Looking to find out what makes SLA and SLS different from each other when both use laser sources to create layers? Well, to compare SLA vs SLS 3D printing process, we must start by understanding the working of each of these technologies.
Both of these technologies have been known to produce highly detailed parts. However, these do offer different mechanical properties to the printed parts. From materials to printing techniques, a lot of things differ when comparing these two.
Hence, we must proceed step-wise to understand the vast difference that SLA and SLS carry while utilizing a common energy source, i.e., laser. While SLA works with liquid resin, SLS makes use of powdered polymers to create 3D models. And, this is just the start.
So, before we go on and differentiate the two 3D printing processes in detail, let’s begin with learning about the working of these technologies.
What is SLA 3D Printing Technology?
Chuck Hall, in the year 1983 developed a prototype of what is now called Stereolithography.
A year later, precisely on August 8, 1984, he obtained a patent for what is called “Apparatus for production of three-dimensional objects by Stereolithography.” And two years later – in 1986 – Mr. Hall co-founded 3D Systems Inc. for commercializing the technology.
3D Systems introduced their first 3D printer with the name SLA-1 in the year 1987.
To date, 3D Systems has manufactured many SLA 3D printers that continue to produce parts and functional prototypes useful in the field of Aerospace and Defense, Automotive, Consumer Products, Jewelry, Teaching, and Training. Over the passing of time, 3D Systems have also started providing on-demand parts.
What is SLS 3D printing technology?
SLS stands for Selective Laser Sintering. It falls under the Powder Bed Fusion category of 3D printing technologies. As the full form of SLS suggests, a laser source is used for the sintering selective material.
The material used for the production of parts using SLS 3D printing technology is in powdered form. The technology is used for prototyping functional polymer components as well as for small production runs.
SLS 3D printed models are of high accuracy, made from a good level of design freedom, and possess excellent mechanical properties.
Developed and patented by Dr. Carl Deckard and Dr. Joe Beamen at the University of Texas, Austin, in the 1980s, Selective Laser Sintering was commercialized by the doctor-duo’s start-up DTM.
As time passed, in the year 2001, 3D Systems – the same company, the founder of which is credited for inventing SLA 3D printing technology – acquired DTM.
What Is The Difference Between SLA And SLS?

Starting with the working of each of these processes, there are many other parameters that clearly depict the comparison between SLA vs SLS in a highly profound way.
Working Technique of SLA and SLS
SLA and SLA use different 3D Printing techniques to process 3D files into the final model. Here is the working principle of both the technologies showcasing how they differ in terms of functionality.
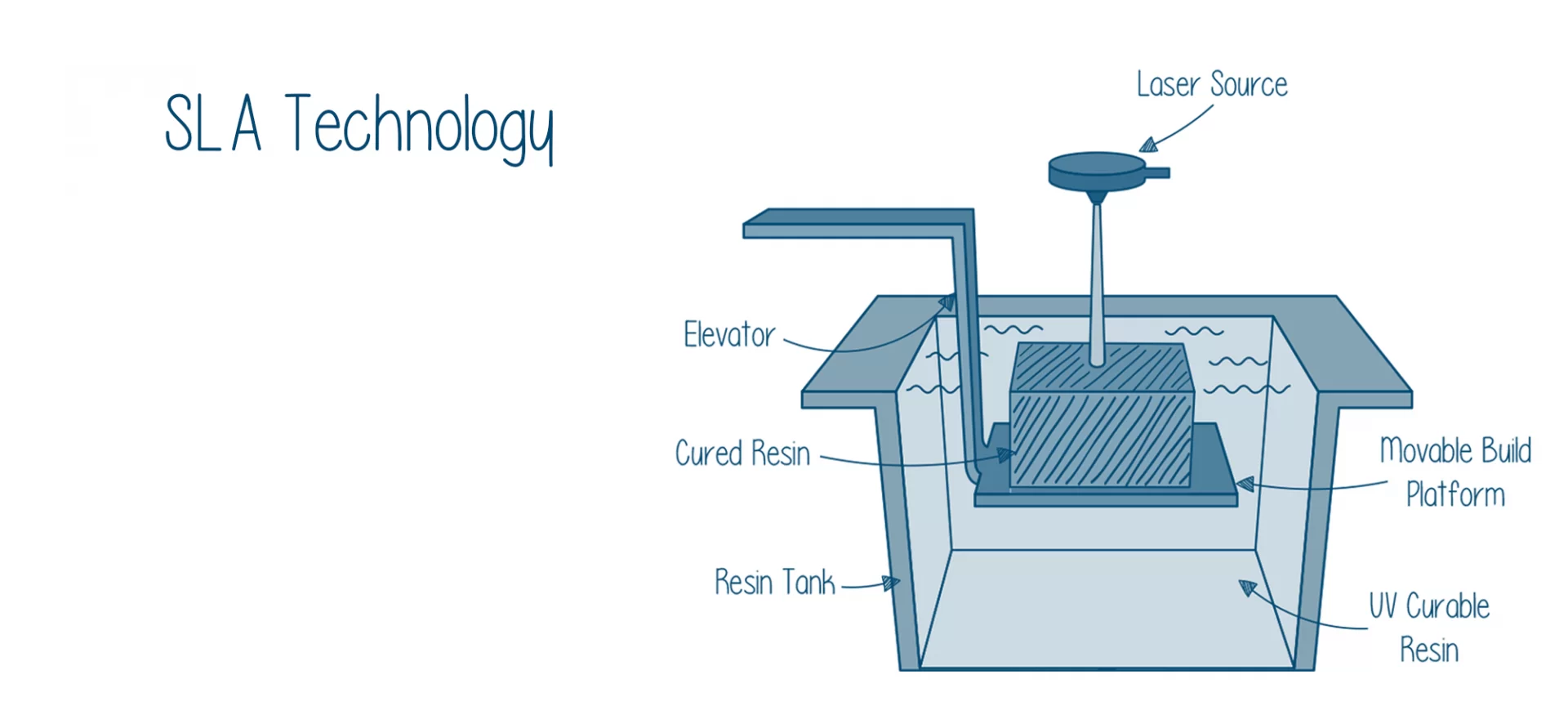
Stepwise functioning of SLA 3D printing
Generally, a photopolymer resin is used for making parts and functional prototypes using SLA 3D printing.
The reason for using this material is that it contains a special property of turning rapidly into a solid from a liquid.
The other pre-requisites for SLA 3D printing technology are:
- A movable table.
- A laser knife-edge.
- The scanner system,
- Photopolymer.
A vat with a sealed chamber arrangement where the complete process can take place.
- The SLA 3D printing process starts with the laser drawing the first layer of the part or functional prototype that you wish to print into the photosensitive resin. Wherever this laser hits, the liquid resin solidifies. The laser is directed via a sliced file that you have fed to your SLA 3D printer. If you wish to relate to it more, imagine an FDM 3D printer’s nozzle system. The laser does the same work of printing the exact geometry of the part or functional prototype in SLA 3D printing, as does the nozzle system in FDM 3D printing.
- After the first layer of the part or functional prototype is printed, according to the layer thickness offered by your SLA 3D printer, the additional resin is allowed to flow beneath the already-manufactured portion. Then, the laser moves on to another layer to solidify it. This process is repeated till the complete part or functional prototype is manufactured. And the resin that remains unused can be reused in the next print.
- After finishing the printing process, the complete print platform of your SLA 3D printer rises out of the resin tank wherein the excess is drained away. Once that is done, the model is removed from the platform, washed off the excess resin that’s present on it, and then placed in a UV oven for final solidification. This post-processing helps the created object reach highest possible strength and become more stable.
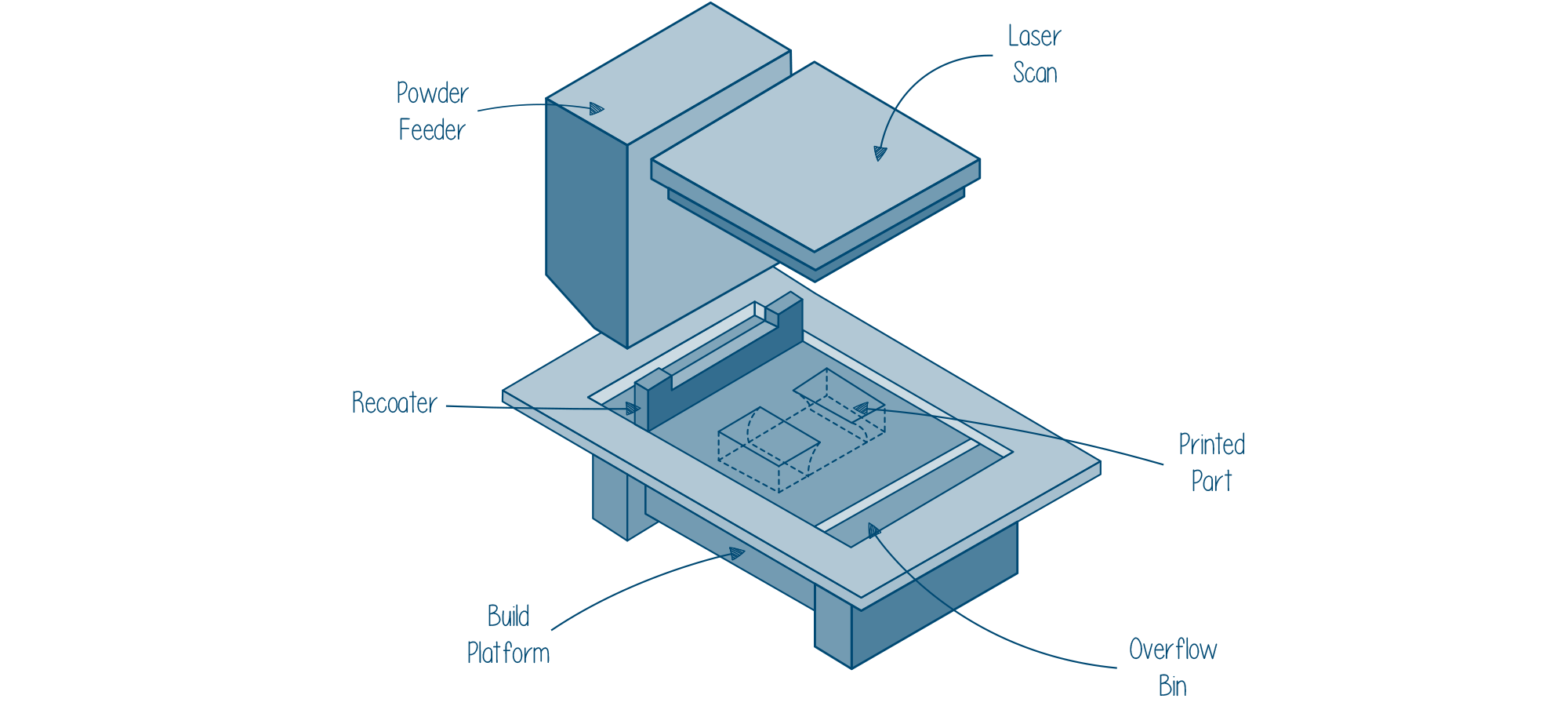
Stepwise functioning of SLS 3D printing
SLS utilizes high powered laser source which specifically sinters thermoplastic polymer powder and builds parts or functional prototypes according to the geometry fed to your SLS 3D printer.
Major components of an SLS 3D printer are: powder bin, build platform, powder re-coater, laser: generally a CO2, diode or fiber, set of galvanometers, set of heaters, and g) a powder feeder.
- The printing process starts with the heating of the powder bin and the build area to the temperature that is just below the melting temperature of the polymer powder. Simultaneously, the recoating blade spreads a thin layer of powder over the build platform.
- After the complete printing material is spread over the platform, a laser beam scans the contour of the next layer and particularly starts fusing the particles of the already spread powdered polymer. After the laser scans the complete build platform, the part is completely solidified.
- Once a layer is completely fused, the build platform moves down and the blade re-coats the surface. This process is repeated until the whole part is printed.
- The unsintered powder and the powder bin are then left to cool down before the parts are packed to be delivered. The parts or functional prototypes manufactured using this technique are then cleaned with compressed air or other blasting media and hence ready to be used or, in some cases further processed.
Technology Difference
Most of the SLA machines make use of mirrors. Due to this, at times, the directing of the laser becomes problematic!
Even slight rotation of the mirror can lead to the laser point becoming ovoid which impacts the precision of the printer.
SLS machines do come across such issues but not to such a high extent as is the case with SLA 3D printers.
Moreover, the power of laser sources used in SLA vs SLS 3D printing technology is lower. That’s why SLS machines are termed more dangerous than SLA machines.
On the other hand, the resultant part or functional prototype is more finished when made using SLS vs SLA 3D printing.
In connection with this logic is the point that the cost of 3D printers based on SLA vs SLS 3D printing technology is lower. Meaning that SLA 3D printers are cheaper than SLS.
Handling of Material
The material handling aspect in SLA vs SLS 3D printing technology is much more. Resins used in SLA 3D printing are more toxic, messy when it comes to managing their post-processing, and dangerous.
Whereas, SLS powders are easy to deal with. Although they are a bit pricey, there is nothing to be scared of while touching them.
3D Parts’ Properties
The finished product via SLA vs SLS 3D printing technology is detailed but brittle, which means that it’s less suitable for any mechanical purposes.
On the other hand, finished product made using SLS 3D printing technology is strong, just like metal and hence suitable for numerous mechanical purposes.
The lack of supports in SLA 3D printing technology is definitely an aiding feature while creating complex geometries.
Printer’s Size
Coming to the size of printers based on SLA vs SLS 3D printing technology, the printers based on the former are smaller in size than the latter.
So, you can expect more desktop 3D printers based on SLA 3D printing technology, just as you can expect more industrial 3D printers based on SLS 3D printing technology.
This differentiation makes SLA 3D printers more convenient than SLS as they have the capability of producing models larger in build volume.
Price
Last but not the least, the price for SLA vs SLS 3D printers. And, you can find a huge difference in the starting cost of the printers available with both the technologies.
While an SLA 3D printer is available for less than $500, SLS machines will start at a price at least ten times more than that.
But with this one must also take into account the cost of materials that are needed to print an object with these two technologies and decide based on that.
SLA vs SLS – What Are The Advantages and Disadvantages?
That was the direct comparison of SLA vs SLS. However, before ending the comparison, let’s have a quick look at the pros and cons of these technologies.
SLA Pros and Cons

Like every other 3D printing technology, SLS has its own set of flaws and advantages that are mentioned below.
- Stereolithography 3D printing technology is one of the most precise techniques for manufacturing 3D parts or functional prototypes in the current market.
- Objects created by this technique possess high-quality, finely detailed features such as thin walls, sharp corners, etc. Complex geometrical shapes with layer thickness as low as 25 micrometers can be manufactured.
- The printed surfaces are smooth.
- You can build a high volume of objects without sacrificing precision.
- The average printing time on an SLA 3D printer is more than others.
- Sloppy and over-hanging geometries require support structures during the printing process. Otherwise, these parts may collapse.
- There is a limited amount of material and color choice and also the printing costs with SLA are comparatively higher.
- Resins used to make parts using this technique are fragile, therefore not suitable for mechanical testing or functional prototypes which are used to test the final part.
SLS Pros and Cons

The highs and lows of SLS 3D printing technology are as follows.
- There is no need for any additional support material, regardless of how complex a part’s geometry is.
- As the parts or functional prototypes are built using a laser, multiple parts can be printed at once after they are scanned.
- More than fifty percent of the unsintered powder can be recycled thereby making SLS the 3D printing technology wherein waste is negligible.
- The cost of printing a part or functional prototype using an SLS 3D printer is very high. It requires a lot of power.
- The technology is still not accessible by common people as the cost of machinery and powders is very high compared to FDM or SLA 3D printing technology.
The Conclusion
As you might have noticed till now, the most striking similarity between these two technologies is the use of laser source for solidifying the 3D printing material.
Because of which, parts or functional prototypes manufactured using these technologies possess excellent surface finishes and have no problem of warping at all.
Hence, when choosing between these two technologies, you must go through the detailed comparison between SLA vs SLS 3D printing.
This would allow you to understand the related advantages and disadvantages associated with each of these 3D printing processes.
Based on your use and application along with the budget aspects, you can select the one that seems suitable for your needs.
For instance, if you need to buy a printer for professional use and you can afford to pay the cost of an SLS 3D printer, go with it. Otherwise, SLA 3D printers are always at your disposal to build parts of commendable quality.







