While discussing additive manufacturing and the types of techniques used in 3D printing, Sheet Lamination (SL) is rarely discussed.
You would find a variety of other technologies such as Vat polymerization, Material Jetting, Binder Jetting, Material Extrusion, and Direct Energy Deposition which seem to take away the limelight from SL 3D Printing.
However, in recent times Sheet Lamination is gaining unmatched popularity. Thanks to its contribution in manufacturing parts and functional prototypes. And hence it becomes important to know about this method in a lot more detail than we already do.
What is Sheet Lamination?
Sheet Lamination belongs to the Laminated Object Manufacturing class of additive manufacturing technologies. This class was introduced for the first time in the market in the early 1990s.
When the world was going crazy over material extrusion systems from Stratasys and vat polymerization systems from 3D Systems, LOM was becoming the third alternative. Especially for the people who could not afford the first two options.
Helisys is the company that did introduce the world to this crazy idea of actually gluing sheets of paper together, layer-by-layer. And as you can get a sense of it, this was the cheapest additive manufacturing technology at that time.
Imagine the thickness of paper; it’s anywhere near 0.1mm. Would you mind a part that has a layer resolution of 0.1 mm? You wouldn’t, would you?
Paper is also something that is extremely easy to cut or shape with any low-powered laser. You do not need a highly coherent laser source producer for cutting paper, as you do for sintered plastic or fuse metal.
Also, the growth of this concept of gluing things to form a part has grown over three decades and has burgeoned from limiting to paper.
Today, we have companies like Fabrisonic that use Ultrasonic Welding for bonding sheets of metal together for forming 3D objects.
The technique of CAM-LEM i.e. Computer-Aided manufacturing of laminated engineering materials uses this process for creating functional ceramic parts.
So, you see there are plenty of reasons why you should know about the process of Sheet Lamination. Want to get started?
Sheet Lamination – In Detail
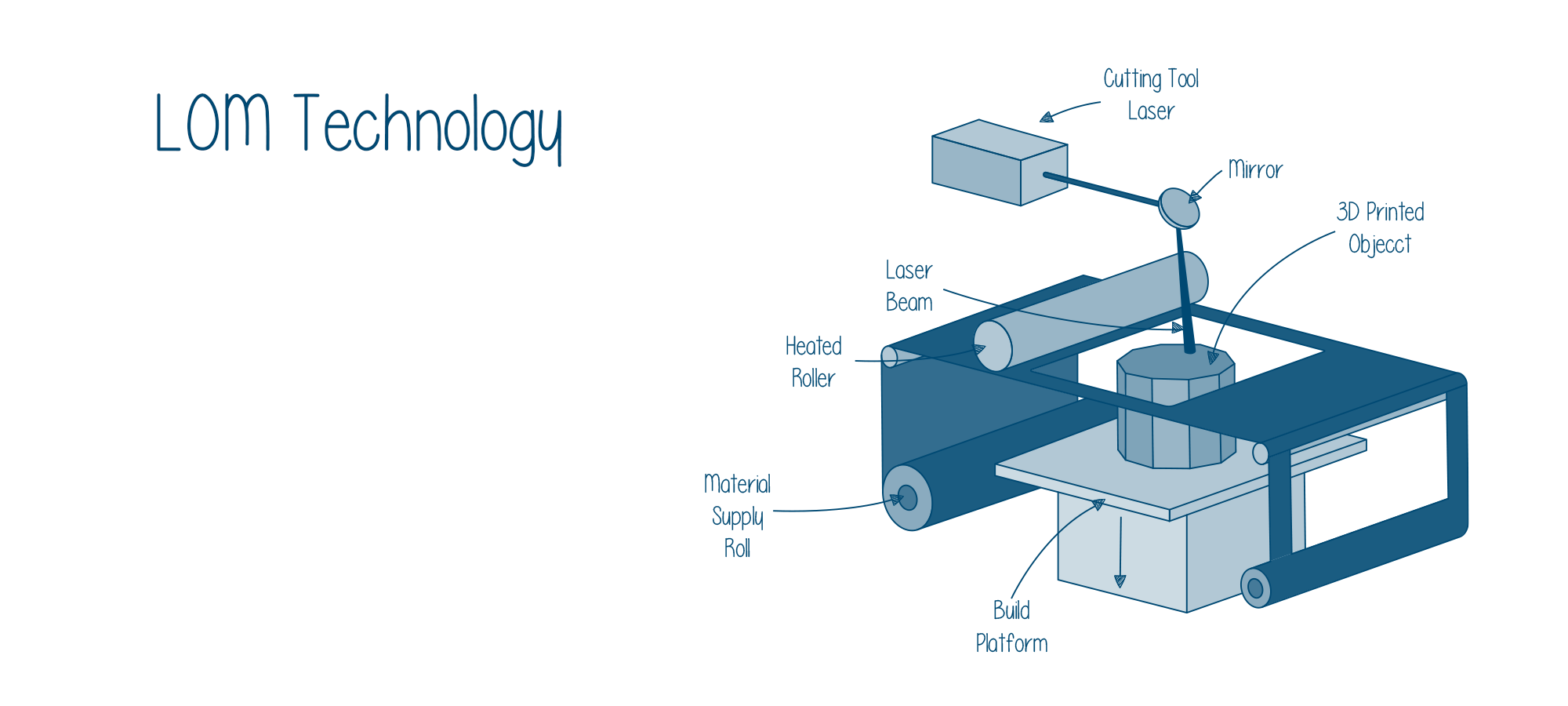
By now you already know that Sheet Lamination is one of the seven types of methods used for additive manufacturing. This is by the definition of ISO/ASTM 52900-2015. It is the process of stacking and laminating thin sheets of any material.
There are various methods that can be employed for laminating sheets of material. It could be done by bonding, ultrasonic welding, or brazing. But the final geometry of the part is achieved, either by laser cutting or CNC Milling.
Because of its inherent nature, Sheet Lamination is able to produce the least amount of resolution when compared with any other type of additive manufacturing.
Having stated so, do not prejudice it to take more print time than other technologies. It takes lesser or equivalent time for manufacturing a part and also costs less than its competitors in the market. And now, let’s look at its types.
Types of Sheet Lamination
There are ways to categorize this 3D printing technology. The first one is to categorize it based on the material used for building apart.
As you may have managed to catch paper, metal, and ceramics in the portion of the article before this, we’d like to also inform you that Sheet Lamination can also be used for making a part with woven fiber composites.
Secondly, the method can be categorized on the basis of methods that can be used for forming a part. There are three ways of forming a part using this 3D printing technique and they are:
- By CNC milling.
- By laser cutting.
- Aqua Blasting.
Thirdly, the method can be classified on the basis of the lamination technique used for bonding sheets with one another. They could be adhesively bonded, thermally bonded as well as ultrasonically welded.
The fourth way is related to the manner in which we will do the process of forming a part. It could be either shaping all the material and then bonding. Or, it could be bonding all the material and then shaping it into the desired geometry.
There are seven different variations of this 3D printing technology and they are as follows;
- Laminated Object Manufacturing.
- Selective Lamination Composite Object Manufacturing.
- Plastic Sheet Lamination.
- Computer-Aided Manufacturing of Laminated Engineering materials.
- Selective Deposition Lamination.
- Composite Based Additive Manufacturing.
- Ultrasonic Additive Manufacturing.
After getting to know the definition and types of Sheet Lamination 3D printing, let’s dwell on the working of this method.
Working
There is a difference in working styles of different types of Sheet Lamination processes; however, the basic principle is the same. And it’s obvious to say that the initial part creation and setting up process is the same for all the seven types of additive manufacturing.
- 3D Model Creation.
- STL file Creation.
- STL file transfer.
- Machine set up.
- 3D Printing.
- Part removal.
- Post Processing.
Having stated so, the first step of Sheet Lamination 3D printing is getting a thin sheet of material from the roller to the build platform of the printer.
If the method is of the type wherein you are first all the sheets into shape and then bonding, you’ll have individual sheets on the build platform, else otherwise.
Steps of working:
- The first step is to place the material that is to be 3D printed on the cutting bed of the machine.
- Once that is achieved, the material should be bonded over the previous layer using a suitable adhesive.
- After the bonding has been ensured, the cutting can start using a laser or knife.
- The next layer is added and the process will be repeated. It is to be noted that steps number two and three can be interchanged depending on whether it is forming and cutting or cutting and forming a type of Sheet lamination.
Selective Deposition Lamination and Ultrasonic Additive Manufacturing involve bonding of layers firstly and then cutting them into the desired geometry. Whereas CAM-LEM does the opposite! Whether it is cutting or bonding, the process continues until all the layers are done and the complete height of the object is achieved.
Once that is done, the print block is removed and the outer edges of the object are removed for revealing the printed 3D object. As you have already read before, in sheet lamination the layer thickness is the same as the thickness of the sheet that you are using to form layers of the part.
Application

Sheet Lamination 3D printing makes use of a variety of materials. Starting with paper, followed by polymer, ceramic, metal, and so. All of them are supposed to be manufactured with different binding procedures.
The most common form utilizes pre-applying adhesive to paper and then heating or pressurizing it for activating the adhesive.
Polymers are the materials that do not require adhesive for bonding them; they rely on melting sheets with each other.
Metal sheets can be bonded using Ultrasonic welding, whereas fiber-based material and ceramics use thermal energy for the same.
Paper-based technologies such as LOM and SDL are used for making full-color prints. On the other hand, metal-based sheet lamination is used for hybrid manufacturing.
SLCOM is used for producing quality composite fiber-like parts. And CAM-LEM can be used for making ceramic parts.
Pros

- Faster print times: Compared to any other 3D printing technology, SL 3D printing can print a part in a considerably lower print time. Although it requires post-processing, even summing the time for pose-processing would not lead to more print time the one needed while the print part with other technology.
- Easy material handling: As you may have noticed during the working process. There is not much hassle required for handling material in the initial stage when this process starts.
- Relatively low cost: The cost of material, combined with the cost of 3D printing is very low than high-quality 3D printing processes such as Binder Jetting or MJF. This is because of the accessibility of material used for SL 3D printing as well as the method employed for creating a part out of that material.
- No support structures: Creating a part without support structures is bliss, don’t you feel so? SL 3D printing gives you this freedom. Support structures are only required during extremely complex geometries.
- Larger working area: This enables you to manufacture parts and functional prototypes of a larger build volume.
- Building a part with multi-materials is possible: This is done specifically using the Ultrasonic Additive Manufacturing technique.
Cons
- Layer height depends on sheet thickness: The resolution range of part can be altered in other 3D printing technologies, but in SL 3D printing that is impossible because the layer height is essentially the sheet thickness.
- Post Processing is needed: Although the finishing of parts can depend on whether you are using paper material or plastic, the post-processing must be done for achieving the exact desired effect.
- Limitations of material: To date, SL 3D printing is confined to metals, ceramics, paper, and fiber material.
- Making of hollow parts is difficult: Especially when you are first bonding the materials and then forming them, the making of hollow parts gets extremely tedious and if not done with a certain amount of expertise may lead to failure.
- Material waste can be high: This is applicable in cases where the part you are looking to build have a smaller build volume than the sheet it is being made with.
What is The Best Sheet Lamination 3D Printer?

CleanGreen 3D is a professional 3D printer operating on Selective Deposition Lamination technology. It uses paper for achieving white 3D prints.
Working with A4 sheets of paper having a standard dimension of 256 mm * 169 mm * 150 mm and a letter paper of 9.39 inches * 6.89 inches * 5.9 inches, the printer is able to generate 100 microns of layer thickness in parts that it creates. It is a 3D printer based on producing zero waste, full-color models.
The printer is easy to install and can be used straight out of the box. It can fit into any office or classroom; you require no special ventilation, fume extraction, or special vacuum cleaners for its operation.
Special features of this printer:
- The printer operates on a clean process from the start to the end. You need no post-processing of parts or washing with chemicals. After you are done 3D printing, all you got to do is simply breaking away the paper support material for revealing your final model.
- All you need for 3D printing your part is paper as the 3D printing material. It’s no dangerous resins or powders, just safe paper, ink, and glue.
- This printer operates on a patented SDL technology using inkjet print heads with specialized paper and adhesive for building full-color, robust, textured, heat resistant, durable, and effective 3D models.
This company i.e. Clean Green 3D operated formerly with the name MCor Technologies.
The Conclusion
The SL 3D printing technology has come a long way since its concept first experimented within the 90s. The advancement in paper-based lamination systems mirrors those in 2D desktop printers.
Printing parts in full-color is a very cost-effective option allowing you to create a photorealistic prototype. And this is one of the main reasons why SL 3D printing is finding its use in various industries.
The list of these industries starts with structural analysis, architecture, visual arts, life sciences and expands long enough to reach education, entertainment, etc.
It’s fascinating to think that the simple idea of gluing and cutting or vice versa can find such an application in the complex world of 3D printing.
Sheet Lamination 3D printing is still expanding and finding newer materials on which this can be applicable.
With materials, researchers in this field are also experimenting with technologies like UAM and SDL for finding better results.
So, overall the scope of this technology is very huge in the future and the main reason for this is the simplicity it is able to bring on to the table.







