3D printing that took time to reach consumers after long years of serving industries with prototyping, has managed to travel a long way. There have been huge developments in the last few years.
Some times back, while there were only a handful of 3D printing processes available, today we are embracing multiple successful methods of 3D printing.
The most popular and one of the oldest of these processes is resin-based 3D printing. It later branched into so many different categories.
SLA, DLP, and LCD are resin-based 3D printing processes that work on the same principle with few changes in their design.
Exploring in-depth the topic: DLP vs LCD 3D printer would help understand what makes these technologies different, in spite of coming from the same family of the 3D printing process.
However, before we dig deeper into the differences and similarities of these two processes, let us get to know a little about resin 3D printing.
What is Resin-Based 3D Printing?
Resin-based 3D printing which is termed as vat polymerization is been categorized in three formats: SLA, DLP, and LCD.
SLA being the oldest among the three contains the gist of how the resin 3D printing surfaced initially. Although we will focus on the differences between DLP and LCD, a brief introduction of SLA would be necessary.
All these technologies are based on curing a photosensitive resin using a light source. This helps solidify the resin and in creating solid layers.
Finally, producing the complete model. The liquid resin is stored within a tank. The resin is then cured against a build platform that rises one layer at a time out of the tank after each layer completes.
The major difference, however, between these technologies is the usage of different light sources for curing the resin.
SLA
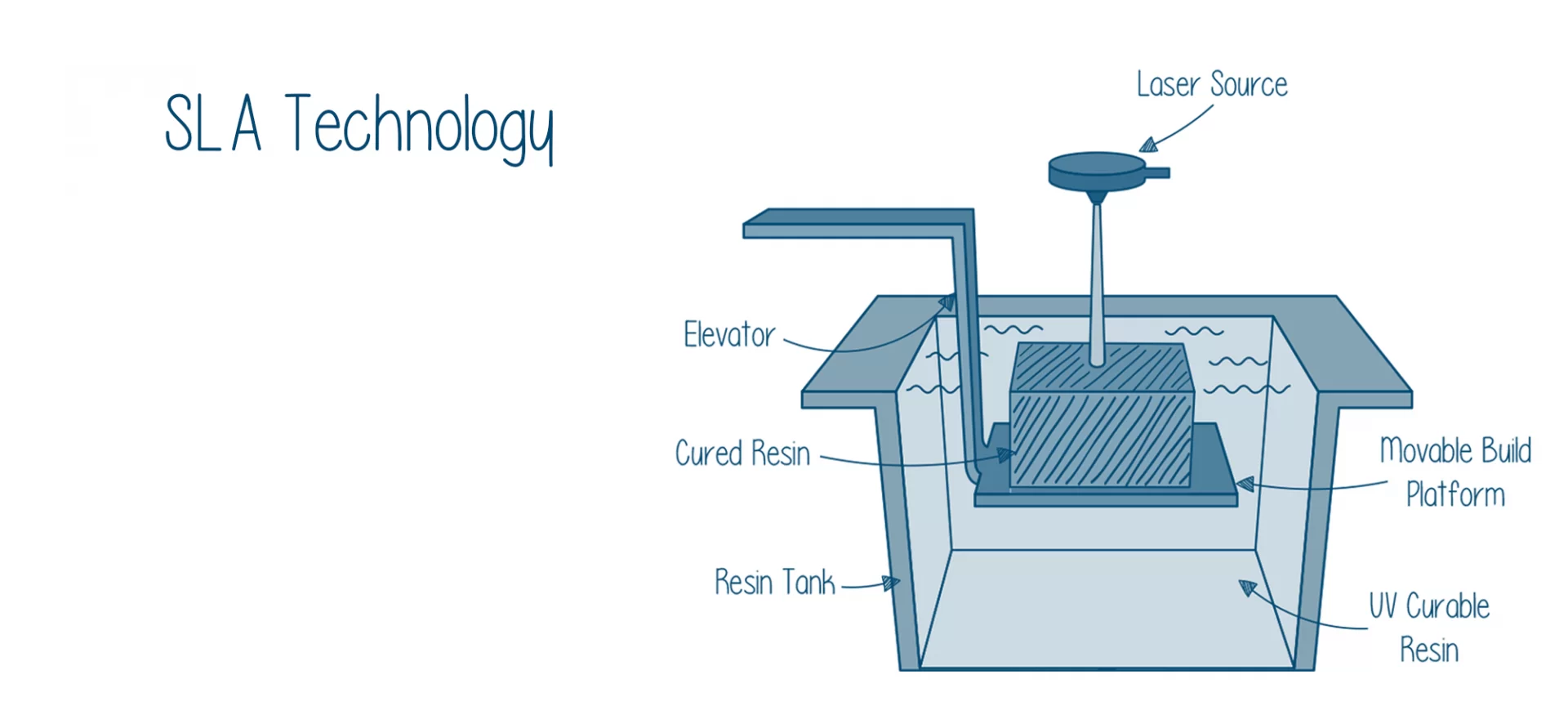
As mentioned, SLA was the first 3D printing process among all three. It is also known as stereolithography. In SLA, the 3D Printer is equipped with a laser source that is directed by galvanometers which helps in curing the resin.
Galvanometer’s job is to direct the laser beam appropriately to the specific point on the build surface through the bottom of the transparent tank to print the models.
DLP
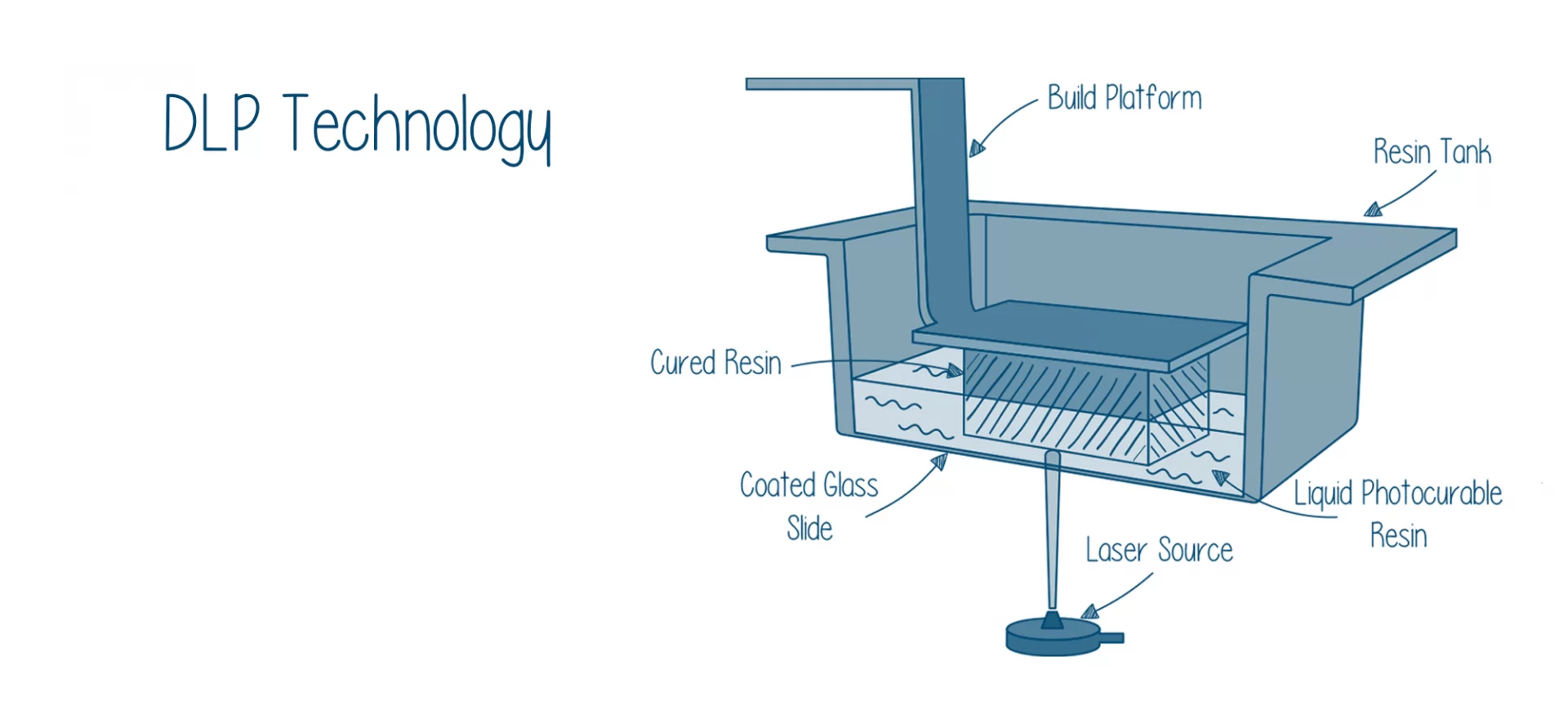
When it comes to DLP, an abbreviation for digital light processing, the machine utilizes a digital light projector to cure the resin.
Instead of going projecting one layer at a time, the entire image is flashed onto the bottom of the tank.
In this setup, to direct the light selectively, the printer makes use of a digital micromirror device (DMD). This consists of multiple tiny mirrors ranging from hundreds to thousands in number to maintain accuracy.
LCD
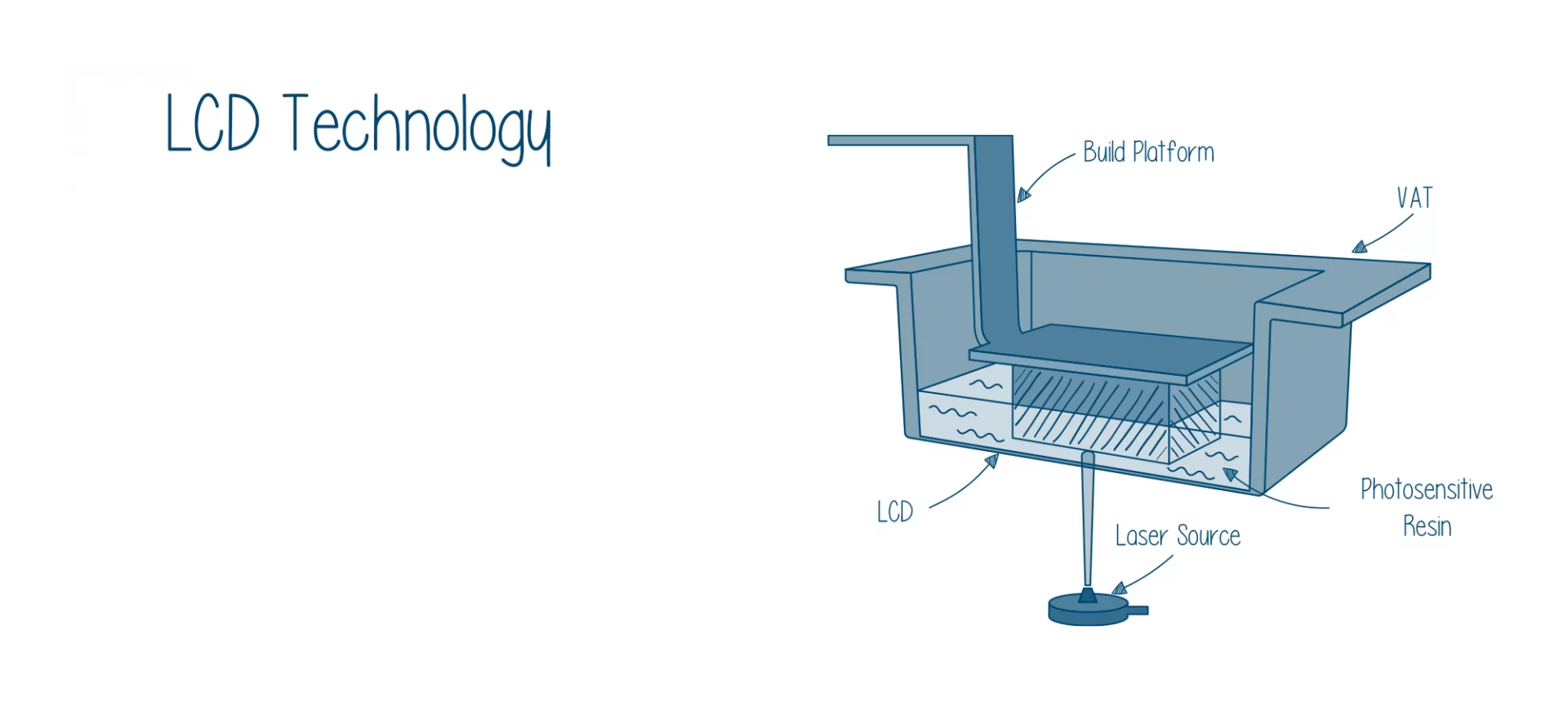
The last one is LCD 3D printing. Being the latest of the three, it is not as common as SLA or DLP, however, finding its way through the user’s workshops.
It is very much similar to DLP as it flashes the entire image at once. But the light source makes them different. It does not use a projector, however, an array of LEDs exposing the UV light through an LCD.
Here, a screen is used to mask the entire image, only revealing the current layer for curing. Moreover, unlike SLA and DLP, LCD does not require any specialized device to direct the light source.
What are the Differences Between LCD and DLP?
Now that we have gained an insight into how these technologies are set up, it is time we can explore further the working difference of DLP and LCD.
Working of Digital Light Processing (DLP)
The working of DLP printers is different from that of the LCD printers. The projectors are used in the DLP printers to flash an impression of a layer.
The light is passed through a lens to reach the DMD. DMD, then further directs the light to the bottom of the tank, filled with resin.
In short, the lenses are used to modify the size of the image, coming from a smaller source to fit a wider screen. However, while doing so, there are probable chances of distorted pixels resulting in the edges.
One more thing to note in DLP printers is that the number of pixels does not change. Either it’s before projection or after projection. Regardless of the size, the number of pixels remains the same.
This signifies that the narrower the model, the higher the precision. You must have experienced a decrease in sharpness when zooming out a picture clicked on your phone.
The same happens here too. As you increase the size of the model, the sharpness is compromised.
In spite of all these challenges, the DLP 3D Printers are a great aid for those printing small prints. Moreover, the professional range DLP printers would help compensate for the zoom out issue to a certain extent, hence furthering the clarity for bigger models.
But the precision with bigger models is still a question mark with DLP 3D Printers. It is just that the 3D printers based on the DLP process are more inclined to producing finer details when printing small size models.
Working of LCD
As mentioned before, LCD 3D printers make use of UV LCDs as a light sources. In LCD 3D printers, the light shines in a parallelly coming through the LCD panels onto the build area.
Moreover, the light isn’t expanded using any lens or other device. Hence, pixel distortion isn’t an issue when working with an LCD 3D printer.
This clearly signifies that the print quality is not dependent on the change in the size of the model after projection. However, it depends on the LCD density. In other words, the smaller the pixels are, the better the print quality is achieved.
Material Used in DLP and LCD 3D Printers

While many would think that both these printers, based on resin 3D printing, must be compatible to provide similar results with all types of material.
However, this is not the case. The strength of the machines brings in a huge difference in the way these devices produce results.
Before you start using a specific resin type for your 3D printer, it is important to go through the resin datasheets to find out its compatibility with your particular 3D printer.
The LCD-based 3D printers use a low-power LED light source. Hence, the materials or resins that could be cured fast with considerably low power light sources are recommended for use.
The LCD printer would produce unmatched results with these fast curing resins. On the other hand, DLP 3D printers are powerful devices, however, they work with a different configuration. Hence, it is not possible to predict its curing behavior with a particular resin without testing.
More About DLP and LCD 3D Printers
There are other ways that these 3D Printers differ or reflect similarities. When talking about the similarities, one can notice both technologies being patted for high print speed.
This is because of the reason that they flash the entire model’s impression in one go, unlike SLA, where one layer is projected at a time.
This gives these technologies an advantage over traditional resin-based printing which used to be slow and time-consuming.
Moreover, the application of LCD and DLP printers are more or less, similar. Because of their ability to produce finer details, these printers are widely used across various niches.
Including but not limited to jewelry, dental, engineering industries, etc. As you can guess, there are also those individuals who are passionate about 3D printing, do own these 3D printers for creating precise and exceptional 3D printed results.
When assessing both the technologies on the pricey side, DLP tends to be expensive than the LCD 3D printers. These are more professionally designed and have been in the market for longer when compared with LCD 3D printers.
In spite of having minor issues with distortion, the reason why DLP is more popular among users is that the expensive DLP printers use advanced and high-quality hardware for fixing the issue to a great extent.
The other reason is that the LCD 3D printers aren’t very primitive and released years after the release of DLP technology. By far, these are mostly created as affordable desktop printers.
To put it in other words, the LCD 3D printers comprises of cheaper components as compared to the DLP 3D printers.
This is to bring the resin-based technology down to an affordable rate. Hence, further extending the reach of resin 3D printing to a larger group of makers and individuals.
In terms of print quality and speed, both these printers are very capable. But as the price range surges, the DLP 3D printers are found to outgrow the LCD counterpart.
To be precise, DLP 3D printers are suited for professionals with growing needs and higher expectations. And, on the contrary, LCD 3D printers are more about providing beginners and consumers with a cheaper option, if they at all wish to invest in a resin 3D printer.
Recommendations
While we have been talking so much about these two technologies, isn’t it worth checking some recommendations of DLP and LCD 3D printers.
FlashForge Hunter DLP
The FlashForge Hunter DLP is a desktop 3D printer manufactured by a company from China, FlashForge. The device has been released as an upgrade to the existing FlashForge Explorer DLP.
The company has come up with a better resolution of 0.0125 mm. Hence, making it highly precise for various applications that requires printing with minute details such as jewelry designing.
The printer is created for professional use, targeting the jewelry industry. It also features a jewelry support mode.
It also comes loaded with printing modes boasting resin preset for faster settings and operation. Apart from the proprietary resins, the printer is also compatible with third-party resins.
The other features include WIFI Connectivity, automatic calibration, HD projector providing a 1920p x 1080p resolution alongside a user-friendly touch screen. It has a build space of 120 x 67.5 x 150 mm.
Zortrax Inkspire

According to Zortrax, the manufacturer of the Zortrax Inkspire, the machine is around eight times faster as well as nine times more accurately than many other DLP and SLA 3D desktop printers available.
Although we do not know how far the claims justify themselves, it is worth noting though.
The printer is capable of producing a minimum layer height of 25 microns. Hence, able to create finer details smoothly.
The pixel size provided by the printer is 50 microns. And the print speed ranges between 20-36 mm/h. The device boasts a build volume of 74 x 132 x 175 mm.
The printer is capable of wonderful tasks and can be used for meaningful applications across many niches.
One can use the printer for dental prosthetics, engineering, jewelry designing and a lot of other tasks. The LCD 3D printer is from an open-source community, hence, it is upgradable as well.
|
The Conclusion
Technology is advancing, 3D Printing is reaching to a greater number of users, from offices to even homes. The world is becoming smaller when talking about the reach of 3D printers.
Technologies like SLA and DLP that were not easily accessible by end-users are now being enjoyed by every group in society. Thanks to the affordable range of desktop printers that have hit the market.
Either it’s DLP or LCD 3D printer, companies are trying to come down on the price point to fit everyone’s needs and budget.
Apart from the differences, both these technologies have instilled their importance within their respective user set. One can count on these 3D printers for detailed prints. And, can utilize the devices for professional jobs as well.
Based on the resin 3D printing, both printers own the best attributes that come along with this specific 3D printing process.
However, at the same time, it maintains a few differences to serve different groups of users. Increasing the accessibility to a wider population.
Understand the DLP vs LCD 3D printer fight, one would make a better decision of what to choose. Hence, try to assess all the details and select the one compatible with your needs.










