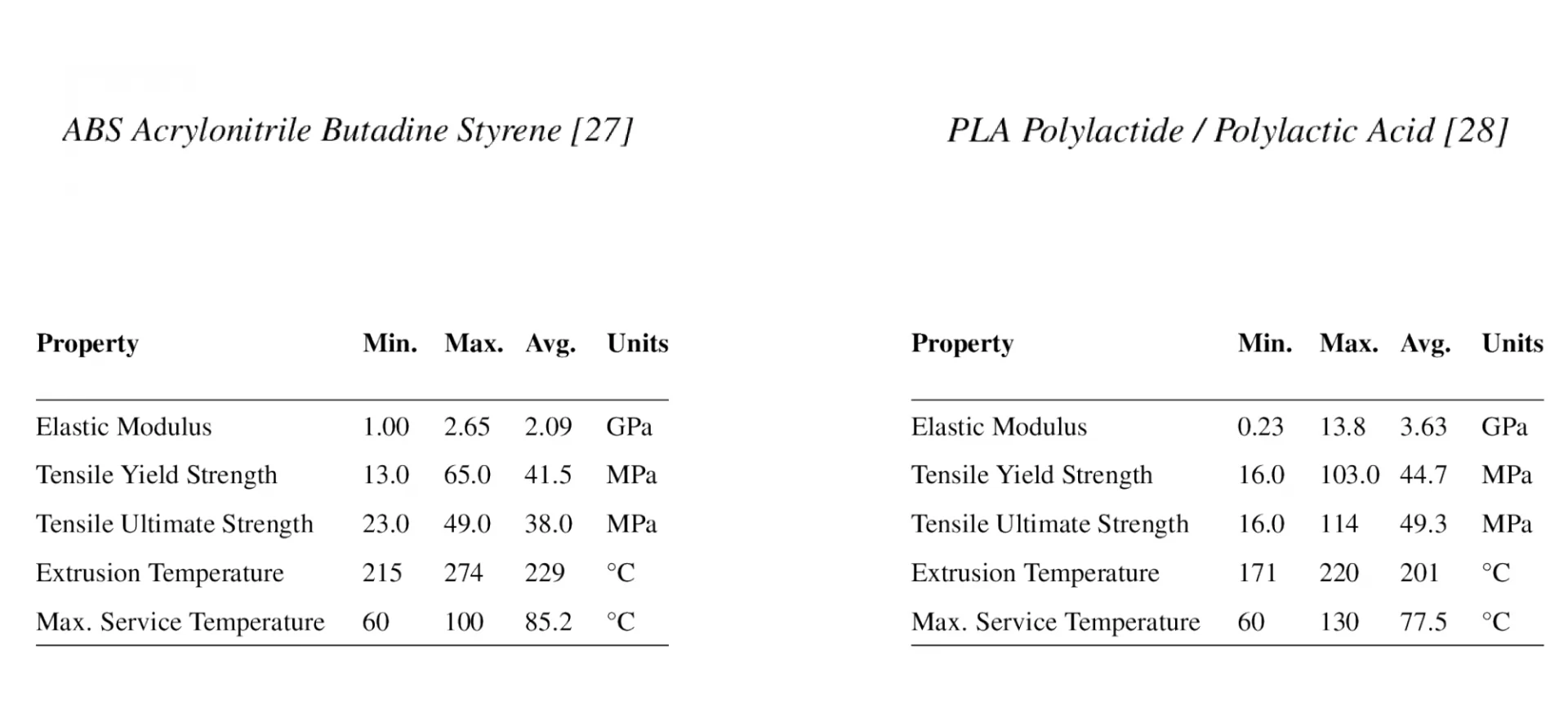
ABS is one of the most popular 3D printing filaments used for various applications. However, the material is also very difficult to print. Its notorious properties make this filament the toughest in terms of its settings.
And ABS print speed, when incorrectly selected often leads users towards failed prints. That is why many beginners ignore working with ABS and choose PLA over the prior. But to expand one’s creation further, it’s important to learn to work with ABS filament.
If you also have similar confusions, and unable to understand how to tame ABS, read through. The article lists some of the major challenges faced by ABS printing and how ABS print speed setting could help correct these problems.
To help you master working with one of the most stubborn filaments, it is imperative that you understand its properties and how a little difference in the settings could help clear problems often associated with ABS.
So, without wasting much time, let us jump to the details and find out the tips that can let you switch from PLA to ABS, the usual printing to more specialized applications.
What is ABS?

Starting with what exactly the filament is all about, here is a short brief of ABS. The filament stands for Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene.
The material isn’t new. On the contrary, it has been one of the most popular 3D printing materials around since long back.
Being reasonably priced and able to print durable parts that hold great mechanical properties, ABS has gained huge importance among many niches.
Known for its properties such as resistance to impact as well as strength, the material can be used for printing parts needed to go through extra wear and tear.
The most common example of the same is Lego blocks. In addition, the material is resistant to considerably high temperatures. This means that the users can easily create parts with ABS for outdoor applications.
With so many perks, there certainly are a few challenges that we must clearly understand. For instance, the material releases harmful odors. Hence, it is necessary to print with ABS in a room with a good amount of ventilation.
Moreover, the parts made of ABS tend to contract during cooling. Therefore, it is advised to include the change in contraction during the 3D designing of the parts. Also, temperature control can also assist in ensuring the best print results.
What are ABS 3D Printing challenges?
Before jumping to the ABS print speed and other settings, we must be aware of the problems that might occur when printing with ABS in advance. Therefore, as mentioned before, ABS is very challenging to 3D print.
So, let us find out the major problems that often come in handy when working with this difficult material.
Warping

When compared to various other filaments, ABS is among those materials that require a higher temperature to print. This definitely helps ABS staying resistant to heat and high temperature.
However, there is a downside to the same. Yes, ABS is highly prone to warping. Whenever printing with ABS, users often encounter the issue and end up with failed prints.
So, what is warping? And, why warping happens? Well, warping is the shrinkage that happens when the ABS parts cool down.
The fact is, it is practically difficult to eliminate this consequence that comes along naturally when cooling a heated plastic.
Basically, ABS parts experience rapid temperature drops during printing. Hence, the problem is pronounced more in ABS printing than most of the other standard materials.
The material turns into semi-solid form long before it finishes contracting. All these scenarios result in higher warping chances.
Therefore, those requiring accurate parts with precise dimensions must consider the changes due to warping during the 3D designing of the parts.
Build Surface Adhesion

Poor first layer adhesion is often a continuation of the warping issue. Whenever warping occurs, the parts start shrinking from corners, eventually lifting from sides and hampering the first layer adhesion.
Although ABS has exhibits great surface energy. And, the material easily connects strongly with paints, adhesives, etc.
However, the warping phenomenon makes it hard for the material to stay put. With warping, the parts start contracting from all directions.
Ideally, the adhesion is strong and the base layer somehow manages to act against the thermal stress. But the sides are often compromised during the process and the corners curls.
Unfortunately, there are times when the results are highly visible, making the entire part useless. And users must go through the entire process of printing, ensuring that the effect isn’t a problem the next time.
This issue can be handled with ABS print speed setting (discussed later in the article).
Harmful Fumes
Another major issue that calls for action is the release of harmful fumes when printing with ABS. Whenever heated, the plastic releases an unpleasant odor which is even toxic and not healthy when inhaled in a larger amount.
You can ask those who have already worked with this material. One can easily get trapped into respiratory problems when not taken necessary precautions.
And, with ABS printing, there are certain things you can consider when creating parts. First of all, it is important to use a ventilated room where you print ABS.
In addition, you can consider buying printers that come equipped with HEPA and Carbon filters. These filters help eliminate the fumes by 99 percent, making it safer to work with ABS.
What Are The Best ABS Print Speed Settings – Tips to Consider?
Coming back to the tips for printing with ABS, here are a few of the basic hardware requirements that you must ensure apart from the ABS print speed settings.
- Bed Temperature: For printing with ABS, you do need a heated bed. And, the build surface must maintain a temperature ranging between 95 degrees Celsius to 110 degrees Celsius.
- Build Surface Adhesion: In case your first layer isn’t too sticky to stay in place, you must keep ABS slurry or Kapton tape handy. You can also make ABS slurry at home. Just mix a small portion of ABS filament and acetone. Once you create the slurry, spread the mixture on the build surface to enhance first layer adhesion.
- Extruder: The printer must have an extruder enabling temperature between 220 degrees to 250 degrees for easy extrusion of ABS. However, there is no need for special hot ends as’s the case with metal filaments.
Different ABS Print Speed Settings
Now, that you have got an idea of the hardware requirements necessary to print with ABS, let’s move on to the different ABS print speed settings.
First Layer Speed
We have already stressed the fact before that ABS printing is often considered difficult because of the weak first layer adhesion to the bed. However, with the right ABS print speed for the first layer, you can overcome the problem.
To do so, set the first layer speed to a slower pace. Usually, it is recommended to keep the first layer ABS print speed to 30 to 50 percent of the overall speed for printing.
Hence, it allows the filament to take enough time for settling down. In case, your print speed is 50mm per second, you can set the first layer speed to 25 mm per second.
Doing this will be very useful in getting your first layer strongly fixed to the print bed.
Retraction Speed
Although not mentioned before, one of the problems when printing with filaments is oozing. In such cases, the web of thin strings forms around the parts, making prints impossible to use for the preferred application.
And, to sort the problem out, one must ensure that the retraction speed setting is in place. With a retraction setting, you can control the speed of the filament with which it is pulled back to the extruder when not in action. Avoiding the unnecessary leakage of the filaments when not required at all.
For different filaments, the settings may differ a little. However, a standard setting is to keep a speed range from 30 to 100 mm per sec. Make sure you choose the right retraction speed settings.
Because, if you keep the speed too low, the filament may come out of the nozzle slowly just before the print head has completed moving.
On the other hand, in case the retraction speed is too high, the drive gear may end up grinding away at your material.
Also, please note that the retraction speed need not match the print or travel speed. You can set it different from the said parameters.
In short, for best results, ensure the retraction speed stays fast enough, however, not allowing the drive gear to grind away ABS.
Cooling Speed
Whenever talking about the print speed for ABS, it is important to note the cooling speed of the printer too. So, why is it so important?
As mentioned before, uneven cooling often results in warping. And with ABS, the problem seems to be more prominent than many other alternatives.
So, what does a cooling fan do? When printing finer details, sometimes the prints may deform or seem melted in few sites.
With cooling fans, users can prevent the parts from overheating. Thus, able to maintain the desired shape.
However, when working with ABS, the fan speed setting is a bit tricky. As ABS has the tendency to shrink when cooled, one must choose the fan speed wisely. It is easy to adjust the fan cooling speed from the cooling tab.
For ABS, it is preferable to keep your fan turned off for the first few layers. This can be done by disabling the fan from the cooling tab for few layers in the beginning. Later, you can turn it on as the prints reach higher layers.
What Are The Pros and Cons of Printing with ABS?

Before wrapping up, let us check out the benefits and challenges when printing with ABS.
- Among the cheapest materials available for 3D printing
- The parts printed using ABS showcase great impact as well as wear resistance
- With the right settings, ABS can be a very friendly material to work with. It is less prone to oozing. Hence, the models often come out with a smoother finish
- ABS parts are resistant to high heat, unlike PLA. Therefore, you can build parts for outdoor applications as well.
- ABS is considered challenging because of highly prone to warping
- One cannot print with success without a heated bed along with an enclosed print chamber
- The harmful fumes with unpleasant odor seem very irritating and can cause respiratory issues when not handled properly
- With shrinkage issues, dimensional accuracy may result in undesirable parts requiring the highest precision
The Conclusion
ABS is a great production choice for those wanting to create functional prototypes or end parts with considerable strength. However, printing with ABS is not that easy. Especially beginners find it daunting to work with the ABS print speed setting. One of the many reasons is the fact that the material comes with its own list of challenges.
ABS may be one of the most difficult filaments to work with. However, its favorable mechanical properties make it the best choice for a variety of applications. Hence, ignoring its usage is not a practical solution to skip the challenges that abide by its printing.
As mentioned before, one must know how to deal with issues that are very common with ABS printing. Once in a while, these problems keep surfacing, leading to unnecessary frustrations. Our article lists all the major challenges that are usually found when printing with this notorious material. However, as stressed a lot of times already, the right settings would lead to a safer print operation.
And, among the different settings, print speed is very common to go wrong with. When talking about speed, other parameters also come into the picture. Such as retraction speed and cooling fan speed. Therefore, we have ensured that you understand each of these settings clearly for a smoother experience. So, find out the apt ABS print speed settings and deal with issues beforehand. Thus, creating accurate prints whenever you need it.







