Among all the 3D printing processes, Laminated Object Manufacturing abbreviated as LOM 3D printing is the least popular technology.
Unable to create parts with complex geometries and difficult designs, this particular 3D printing process hasn’t been able to occupy similar space in the manufacturing industry as other choices.
However, there are certain characteristics that highly favor the use of LOM within industries.
Starting from the capability to print relatively larger parts and working with cheap raw materials, this technology is able to serve a large number of niches.
The demand for this additive manufacturing process is limited, yet considerable. And, for some applications, the technology fits better than those requiring expensive materials and special environments such as enclosed chambers.
Above all, LOM 3D Printing is one of the safest processes. This is so because there is no need to perform any kind of chemical reaction. With so much to learn about this technology, why not jump to the various details associated?
So, here is a brief idea of how LOM works and what are the different perks and limitations that come along with this technology.
Introduction
Laminated Object Manufacturing, as the name, suggests deals with the lamination of different layers together to create the final part.
The technology was developed in the 1980s by Helisys and made available for users in 1991, becoming the first-ever 3D printing technology used for commercial applications.
However, Helisys ceased operating in 2000 but the technology does exist today as well. Currently, the major supplier of LOM 3D Printing is Cubic Technologies.
What is LOM 3D Printing Technology?
As the name suggests, it has something to do with lamination or fusing the layers together. In simple words, the sheets of materials are fused together using heat and pressure.
After which, the cross-sections are cut and shaped using a blade or laser source.
That must have sounded easy. And, it is actually a simpler 3D printing process as compared to the other alternatives.
However, you must ensure that the proper production steps are followed precisely to obtain accurate prints.
Working Principle
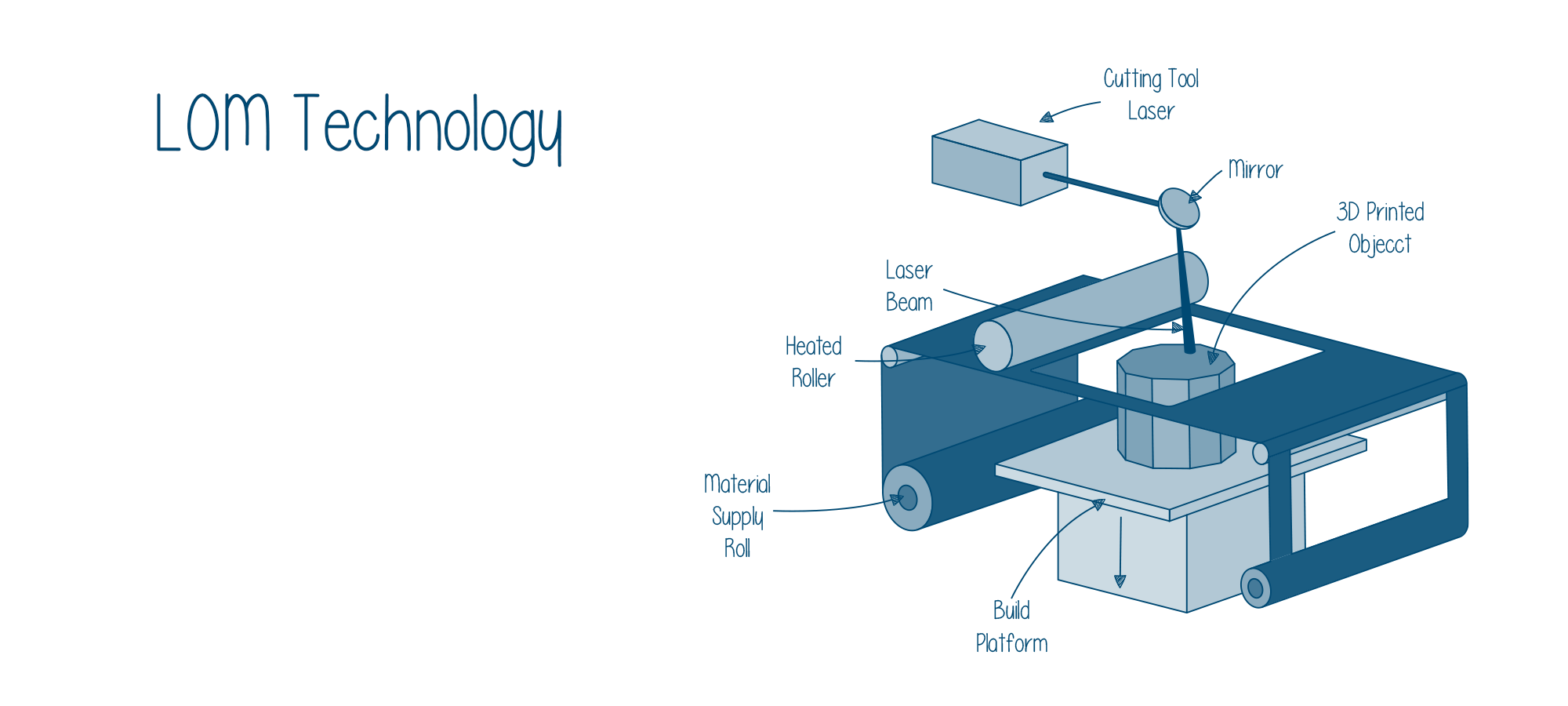
The 3D printing process involves a few steps before perfecting the final part. Here is what you can expect to handle while working with a LOM 3D Printer.
Design the 3D File
As it goes with other 3D printing techniques, you must design a 3D file for the part you wish to create. It must be in the format that is acceptable by the 3D printer.
Preparing the 3D Printer Apparatus
Next comes 3D printing of the STL file. And, the process starts with feeding a continuous sheet of material with the use of rollers. To ensure the sheets stick in place, an adhesive is used to coat the material.
Creating the 3D Object
For starting the printing of objects, the machine lays a single layer of the sheet at a time. Once laid to the build surface, a heated roller passes over the material to melt the adhesive and press the sheet tightly onto the build platform.
This is when the laser or blade cuts the desired shape as per the 3D design file in a crosshatch pattern. Hence, enabling the removal of excess material later when the printing of the 3D object completes.
After the first layer completes, the build platform lowers exactly by the thickness of one layer. Then the next layer is pulled and laid across the platform and the complete procedure is repeated. This goes on until the complete design is printed.
Removing Excess Material
Once the object completes printing, the part is removed from the build platform. Users can work with laser, blade, or simply knife, depending on the material to remove the excess parts. When printing with paper material, users often paint the final part to save it from moisture.
Materials Used in LOM 3D Printers
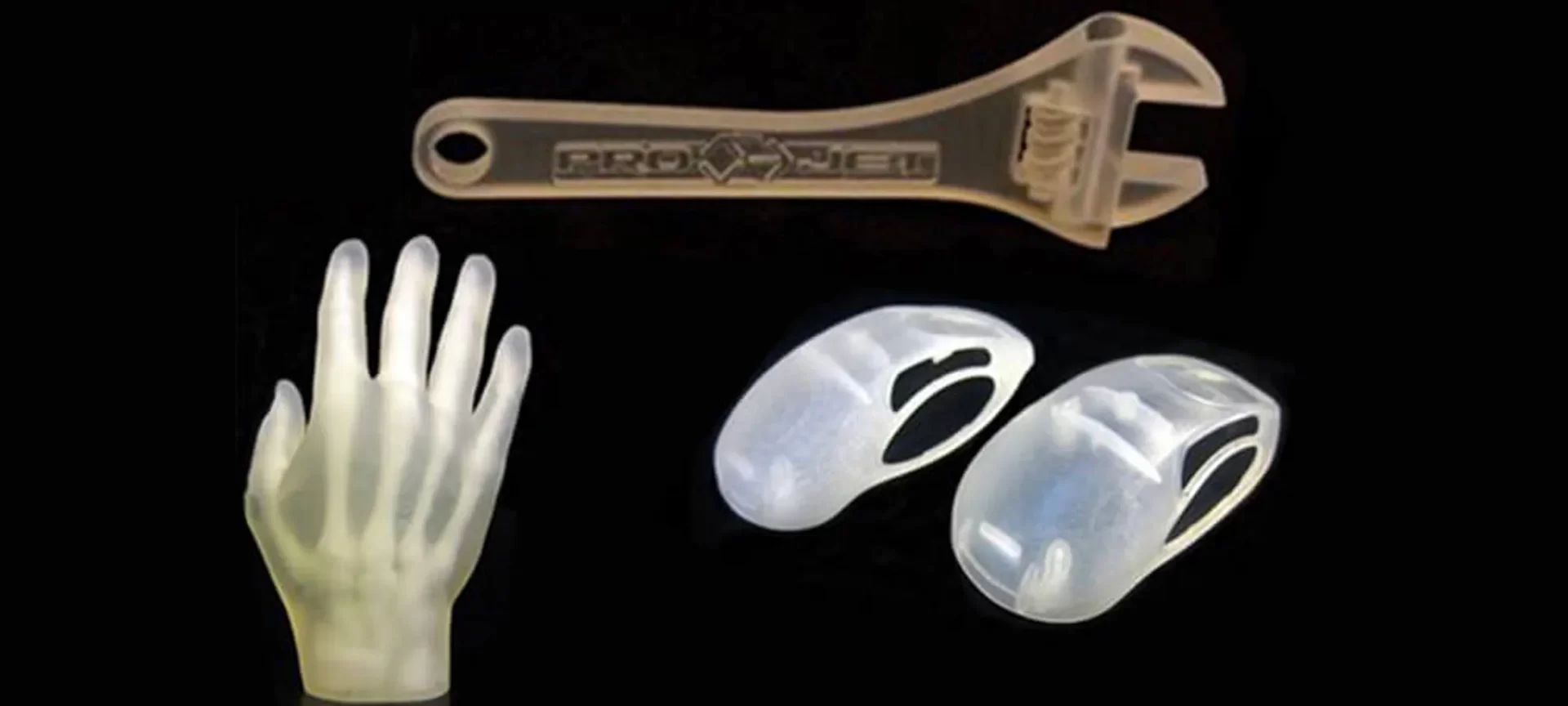
If you look at the brightest side, you can use materials that can be glued together. That does make this technology very versatile and applicable to a number of applications.
In this additive manufacturing technique, we usually coat the material using an adhesive to ensure that the layer bonding is strong.
So, materials such as paper and plastic are more common when printing using the Laminated Object Manufacturing method.
Metals can also be used as a material but are rarely utilized. And, there is a genuine reason for the same.
When working with the printed parts, the process requires one to remove the excess material with a laser or blade.
Hence, when the material used is paper, the process is much simpler. However, when using metals, the cutting and shaping process becomes tedious and sometimes infeasible.
Therefore, companies usually work with papers when creating objects using LOM 3D Printers.
The resultant object showcases wood-like properties. And, later can be painted to ensure protection from moisture for longer life and highest usability.
Here is a list of certain materials that are used with LOM 3D printers, some more often and others not so often:
- Paper
- Plastics
- Metal foils
- Composites
- Ceramics
- Polymer film
Things to Keep in Mind
There are certain things that you must keep in mind before opting for LOM 3D printers. While these are highly simple to operate and faster when compared with most of the other 3D printing processes, you cannot just weigh its cheap price to make the final decision.
- When printing, the precision of the objects would depend completely on the layer thickness of the sheets of material you use.
- The technology isn’t very handy when wanting to create complex geometries and objects
- Moreover, withdrawing support parallelepipeds could turn highly exhausting sometimes.
- In case the supported withdrawal isn’t done properly, the final object can break or damage.
What Can We Print Using Laminated Object Manufacturing Technique?

We already discussed a few limitations of this technology when creating parts. For instance, it cannot create complex geometries.
So, what can you exactly print using these machines? Apart from the complex geometries and designs, the printer can actually make a great companion for those wanting to create larger objects.
Yes, because these machines do not need an enclosed chamber, the resultants parts can be relatively larger than the ones created using other 3D printing techniques.
Moreover, not fit for functional prototypes, the technique helps in printing scaled models as well as conceptual prototypes. These models are usually for testing the design of the parts.
Moreover, the machine can also create patterns utilized by conventional manufacturing methods such as metal casting or sand molded casting.
What Are The Applications of LOM 3D Printing?

Instead of the limitations the technique carries, there are certain applications where these machines hold huge importance.
Rapid Prototyping
Well, you cannot use the printers for creating functional prototypes. However, these could majorly help users with scaled models.
For instance, if you wish to check the parts in terms of design perspective, you can create a larger model using LOM machines.
This helps a lot in making changes to the parts and testing them again on similar grounds.
The same goes with the conceptual models. In order to ensure that the design is relevant and perfectly fits your needs, you can try creating a prototype using LOM machines.
Not only these use cheap materials that you anyway will discard later, but these printers could also help create prototypes faster.
Even for larger models, these machines could help prepare bigger prototypes in one go.
Architectural Models
One major application of LOM 3D printing is for the creation of architectural models. Being able to print bigger models, the printing technique is highly popular among architects and designers.
With Conventional Manufacturing Processes
LOM machines can create cheap patterns for sand casting or metal casting. Hence, the conventional manufacturing industry can also make use of these printers for making patterns and shapes.
Educational Purpose
With its cheap raw material that is easily available for use, this particular technique is also a great option for educational purposes.
Preparing science models or helping students learn about 3D printing and 3D designing could be made available with LOM 3D printers.
Moreover, these can be run without a need for enclosed chambers. Hence, students can actually check the entire working process while the machine is operating in real-time.
What else could be the best way to provide exposure for additive manufacturing to students?
Although the machine isn’t cheap, to begin with, the running cost is actually too low when compared with other options. Thanks to the cheap and readily available raw materials. Hence, suitable for a larger group of learners.
What Are The Advantages and Disadvantages Of LOM 3D Printing?
Now that we have learned a lot about LOM 3D Printing, why not have a look at the specific pros and cons for better insight into the technology.
Pros
No Support is Needed: Isn’t that a relief already? With LOM 3D printers, the users do not need to add extra support. This is because the extra materials happen to do the job for the same. As these excess materials are removed once the model is completely printed, these offer support to the overall design without any hassle.
No Enclosed Chambers: Like in many 3D printers based on other technologies, we often need to have a consistent temperature around the build platform. However, with LOM 3D Printers, this is not the case. Moreover, there is no need for carrying any kind of chemical reactions that must be contained. Hence, one does not need to have an enclosed design when working with LOM 3D Printers.
Supports Printing of Larger Models: When it comes to 3D printing larger objects, most of the 3D printing technology takes the back seat. However, when it’s about LOM 3D printing, you can expect to create relatively larger models, at a faster rate too.
Faster Production Speed: The technology offers high-speed production. You can create larger designs and also complete these parts in less time when compared with other techniques. This provides LOM an upper hand over many other 3D printing technologies.
Cheap Materials and Production Cost: Starting with low-cost materials, the overall production budget comes down considerably. In addition, the materials are readily available in abundance.
Cons
Problems Connecting Consecutive Layers: Although the adhesives are used to add one layer over others, the entire process may fail sometimes to accomplish the desired results. Therefore, the layer bonding may not be too strong.
Poor Surface Quality: Not as precise as SLS or SLA 3D printing technology, the parts aren’t very smoother. Due to poorer surface qualities, the LOM 3D Printers usually are sufficient for prototypes and aren’t suitable for end parts.
Complex Geometry Isn’t Possible: This again is a huge limitation that the technology hasn’t been able to overcome to date. With sheets laminated one over another, and the excess materials sliced later, it is impossible to create intricate and complex geometries.
Expensive 3D Printers: We have been talking about cheaper production costs. However, the initial investment isn’t cheaper. Comparing the LOM 3D Printers with FDM desktop 3D printers, you can find a huge difference in the starting price range. While FDM printers start at around $200, the LOM 3D printers start from thousands of dollars. For instance, SD300 by cubic is priced at around $15,000.
The Conclusion
Additive manufacturing is a very diverse technology, offering assorted processes for different needs. Since the beginning of the development, experts have been able to come up with a variety of different techniques to ensure the highest satisfaction to the users with an array of requirements.
And, Laminated Object Manufacturing, although less popular, does enjoy some amazing features to help plenty of different applications.
LOM 3D printing is often considered a cross of additive and subtractive method because of the removal of excess material later.
However, its layer-by-layer creation puts it within the 3D printing ecosystem, without any confusion.
Unable to create complex geometry, the technology efficiently compensates for its limitations by offering support for larger print and cheap production costs.
Plus, the faster processing speed is a huge perk for those relying on speedier completion of 3D printing jobs.







