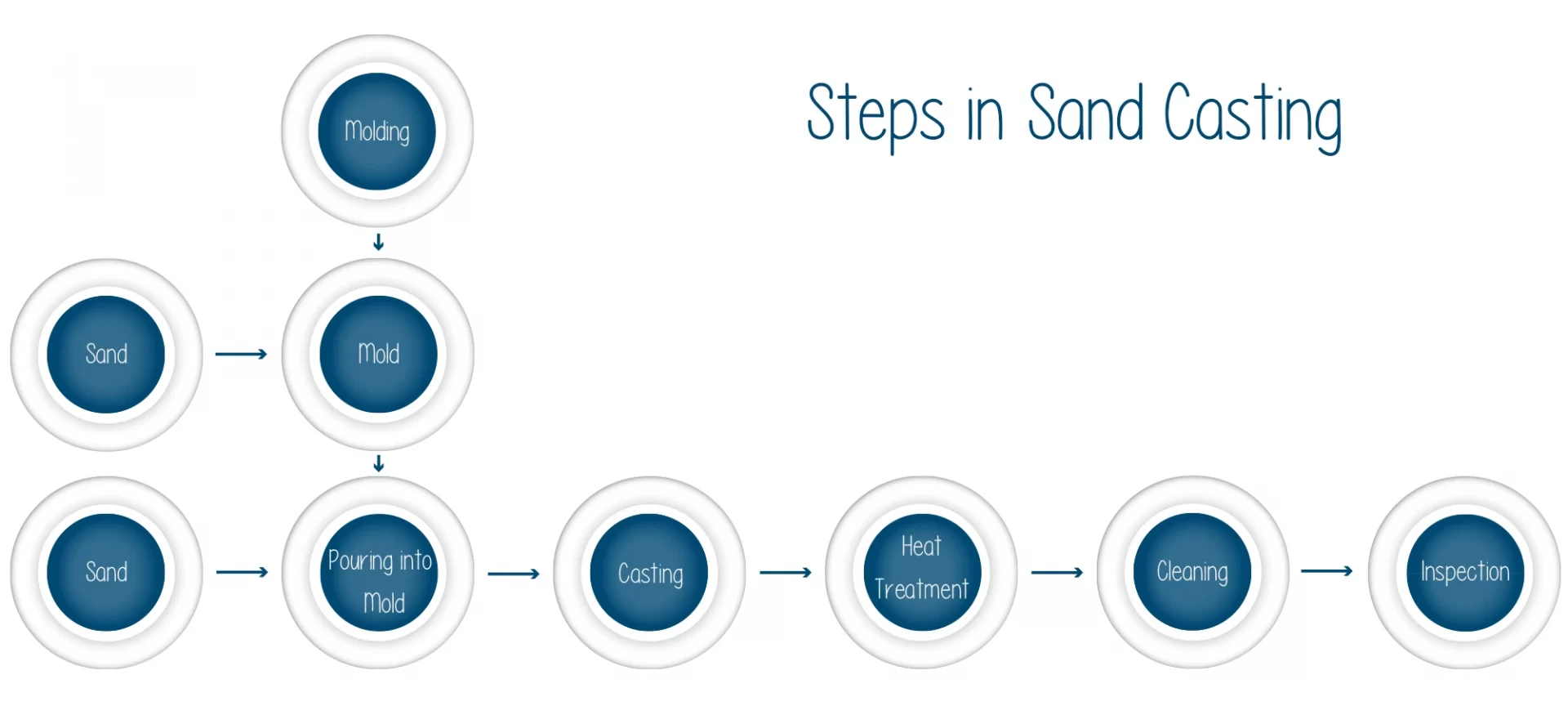
Whether it is sand, investment, plaster, or die casting, they all need to undergo some general casting steps. What are they? Well, let’s find out.
Pattern Making
A physical model used to make the mold and replicates the exterior of the casting is called a pattern.
It’s not that hard to understand the definition, as it is close to the real meaning of the word “pattern.” Pattern making can be done using several materials.
In some cases, the interior of the component of the actual parts needs to be hollow, like in pipe fittings. Making of such parts, require the creation of additional patterns called cores.
They are a separate part of the mold, the function of which is to prevent the liquefied material to fill in that empty space.
The creation of internal cavities, like the ones in pipes, and other features that cannot be generated by the mold is where the core plays an important role.
The tooling used for making the core is called a core box i.e. another way to call the mold that creates the core. The materials needed for core making should satisfy the following requirements:
- The material should have enough strength to resist the turbulence caused by the molten material.
- It should have an adequate amount of hardness.
- The material should be in a higher permeability range so that the gases formed during the casting process can easily escape it.
- It should be able to resist the high temperatures from the molten material.
- At the same time, the material should be weak enough to break when the molten material cools down and shrinks, facilitating its removal after solidification.
- The materials should have a smooth surface finish and a minimum gas generation when exposed to the molten material.
Molding
The method of creating the mold to receive the molten metal is called molding. There are multiple operations involved in this process. Each of which assists in forming the mold around the pattern!
The process of molding starts with the mold contained in a flask, a frame consisting of two parts: a cope and a drag. The flask is filled with the molding sand around the pattern, after which the pattern is removed.
The positioning of gating systems, and channels that allow the molten material to enter and flow through the mold, are in the drag, the similar arrangement that receives the cores.
The channel used to introduce the molten material into the mold, called the sprue, is placed in the cope. After all this, for closing the mold, the cope is put on top of the drag. And finally, both parts are clamped together.
Melting and Pouring
Melting is the process of transforming the solid metal material into a liquid state. This is done to make the metal pourable into the mold.
As you might’ve guessed, the process is performed at an extremely high temperature and in a piece of equipment called a furnace.
These are heating chambers designed based on multiple factors, mostly according to:
- The type of material
- The fuel that will be used to achieve the required temperatures.
It is to note here that the temperatures required can go over 1600°C. Exposing metals to this high temperature can usually generate harmful gases causing defects in the casting.
But the gases can be removed as the molten material is refined, a step that also purifies the metal material by extracting other unwanted elements. This process does not alter the chemical composition of the material.
And after refining, the molten material is set to be tapped into the ladle – the vessels used by foundries for safely transporting and pouring molten metals into the mold.
Liquid metal is then poured into the mold and left to cool down until it reaches room temperature.
After the material is solid again, it will go through a process of separating and removing the sand from the casting by vibrating the molds. This process is called shakeout.
Cleaning
After the casting is ready and freed from the mold, the gating systems, and remaining residual materials are removed and the excess materials are trimmed.
Post-processing treatment may be done for improving the appearance and surface of the casting. After which, the casting is sent forward for quality control.
Now that we’ve been through the general process of Casting, it’s time to see how exactly sand casting takes place.
What is Sand Casting?
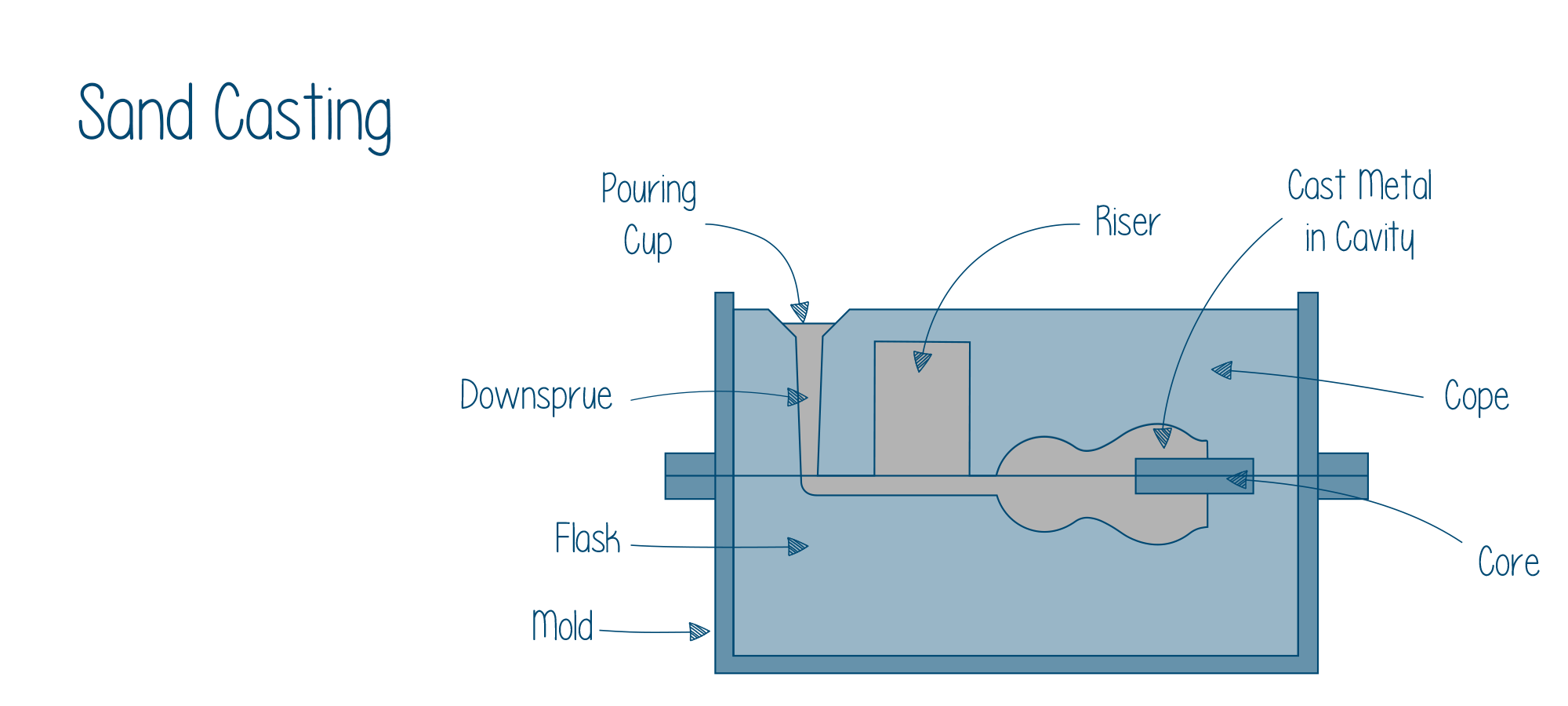
As mentioned above, Sand Casting is the most common technique for manufacturing metal castings. The technique accounts for over 70% of all castings produced.
If there is one thing that the Sand Casting process is particularly known for, it has to be its versatility. It’s a process that can produce castings of all sizes and weights with exceptional complex geometries utilizing the majority of metals.
Another main characteristic of the Sand Casting technique is that it takes into account and the molding medium.
Doing so leads to significant cost reduction in making molds instead of other materials and this is a great advantage.
Especially while mass production when mold making costs account for a big chunk of the expenses.
Sand Casting is ideal for metals such as titanium, steel, and nickel, in short for metals melting at high temperatures. It is also the only casting method amongst all the other ones that can handle these materials.
And it is not surprising that sand casting is the first choice for the production of parts in the aerospace and automotive industries.
Sand molds are made using four components:
- Base Sand: It is the type of sand that’s used to make the mold in its pure state. For holding it together, a binding agent is required. It is important to note that the base sand also makes the core. The most common ones are: Silica Sand, Olivine Sand, Chromite Sand, Zircon Sand, and Chamotte Sand.
- Binders: As mentioned above, binding agents are responsible for gluing the sand particles together. Clay and water, Oil Resin, and Sodium Silicate are the most common types of binders typically used in application.
- Additives: What improves the mold in terms of surface finish, strength, cushioning and refractoriness are additives.
- Parting Compounds: A liquid or fine powder that facilitates the removal of the pattern from the mold is called a parting compound.
What Are The Pros and Cons of Sand Casting?

Like every other manufacturing technology, sand casting has its own limitations and advantages that are mentioned below.
- It can be used to manufacture parts using almost all metal materials, including those with high melting points.
- Sand casting is easy to scale.
- Even complex geometries with thin-wall sections can be created using sand casting.
- Castings of all sizes and weights can be produced using this method.
- The production cost of sand casting is lower compared to other casting methods.
- Producing parts at a higher volume production requires a high degree of automation for sand mold making.
- Sand Casting has a lower degree of accuracy than other manufacturing methods.
- Parts with rough surface finish produced using sand casting usually require post-processing treatment which demands time and effort.
How Did 3D Printing Revive Casting?
3D printed molds for sand casting are an invention that has changed the fate and face of casting. The inclusion of additive manufacturing as a method for making molds is reviving the casting process by solving some of its limitations.
This hybrid model of additive manufacturing and casting provides a real competitive advantage over the traditional production process due to the methods’ economic and design benefits.
Sand Casting can be carried out using Binder Jetting 3D Printing, the 3D printing technology utilized for creating molds and cores from the sand.
Binder Jetting 3D printers build parts layer-by-layer, using a binding agent for bonding and strengthening each layer. The most common sand materials used in sand casting 3D printing are Silica and Zircon.
What are the Benefits of Sand Casting 3D Printing?
After having gone through the limitations of sand casting, it wouldn’t be difficult to go through the benefits that sand casting 3D printing brings to the table.
- The main benefit of sand casting 3D printing is cost reduction. On average, your customers can save 75% of the cost involved in mold making.
- Another benefit of this technology is related to the time taken for manufacturing parts and functional prototypes using Sand casting. Compared to conventional techniques, which are known to take up to several weeks for making the molds and cores, sand casting 3D printing molds only takes a few days because they are automated.
- The next benefit is in line with the above-mentioned one. Because the complete process is automated, there is more room for improvement and design changes. For those who are not familiar with 3D printing, it is worth noting that the production of molds and cores only requires a CAD file.
- Lastly, the complexity of the geometries and their accuracy is also much higher with sand casting 3D printing than only sand casting. As for the size, parts can be as large as 400 cm x 200 cm x 100 cm and dimensionally accurate.
The Conclusion
Seeing and realizing the benefits of sand casting 3D printing, more and more companies are starting to make machines that can process parts and functional prototypes out of this process.
The companies like Voxeljet and ExOne are leading in this field of making sand 3D printers that can process based on powder bed fusion 3D printing technologies and produce sand cast parts that find applications in various fields.
That been said, the field is very new and has still got much room for experimentation and innovation. It is not as developed as other additive manufacturing processes.
More and more researches comparing older and evolved forms of sand casting should be encouraged.
One such study by researchers from Indiana University – Purdue University Indianapolis (IUPUI), Commissioned in 2015 by the India-based research and consulting firm Development Solutions Inc., systematically compared the conventional sand-casting process with the 3D printing process for sand molds.
This study revealed the most obvious benefit of sand casting 3D printing, according to one of the researchers, printing all of the mold’s components took 26 hours, compared to the six-plus weeks that it took when made using the traditional casting. But researchers claim that this benefit is far from the only one that was found.
With such researches, the real benefits and challenges faced by sand casting 3D printing can be analyzed, and only then can a real shift be expected from individuals and businesses employed in sand casting.
However, seeing the bright scope of 3D printing in other areas of manufacturing, it wouldn’t be unfair to state that with the technology becoming more and more accessible, there’d be more and more outcomes.
And if sand casting 3D printing becomes mainstream, we’d be able to overcome the limitations faced by traditional sand casting!







