Polyjet is the abbreviation of photopolymer jetting. This 3D printing technology belongs to the subclass of the Material Extruding or Jetting 3D Printing technology.
Material jetting is the name for any 3D printing technology in which the liquid which is the building material just like resin in SLA 3D printing is sprayed or jetted from a print head. Let’s look at the history of polyjet 3D printing.
History of Polyjet 3D Printing
Objet Geometries in the year 2000, developed the first 3D printer that jetted photopolymer droplets and cured them with UV light.
After getting successful results in their experiment, the company carried on the development of this technology which was named by them polyjet. Objet Geometries holds a number of patents in this technology.
Over the course of time, in 2011, Stratasys acquired Objet Geometries with the goal of expanding the range of its products to MJ solutions.
As a result, the name Polyjet remains as it is, but is currently used for printers from Stratasys.
But what is to be noted here is that multi-jet fusion and PolyJet are the same technology with different names.
But because the development of the technology is shared between two companies, there some minor differences that exist between their respective machines.
But the basic printing principle remains the same. In this article, we will explain to you the principle and the working of polyjet 3D printing.
What are Photopolymers?
Scientifically, photo means light and polymers are substances formed by the amalgamation of many monomers.
Combining the two, a photopolymer is a substance that changes its physical properties whenever it is exposed to light.
Photopolymers are a very popular build material used by 3D printers, especially the PolyJet printers.
Typically, polyjet 3D printing machines use liquid plastic resins that harden when exposed to a light source like UV light, lamps, projectors, etc. These liquid resins are one type of photopolymer.
The Eccentricity of Polyjet 3D Printing
The field of 3D printing technology has two giants when it comes to talking about Multi jet fusion 3D printing technology. The first one of those is Stratasys and the other one is 3D Systems.
After reviewing their 3D printers, the main difference between them which was observed was the type of material they used for support structures.
On one hand, the polyjet technology from Stratasys used dissolvable support material, which could be made of polyethylene, propylene, and glycerin.
Here in the parts after getting printed, could be removed from the build platform and exposed to pressurized water.
This process is enough for removing as much support material as possible without dissolving it into the actual part or functional prototype.
Afterward, these parts or functional prototypes emerged in a chemical solution, in which the remaining part of the supports dissolve, and leaves behind a clean part.
On the other hand, MultiJet 3D printers utilize paraffin wax as a support material wherein after a part is printed the supports need to be melted away in an oven.
PolyJet is a 3D printing technology that is known for producing parts and functional prototypes that have smooth layers.
These parts have accuracy along the edges. The prototypes tooling produced by this technology is known for producing precise results.
The microscopic layer resolution and accuracy of these printers are down to 0.014 mm.
Imagine the thinness they can produce in walls and complex geometries by using the widest range of materials available with the technology.
Amongst the many benefits of PolyJet 3D printing are the creation of smooth and detailed prototypes that convey final-product aesthetics.
Followed by the production of accurate molds, jigs, fixtures, and other manufacturing tools.
With polyjet 3D printing, you can achieve complex shapes, intricate details, and delicate features.
You can also incorporate the widest variety of colors and materials into a single model for unbeatable efficiency.
How to Build Materials for Polyjet Printers?
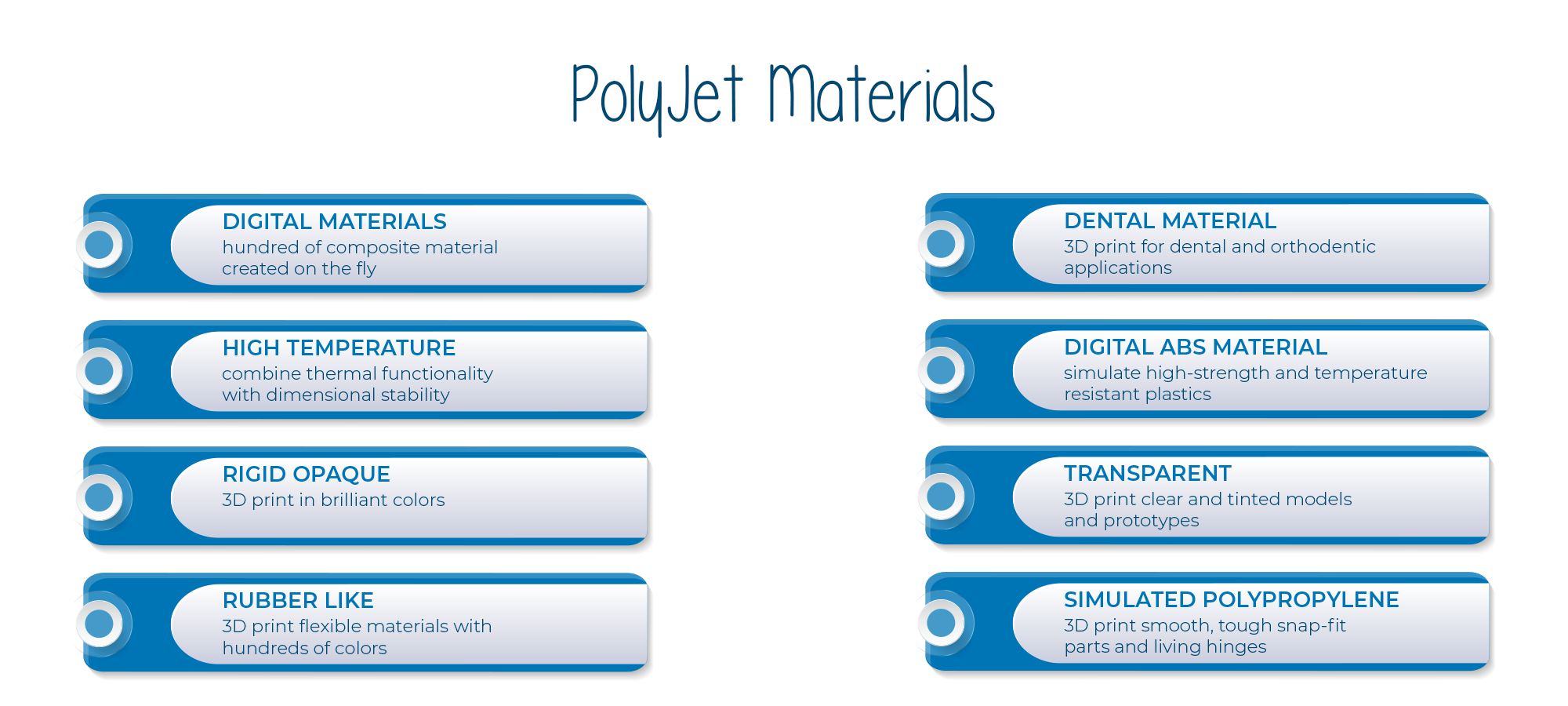
The availability of a different range of raw materials today for 3D PolyJet printers is simply amazing.
So, you already know by this time that polyjet 3D printers mainly use photopolymers, but since the inception of this technology, there have been inventions and attempts to increase the scope of materials that can be used with the 3D printer.
Apart from the standard photopolymers, the build material of polyjet 3D printers also includes clear, rubberlike, and biocompatible photopolymers and tough high-performance thermoplastics.
A few of the very popular 3D PolyJet printing materials are: 1) Digital Materials. 2) Digital ABS Materials. 3) High Temperature 4) Transparent 5) Rigid Opaque 6) 7) Simulated Polypropylene 8) Rubber-like 9) Bio-compatible and 10) Dental Material.
What is the Difference Between FDM and Polyjet 3D Printing?
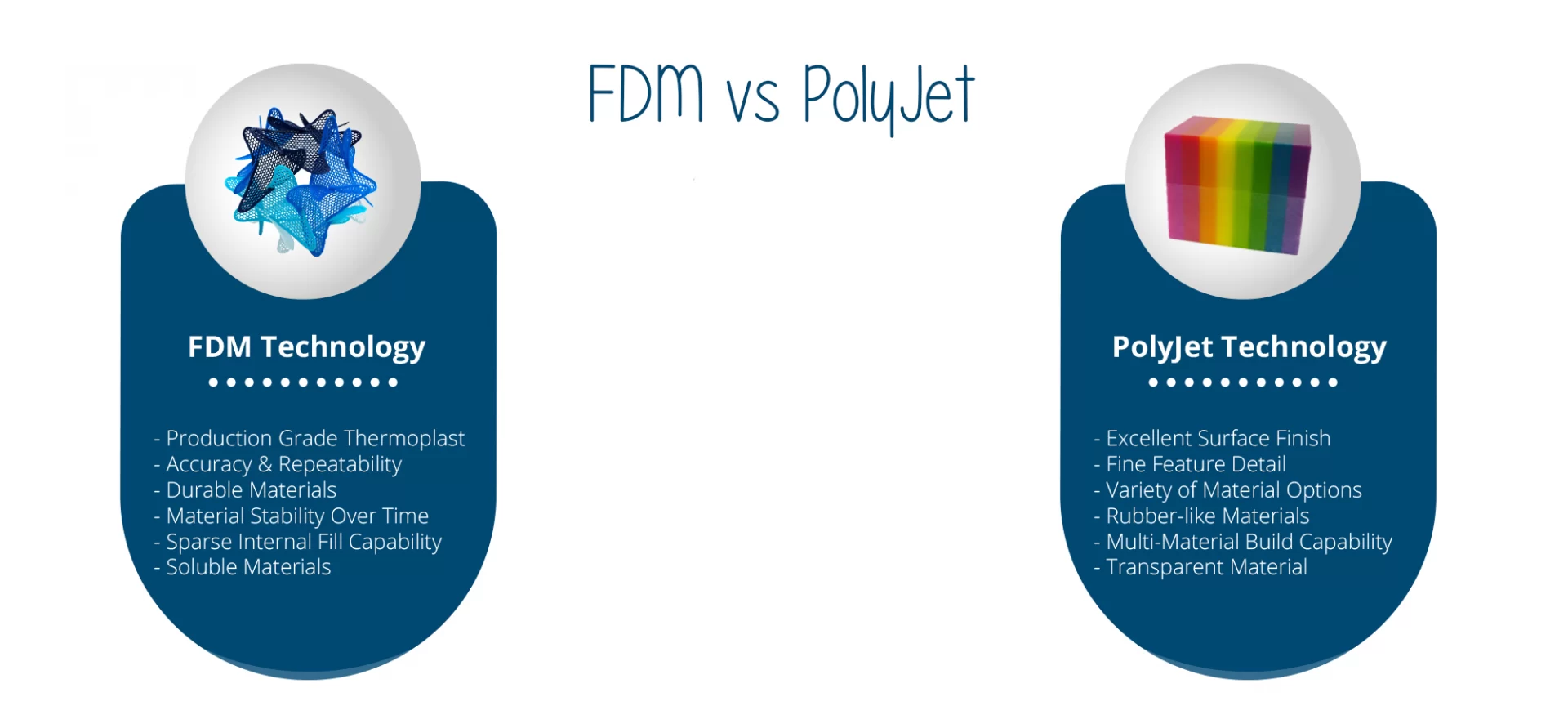
Understanding this difference is interesting in the sense of whether you are buying a new 3D printer or upgrading your older one.
The fact that there is always an impression on people’s minds that both techniques result in the same kind of part or functional prototype is what makes them confused very often.
But when you see real parts made out of these technologies you can see them and differentiate which one is made by which technique.
There are various aspects in which the former differentiates itself from the latter. And they are mentioned below one by one.
Extrusion
Both, printers based on Fused Deposition Modelling (FDM) and Polyjet printers build 3D parts and functional prototypes layer by layer.
However, it is the process of making them differ one from the other.
On one hand, where FDM 3D printers heat a thermoplastic filament in order to create a layer when you are building a part with Polyjet 3D printing, the printer relies on the use of liquid polymers, jetted onto the printer bed.
The second point to consider here is that, during FDM printing, a coil of fine thermoplastic is wound on a spool is heated and extruded in a continuous bead of semi-molten material.
And after this filament is deposited, it cools and solidifies to form a new layer just one of many that form the finished model.
In contrast to this technique, when you are printing a part or functional prototype using Polyjet printing, after being jetted onto the subsequent layer, the layers of liquid polymer are cured through exposure to ultraviolet light.
Fidelity and Durability
When you compare FDM models to Polyjet models, the former more robust than the latter. However, it generally depends on your choice of material, FDM models can also be made to withstand high temperatures. But that being said, it only happens when there is more demand in their working conditions and environments. Otherwise, they aren’t made more durable than Polyjet models.
Choice of materials
Speaking of the applications of materials, Polyjet wins hands down on materials variety because of a choice of more than 1,000 materials in the technique.
And in it also there is an option to blend multiple digital materials within the printing process. So, overall Polyjet printing is extremely flexible compared to FDM.
It is the blending of multiple digital materials which makes a 3D printing technique more impressive and advance as 3D printing technology.
And it is seen how the latest Stratasys J-Series machines, such as the Polyjet J850, uses this internal mixing ability to great effect.
By the use of multiple model materials loaded all at a time, the mixed material parts, the mixed material builds and full-color parts are all easily achievable. Which is a lot of fun as a user to check out.
Other materials that can be used across the Polyjet range include medical and dental printing materials.
There are also rubber-like and rigid opaque materials with which you can 3D print parts and functional prototypes.
You can also print transparent parts using Polyjet printing and produce fully flexible models with a scale of rigidity that can match anything from a soft gasket to a vehicle tire which is otherwise not possible.
Working with Polyjet 3D Printers
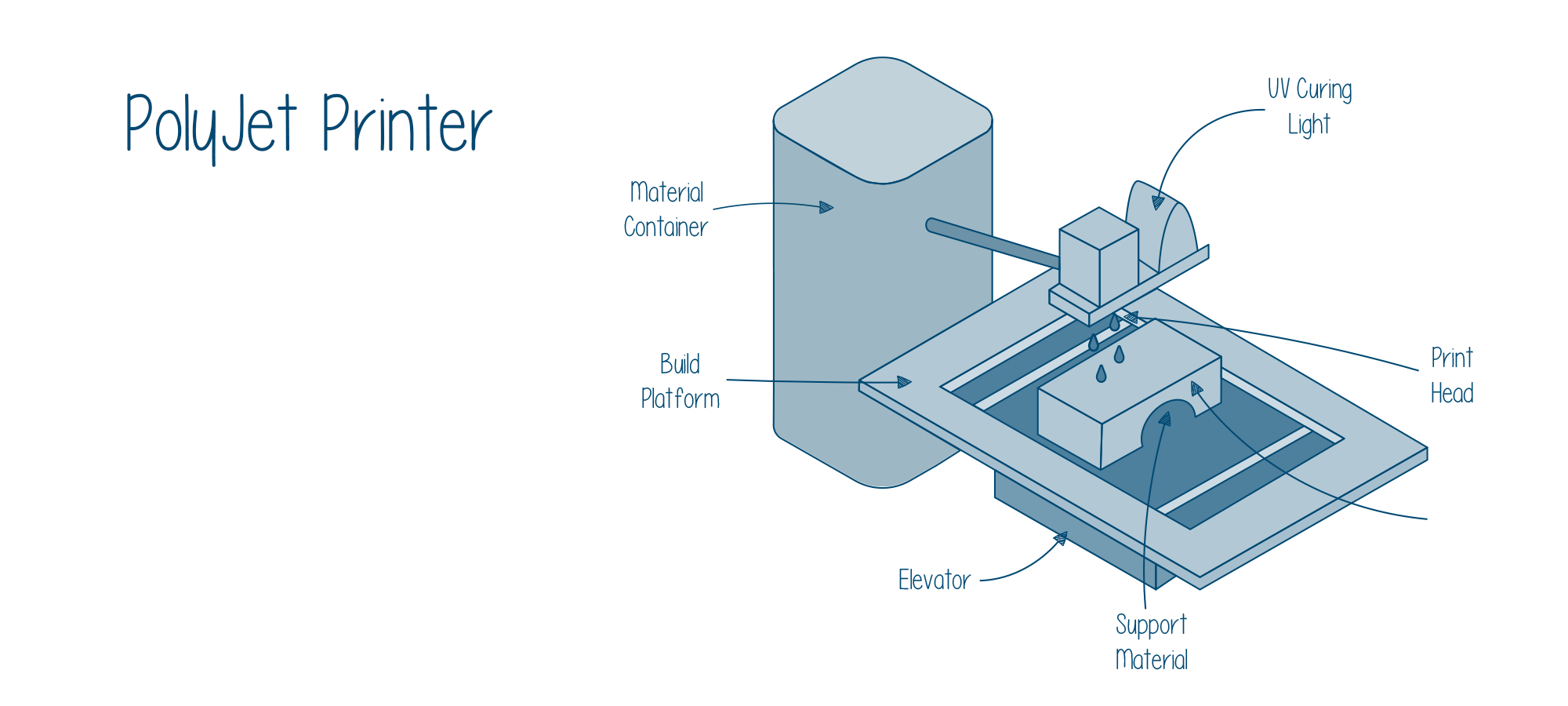
If you have read the anatomy and printing process of a 3D printer based on material jetting technology, you will find it completely similar to that of the Polyjet 3D printer.
As we have already read too many times in the article about material jetting 3D printing being another name to polyjet 3D printing, we won’t go into details about that too.
Starting with the basics, the main parts that are needed to be observed while printing with a PolyJet printer are 1) A material container, 2) A build platform (and its elevator), and 3) A carriage on which UV lights and jetting print heads are mounted.
It is obvious that printing cannot begin with the raw material that you require to build parts and functional prototypes, so before printing begins, photopolymer resin must be poured into the material container and heated to start the printing process i.e. deposition of a layer.
What this permits is the substance i.e. resin to reach the desired viscosity. After this is done, there is a little bit of traveling across the X-axis i.e. across the build platform.
As soon as the traveling starts, the print heads selectively jet the resin. The work that is done manually in the SLS or SLA 3D printing technology is done here with the help of the printer.
This jetting is in the form of droplets, sprayed onto the build platform. After this process is done i.e. once they’re jetted, the UV lights cure them into an ever-growing solid.
And here the point of flexibility is that there isn’t just a single print head, but there are multiple, so different materials can be printed at once.
A typical example of this functionality is a part requiring supports. Generally, when parts need support, both the support materials as well as the main material are built together.
After a single layer is complete, the same process that happens in FDM, SLA, and SLS is done i.e. the build platform moves down one layer in height.
The process continues until the part is finished. As seen above while comparing PolyJet 3D printers with FDM 3D printers, the former work with a range of different materials, amongst which there are even bio-resins.
Application of this 3D Printing Technique

There are many industries which have already recognized the potential of PolyJet 3D printing and are trying to implement the technology for enhancing their workflow and save money.
Where this technology is extremely useful is at developing realistic prototypes, because PolyJet is a technology that can produce highly detailed parts in a matter of hours.
We all are familiar with how making a realistic prototype is equivalent to saving a lot of money, so that’s where this technology can be a key benefit in terms of saving some money or time.
Another great thing about PolyJet, and forgive us for repeating it again and again but it is the ability to 3D print with different materials at once.
Not only this allows for making complex geometries but also, saves time.
Apart from prototyping, the application of this technique can be found in the dental industry.
Wherein modern clinics utilize PolyJet for making 3D printed molds of someone’s mouth based on a previously-taken scan.
This process makes things happen faster and accurate like no other.
The Conclusion
Overall Polyjet 3D printing is a technique that people use for achieving parts with higher dimensional accuracy.
Arguably, the price of polyjet 3D printers is very high than printers based on other technologies but compare to other technologies the minimum layer thickness offered by polyjet printers is also very high.
So, when you compare the cost of buying a higher-priced 3D printer, also calculate the cost of buying a product that has very little layer thickness.
Also if you do not wish to buy the 3D printer, you can rent a 3D printing service provider that can produce you the same thing which you want at affordable prices.
Technological advancement has really made the dream of collaborating with the best in the market, sitting from anywhere around the globe, a reality.







