Currently, 3D Printing is believed to be in its evolving stage. It is still not as efficient as traditional manufacturing technologies in many ways. And, one such limitation is the challenge to print with as many materials as available with conventional manufacturing.
However, things are changing with time, And, luckily there is an alternative for 3D printing with rubber-like products, which is, TPE.
The full form of TPE is Thermoplastic Elastomer. Parts fabricated using TPE 3D printing are known to have unmatched flexibility, just like rubber-made products.
What makes TPE so flexible? What are the characteristics of this elastomer that separates it from other elastomers? What are the printer settings that you need to carry out for successful TPE 3D printing? How to deal with the challenges that you will face with the TPE filament?
These are the key questions that we would be addressing in the latter part of this article.
Remember the material is more flexible than the normal ones. So, obviously, it will require more care than others. But, if given proper attention, it promises to produce some of the most outstanding elastic parts you’ll ever come across.
The benefit of elastic prints by TPE filament is that these are stretchable to almost double their lengths and still these manage to go back to their original form.
All that movement would happen without any damage to your prints. Reads just like rubber, doesn’t it? So, without consuming more time, let’s start our journey of exploring the amazing rubber-like material Thermoplastic Elastomer.
What Are The Properties of TPE?
Apart from being flexible, TPE is commendably impact-resistant. It imitates most of the desirable properties of rubber in solid form. You can print TPE using FDM 3D printing technology.
It is important to note here that we are not referring to TPU which is technically closely related to TPE. The former is a little more rigid than the latter.
So, while differentiating between the two the level of hardness becomes an important factor. Materials above 90A shore hardness are considered TPU and vice versa.
Flexible
A variant of TPE that you will get to see in the market is named Soft TPE. The filament material simulates real rubber in the most possible manner.
Usually, a printed part with TPE can be stretched twice its length, it will still revert to its original size and shape without any damage.
Although flexibility is the reason why TPE is favored over other 3D printer filaments, it sometimes becomes challenging to deal with. Extreme softness is often the only limitation because of which TPE is often frustrating to deal with.
High coefficient of friction
TPE printed part exhibits inherently non-slip surface, like the ones that of rubber. Because of this, a little harder version of TPE, TPU is a top choice for making linings of containers or mounting sections for ornaments as well as other household items.
TPU also finds its use in creating custom-made phone cases because it provides excellent impact resistance.
Durable
TPU becomes a hard material to be used in applications which are subjected to deformation under a sudden or sustained impact.
But this means that TPE is a very preferable material for making such parts that can regularly sustain impact, vibration as well as abrasion.
What are The Challenges You Need to Overcome for Successfully TPE 3D Printing?
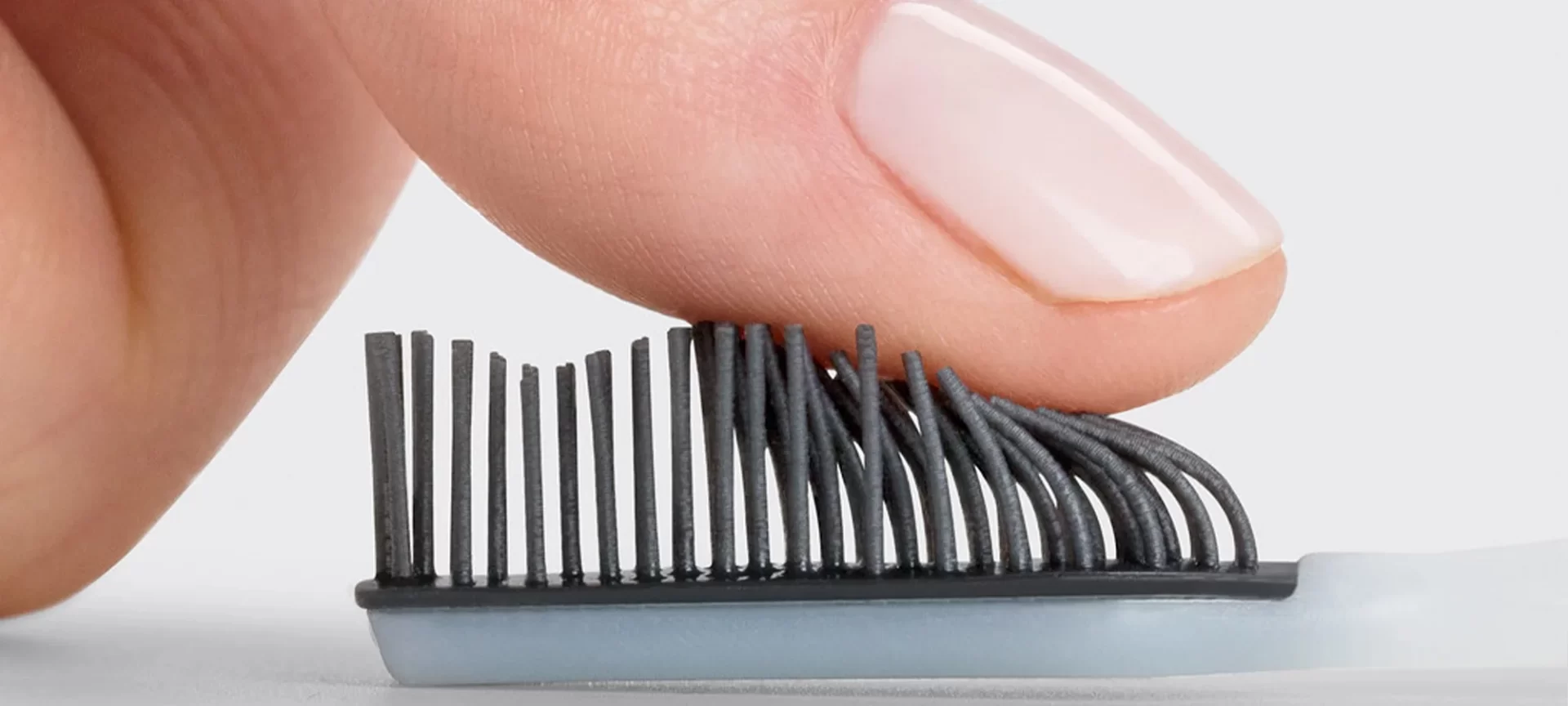

Like every other 3D printer filament, TPE has its own set of challenges. Also, these issues are different than other filaments because TPE is softer than any other 3D printer filaments.
So, you may find it more difficult to feed TPE filaments into an extruder. If you forcefully try fixing it, there is a risk of getting the filament spool stuck and deformed. And this may lead to the jamming of the extruder.
For feeding your filament from the drive gear towards the hot end, you must have a direct path for it. This is some issue that you might not have faced with other filaments as they are stiffer than TPE.
Buckling
With the flexible nature of TPE filament, the nozzle’s pressure may turn out to be more than regular for it. This will cause the filament to buckle when you are trying to push it through the extruder for starting TPE 3D printing.
Although the primary reason for this phenomenon to occur is due to the hassle shown by you, the narrowness of the pathway and its tightness can also cause buckling to take place. A result of any of these is jamming of the complete process.
Sticking of the material
TPE is not one of those filaments that have excellent bed adhesion. For this reason, you would need help in getting the first layer stick to the print bed.
A simple solution for this is to get good adhesion and avoid shrinkage by adjusting the temperature of the printer’s build plate.
Other than this, incorrect leveling is also a reason for bad adhesion. So, also ensure correct leveling of the build plate before starting TPE 3D printing.
Messy parts
Ensuring that pressure has not accumulated in your extruder is a way to get rid of extra oozing out of TPE filament.
Not doing so can create a stringy or messy part. For this scenario to not take place, get the retraction settings, speed, and temperature correct.
Tips for Triumph with TPE 3D printing
After taking you through the challenges of printing with TPE filament, it’s time to explore the tips that will, either ensure that you do not have to face those challenges or help you overcome them easily.
Don’t hurry up while printing
Experts recommended a normal print speed ranging anywhere from 30 millimeters to 40 millimeters per second while printing with TPE.
Doing so ensures an excellent surface finish of parts. Printing with a slow speed means that you are not giving any chances for the pressure on the extruder to exceed beyond a certain level.
As mentioned above, it is not favorable to have more than a certain amount of pressure on the extruder otherwise it makes your prints messy and stringy.
If you are using a brand of TPE filament named Flexifil, the recommended print speed range is even slower than usual i.e., 10 mm to 20 mm per second.
In printing projects where quality is a very important factor, a very slow speed of 5 mm per second is also advisable. This would better the chances of getting a better-quality print.
Attempt to use an extruder of direct drive
While TPE 3D printing, jamming of extruders is the most common problem. And when that happens, it consumes a lot of your time.
So, it is advisable that you take all the precautions to not land in such a situation. A general solution to this problem is to lessen the space between the nozzle and the cold end.
Avoid using Bowden extruders because it will get more challenging. Although you will manage to get successful prints using the same, most of the time you will face issues with it.
Extruder temperature should be higher than normal
If the extruder’s temperature is correctly maintained, the TPE filament will find no issue in flowing easily through the nozzle. But, please make sure that you’ve not kept the temperature higher than needful.
Because there are high chances that by doing so you may land upon the problem of oozing. Also, there are chances that your prints would be uneven or stringy.
For getting the best prints, you will need to test the TPE material on your printer to get to know which settings are the most appropriate ones.
So, do not hesitate while testing and failing as that’s the only way to find out the correct temperature range for TPE 3D printing.
Alter retraction settings
This is one way of lessening the hot end’s pressure and stopping the filament from moving towards the nozzle while the extruder isn’t involved in printing.
Having a lower or higher retraction depends on the issue that you are facing. In case your extruder clogs, it’s advisable to have lower retraction and vice versa.
You will also find examples of others printing their design at zero retraction. That’s also a possible scenario.
A safe way to go with this variable is to find out the least amount of retraction that’s needed. Doing so would ensure facing the least number of issues and never a stringy print.
If extra material is coming out from your nozzle, try increasing the retraction speed or distance to not face such an issue.
Managing the hotbed temperature
Usually, hotbed temperatures depend on the kind of printer you are buying. The general recommendation for hotbed temperature with TPE material ranges from 40 to 50 degrees Celsius. Also, a lot depends on the brand of TPE filament you’ve started 3D printing with.
What Are The Printer Settings?
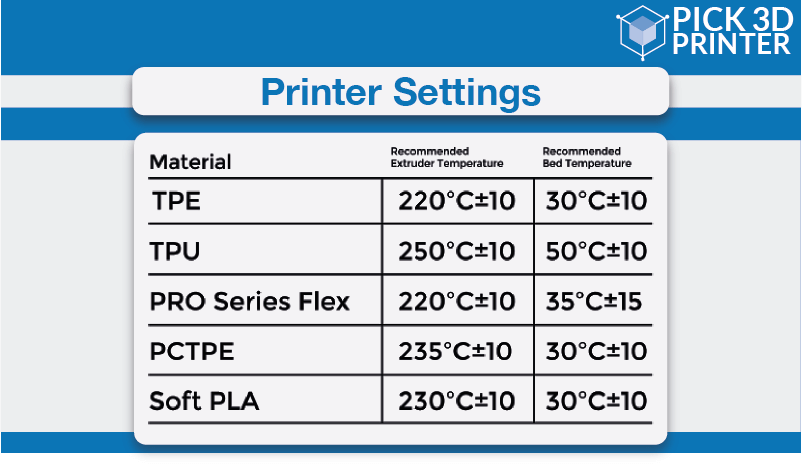
- The normal temperature range for 3D printing TPE is 210 to 230 degrees Celsius.
- Although the usual printing bed is recommended to be heated around 40 to 50 degrees Celsius, it can go up to 60 degrees Celsius.
- For good bed adhesion with TPE 3D printing, it is advised to use a Kapton tape or hairspray.
- For avoiding stringing, you will have to search for correct retraction settings on your 3D printer.
- Use a slower speed of 3D printing than you use with other 3D printer filaments. Normally, 30 millimeters per second is considered a suitable print speed for printing TPE.
- For achieving good layer-to-layer adhesion, turn off your printer’s cooling fan.
What Are The Applications of TPE?
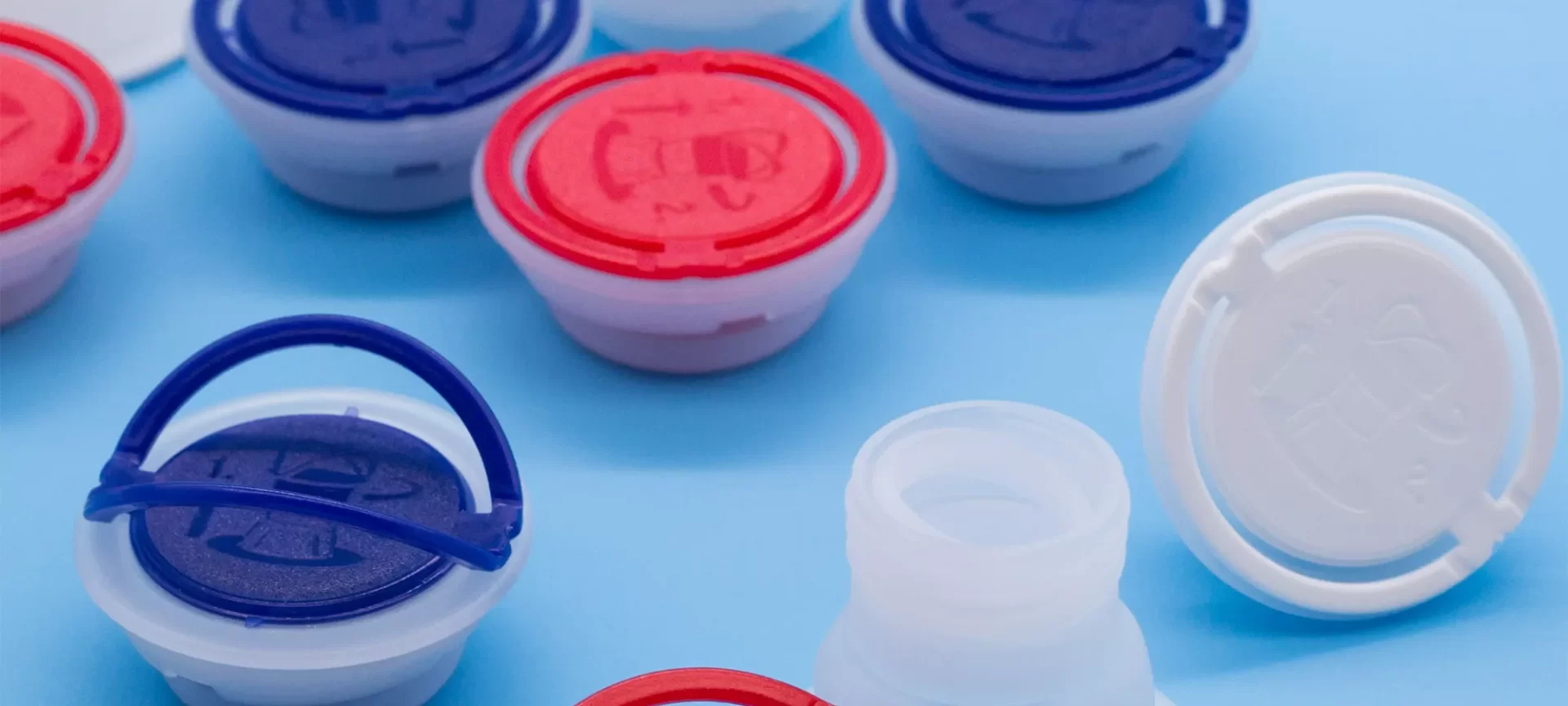

The inherent nature of TPE makes it flexible, durable to deform without being damaged therefore making it useful for standard household items.
You can even make your own anti-slip shower mats out of this material. TPE also goes into making cell phone cases.
Using TPE filament you can customize engineering components according to your requirement. Dampeners and stabilizers are two examples of products for making which TPE can employ.
Basically, TPE can be utilized to make parts and functional prototypes of machines that undergo more than a normal amount of vibration and impact.
So, seals, liners, gaskets that are usually made from rubber can be easily replaced with TPE which has moderate stability up to 140 degrees Celsius.
Additionally, TPE is an FDA-approved material for food contact. Hence, it’s been used for spouts in drinking water bottles, toddler cups, and feeding items for babies.
Apart from that, TPE can also be used in making medical applications that need to withstand high temperatures during autoclaving.
For making prosthetics, TPE is sometimes used as a replacement for latex or silicone.
- TPE is a non-toxic and safe 3D printing material.
- It produces durable prints.
- An excellent choice for anti-slip objects.
- Used for making parts that are used in daily life, such as, phone cases, door stoppers, springs, belts, etc.
- Feeding TPE into the extruder is difficult.
- It’s very easy to land upon buckling while working with TPE 3D printer filament.
- Oozing out of the filament is a very common phenomenon while dealing with TPE. Also, you might get messy prints very often.
The Conclusion
Recently there has been a rise in the number of brands offering TPE filament. Although the amount isn’t yet as much as you have for ABS and PLA, it’s constantly rising.
And this tells us about the demand for printing with a rubber-like unique filament that can be put into numerous applications. This trend is expected to rise to go on forward from here onwards.
TPE 3D printing is a little more complicated than general ABS or PLA, but at the same time, it is the only filament that’s able to offer the correct balance of flexibility and durability.
And this is something you do not get either with ABS or PLA. Also, once you make a checklist of points that we’ve mentioned above, printing with TPE can become as normal as with other filaments.
So, utilize this eccentric rubber-like 3D printing material that is available at your disposal and achieve some enormously great structures!







