One of the most widely used thermoplastics in the field of 3D printing is PETG, an abbreviation for glycolysis polyester. This one is especially known for inheriting the simplicity of PLA and the strength of ABS.
Chemically, the material is an amorphous plastic, 100% recyclable, and has the same chemical composition as does polyethylene terephthalate PET.
In this article, we review the characteristics of PETG for 3D printing, mainly PETG print speed along with its other parameters and its main applications. But before starting with it, let’s to the basics of PETG!
Whats is PETG?

PET is a well-known material in the industry because it has been used in the manufacture of our food bottles and packaging since the 1990s. This is was a great triumph over PVC. Moreover, this material allows the production of synthetic fibers for clothing; it is also one of the most widely used polymers on the market.
PET accounts for 18% of global plastic production worldwide. The thermoplastic has extremely good impact resistance, transparency as well as dimensional stability.
The only backdrop of this material is that there are some issues with overheating when used for 3D printing. Because of this issue, not PET, but PETG is used for 3D printing various parts and functional prototypes.
PETG is the perfect filament in case someone is looking for a filament that has a combination of strength and ductility. This quality makes its use possible in so many mechanical parts and robotics.
The material has great chemical resistance with good water, acidic and alkali resistance. Also, this is a great material for artistic prints like bracelets, rings, collars, etc. You can even achieve a nice shiny transparent or see-through look which reflects the light nicely.
As mentioned above, PETG is a copolymer that has a combination of the properties of PET and glycol. Because of the addition of the latter, the chances of overheating issues reduces therefore its overall appearance is brittle.
Among the main characteristics of PETG are: its hardness, impact, chemical resistance, transparency, and ductility. PETG is an easily extruded material having good thermal stability, particularly appreciated for its food compatibility.
The material has its own set of limitations like it requires a heating plate which will let you avoid the warping effects like the ones that are found in ABS 3D printing.
Even if the warping rate is low, it is advised to use a BuildTak sheet to ensure the material grips. Also, PETG is more prone to scratches than PLA and can quickly take moisture so, it’s better to store it in a cool and dry environment.
Printer Settings with PETG
In scenarios wherein your slicer has built-in PETG material profiles, those will be a great place to start. Otherwise, what you can do is, take your ordinary PLA settings and make a couple of changes in the same.
Fine-tuning your settings to PETG filament will yield optimal results.
- Increase the normal nozzle temperature of your 3D printer as per manufacturer recommendations and keep it usually between 220 and 260 degrees Celsius.
- Also, increase the normal bed temperature of your 3D printer as per manufacturer recommendations and maintain it anywhere between 50 and 85 degrees Celsius.
- For the fan speeds, you are recommended to decrease it and bring it to somewhere in the range of 20-50%. Additionally, please not always use a fan with PETG as it tends to cool the filament in the hot end and help you with retractions. Also, you are recommended to keep your retraction speed slow at 40mm/s or less.
- Application of around one coat of Wolfbite by painting on cold glass with long strokes is strongly recommended. Wolfbite is a solution that’s specially engineered to bond PETG and ABS plastic parts directly to a heated glass bed 3D printing surface without even lifting it. After the 3D printed parts have cooled, they will dismount from the printing surface with almost no effort at all, thereby leaving a clean and smooth bottom surface.
- Normally PETG print speed should be around 40-60mm/s. A little less PETG print speed would is not necessary, whereas a little more would ruin the quality of the part that you need.
- If you need printing supports while PETG 3D printing, remember that they would not be suitable because the PETG has a sticky appearance which will anyways make them difficult to remove.
How To 3D Print With PETG?
Using the settings mentioned above, try printing a test piece and notice two things about PETG:
- It’s quite prone to stringing and
- Excessive cooling can delaminate layers.
Using the test piece, modify your print settings accordingly. In scenarios wherein the layers aren’t staying together, decrease fan speeds or in the other way increase the print temperature.
Whereas, if the stringing is severe, increase the retraction speed or the distance! Also note, if the parts are curling or deforming, lower the print temperature.
Investing in a Good Build Surface

Some 3D printers are known to come with a glass bed or blue painter’s tape installed on the bed. Although these print surfaces are known to work just fine with PETG, experts recommend using a heated build platform for the best results.
Doing so will significantly improve the first layer adhesion, making things much easier for the layers and prints to come there onwards. Also, many of these heated beds come with a glass surface, thereby allowing you to print directly on the bed without demanding any application of additional layers of tape or glue.
Getting the Retraction Correct
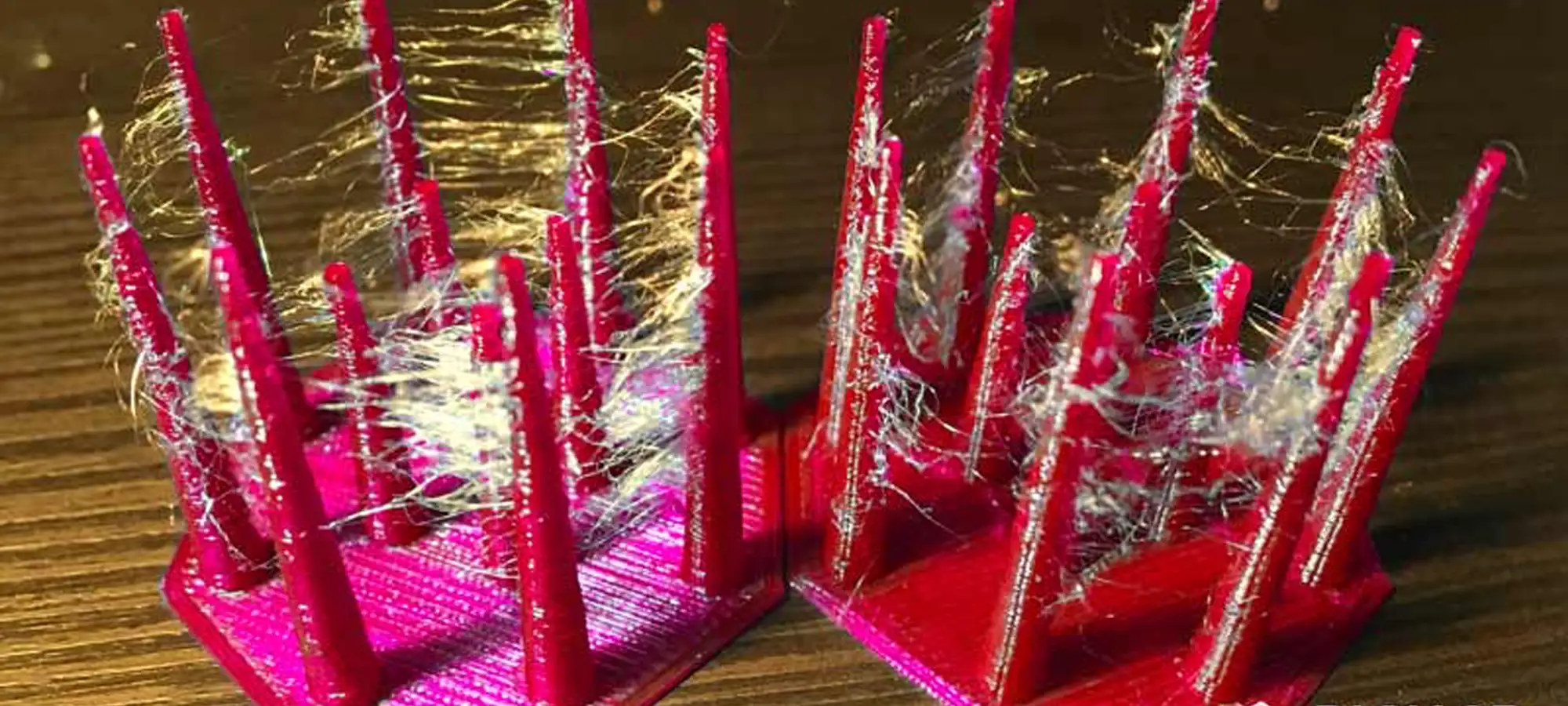
PETG is a material that has a high tendency to string and ooze, the material’s toughness makes it difficult for the strings of molten plastic to break, thereby leading to unsightly webs and wisps on your prints.
These troubles can be pacified by properly tuning your print settings. In particular, you are recommended to try to:
- Increase retraction distance.
- Increase retraction speed.
- Increase the travel speed and thereby the PETG print speed within reasonable limits wherein you do not lose on the quality of the final part.
Finally, if all else fails, take a little help from a heat gun without not hindering any remaining strings.
Optimize Extruder Settings
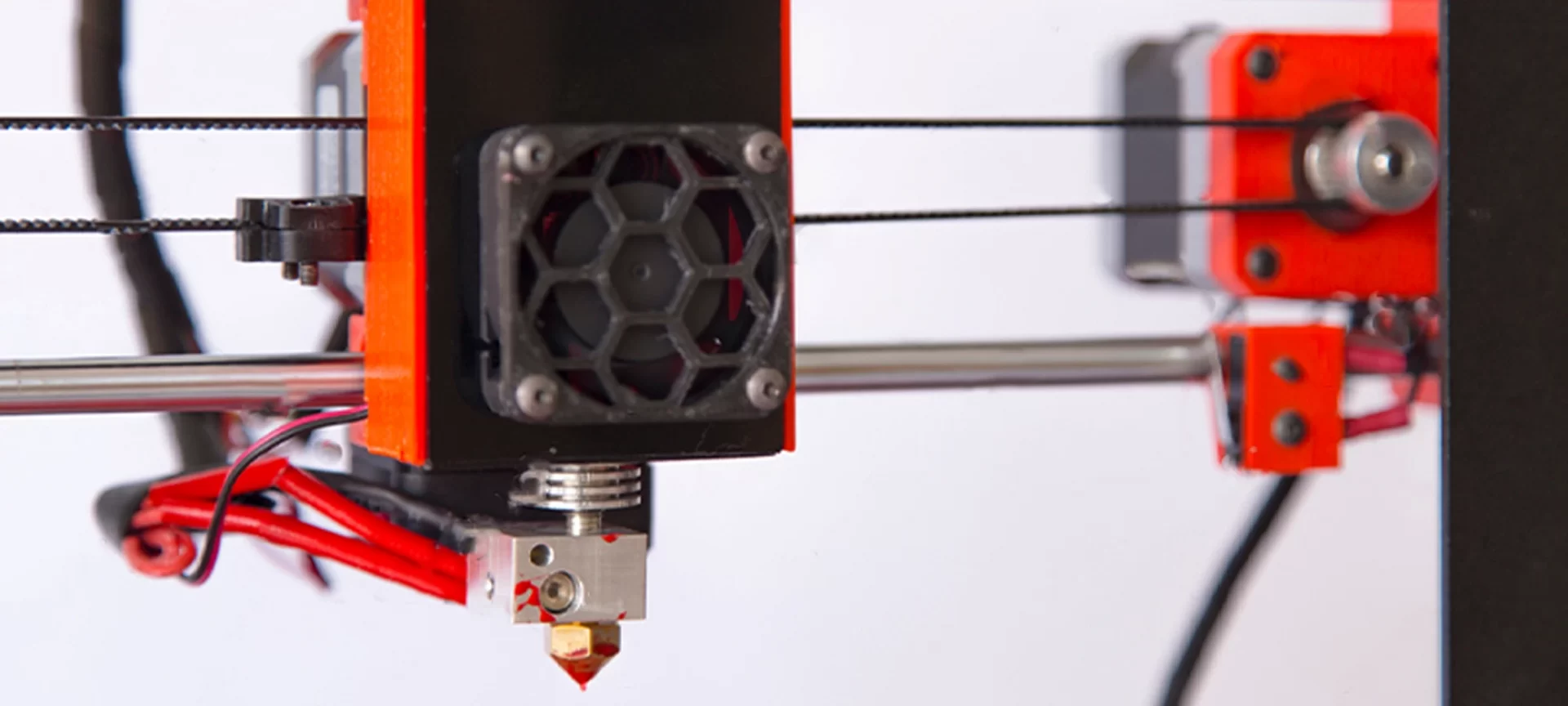
When you are PETG 3D printing at higher temperatures it is natural for you to notice small blobs or zits on the surface of your model.
These print defects particularly occur at the beginning or end of each segment. Especially when the extruder has to suddenly start or stop extruding plastic, and there are several ways to eliminate these print defects such as by enabling: a) Extra Restart Distance or b) Coasting options located in the Extruder tab.
Some slicers also include an option for performing a dynamic retraction, wherein the filament is completely retracted while the extruder is still moving. This sort of arrangement completely eliminates the blobs that are otherwise typically formed from a stationary retraction.
Give Proper Storage

This is something you will conclude only after printing with PETG for a while. The deteriorating print quality and strength of the material is because the material is hygroscopic, meaning that it easily absorbs moisture from the air.
This moisture leads to deterioration of the material itself and can ruin an otherwise fine spool of filament. Because of which you are requested to keep your filament stored in a dry environment.
Something like an airtight bag or a box filled with desiccant packs. Doing this should not only preserve the filament but also prevent it from absorbing too much moisture.
In scenarios wherein your filament is already wet, you can dry it out with an oven set at around 60 °C. Leave the filament spool in the oven arrangement for a few hours while the moisture is cooked out.
What Are The Applications of PETG 3D Printing?

The material is used in a variety of:
- Signages
- Packaging
- Industrial and medical applications like Medical braces.
- Bottles
- Electronics
- Guards
- Glazing
- Covers
- Point-of-purchase and graphic displays.
The Conclusion
As you can deduce from the above printer settings and tips, PETG is not the kind of material that shows many tantrums. Printing with the material is manageable in a lesser uncomplicated manner than you can with PLA or other delicate materials.
Obviously, you need to take into account some factors such as the bed adhesion, final 3D printed part removal, retractions settings, PETG print speed settings, extruder settings etc. The most important of them all is storing this filament.
You need to cautious about this simple setting. Added to it is the PETG print speed range, not printing within specific ranges may lead to print failure or not achieving the kind of quality you wish to have. Apart from this, there is nothing to worry about PETG 3D printing, you are all good to do!







