The success or failure of any 3D printing project depends a lot on the type of technology that you employ. And you can only decide upon a certain technology by knowing the basics of the options present in front of you.
Although there are many 3D printing technologies that we can compare, we chose the most primary ones that are employed more frequently than all others. Doing SLA vs SLS vs FDM comparison on various parameters will make your decision of choosing the correct one for your project a simple task.
All three of the technologies offer their own set of materials, printers, layer resolutions, and build volumes. Moreover, each of these has its own set of benefits and limitations which are important to know. Also, their equipment cost, material cost, and labor skills needed to operate the equipment varies.
This goes even if you are not thinking of buying an SLA, SLS, or FDM 3D printer and planning to get the job done via a 3D printing service provider, online. SLA vs SLS vs FDM is worth knowing because the difference between them is very subtle. Having stated so, let’s get started with the comparison.
SLA vs SLS vs FDM
A lot can be said about all three technologies and they can be compared on numerous parameters. For the current comparison, we’ve chosen the most basic factors, all of which are generalized, and a range in which that particular technology can deliver it is figured out to make the comparison much more comprehensible.
Working Principles
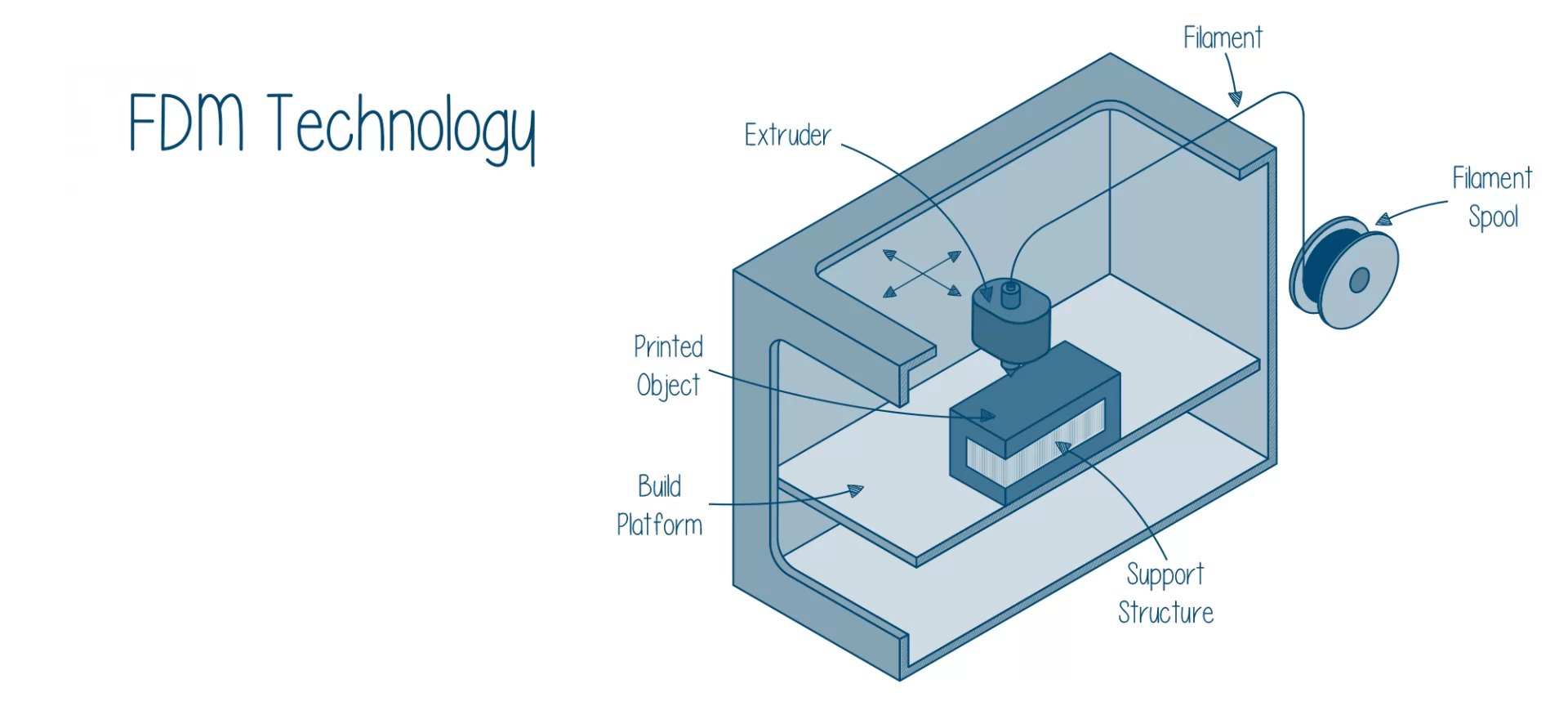 FDM 3D printing technology uses a solid filament spool of thermoplastics, extrudes it, deposits it on the print bed according to the geometry of the part layer by layer, and then cools it to form the desired geometry.
FDM 3D printing technology uses a solid filament spool of thermoplastics, extrudes it, deposits it on the print bed according to the geometry of the part layer by layer, and then cools it to form the desired geometry.
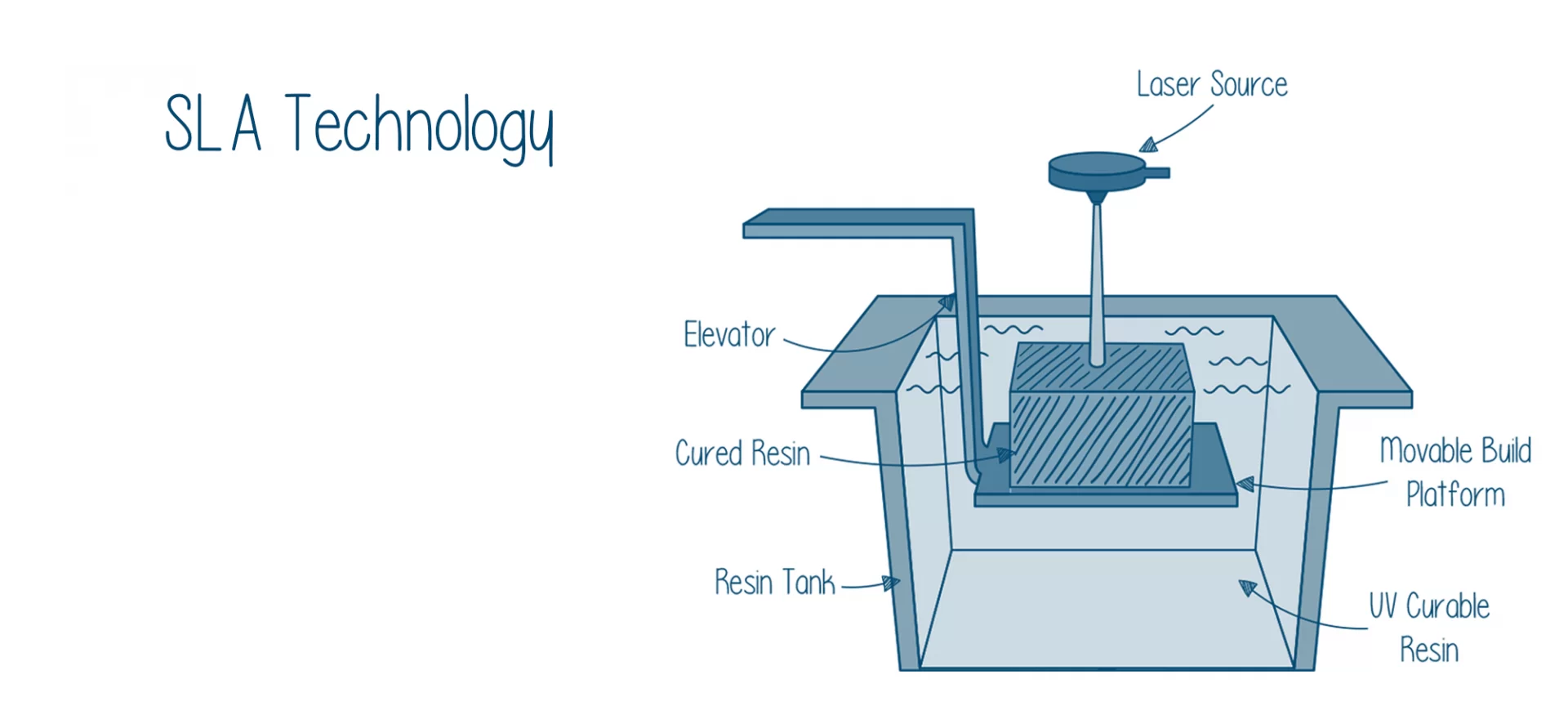 While, SLA 3D printing technology utilizes a liquid resin of thermoplastics, cures or solidifies them using high power UV LED light source to form an object. And then post-processes it according to the application.
While, SLA 3D printing technology utilizes a liquid resin of thermoplastics, cures or solidifies them using high power UV LED light source to form an object. And then post-processes it according to the application.
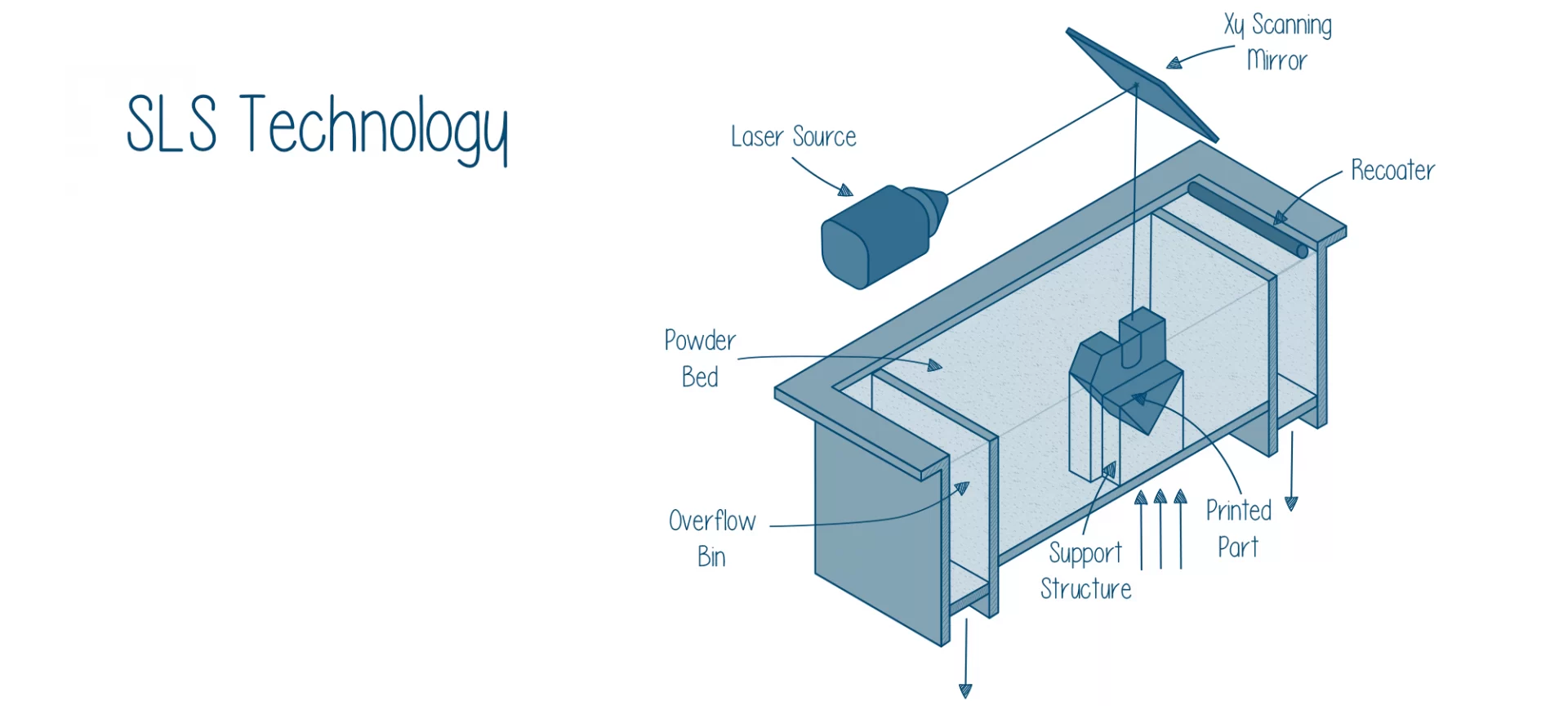 SLS 3D printing technology consumes sinterable powder polymers such as polyamides like TPU and TPE with the help of a laser source to form a part or functional prototype. Note that, FDM and SLA can make use of support structures for printing complex geometries but that is not true for SLS.
SLS 3D printing technology consumes sinterable powder polymers such as polyamides like TPU and TPE with the help of a laser source to form a part or functional prototype. Note that, FDM and SLA can make use of support structures for printing complex geometries but that is not true for SLS.
Also, in terms of working principles when you do SLA vs SLS vs FDM, FDM turns out to be the simplest and the most used 3D printing technology. There are a greater number of printers employing FDM than SLA or SLS. Whereas, SLS has the most sophisticated working principle because it prints by deploying a laser source for curing the powdered material.
Build Volume Offering
Although there is much variation available in terms of the build volume offered by all three technologies, for the sake of comparison we will consider the most accessible type of printer i.e., desktop and benchtop 3D printer.
A typical FDM 3D benchtop and desktop 3D printer offer on average a maximum build volume of 300 mm * 300 mm * 600 mm for printing parts and functional prototypes. This does not mean that there might not be any desktop FDM 3D printer offering more than the mentioned one.
Coming to desktop and benchtop SLA 3D printers, in terms of build volume, the maximum that they offer users is 300 mm * 335 mm * 200 mm. Notice that there isn’t much difference between the build volumes of SLA and FDM 3D printers, however, there is a difference in their cost and accessibility.
Lastly, SLS desktop and benchtop 3D printers can only offer a maximum build volume of 165 mm * 165 mm * 300 mm on average. So, when talking about the build volume offering while comparing SLA vs SLS vs FDM, FDM manages to steal the show by offering a little more than SLA.
Print Quality
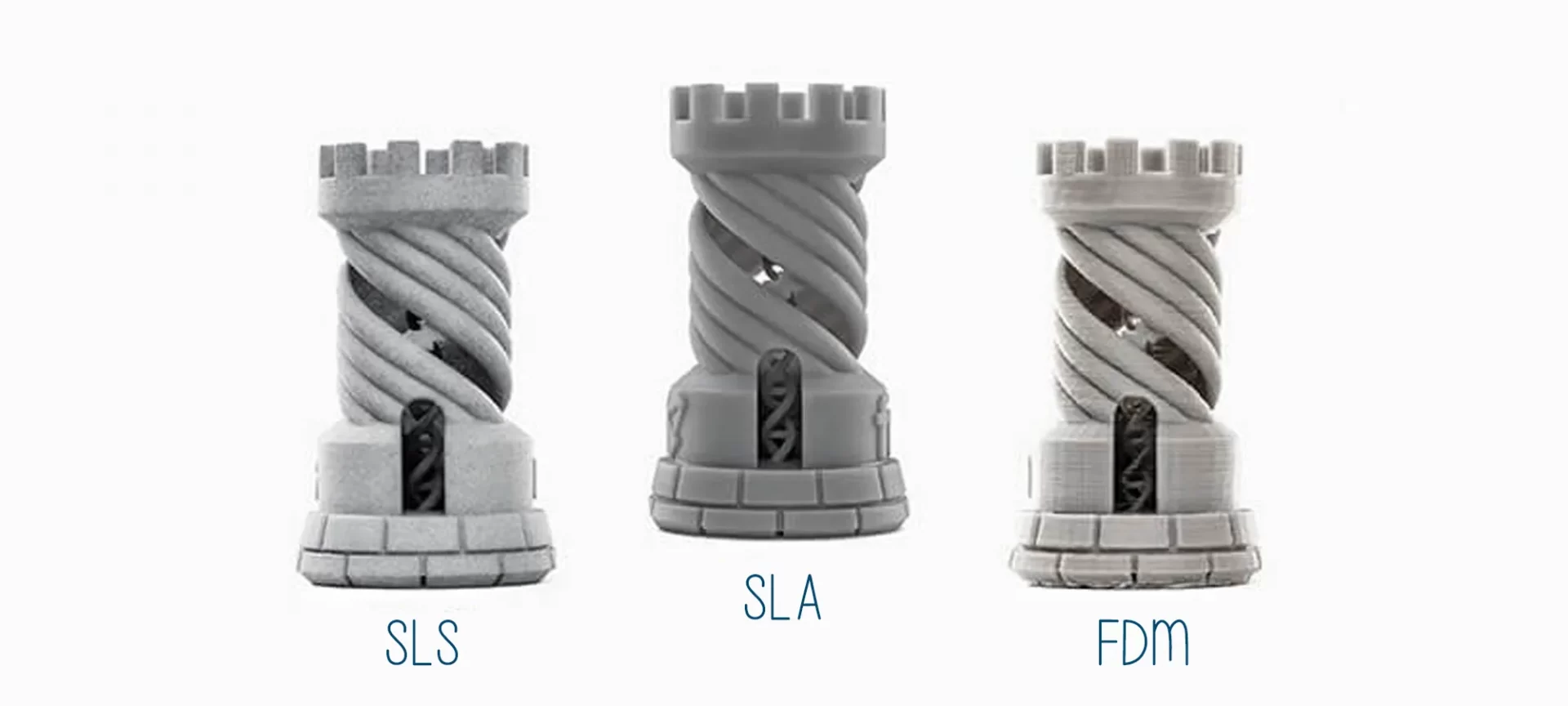

After comparing the technologies in terms of the build volume offered by them, let’s have a look at where they stand in terms of the quality they have to offer.
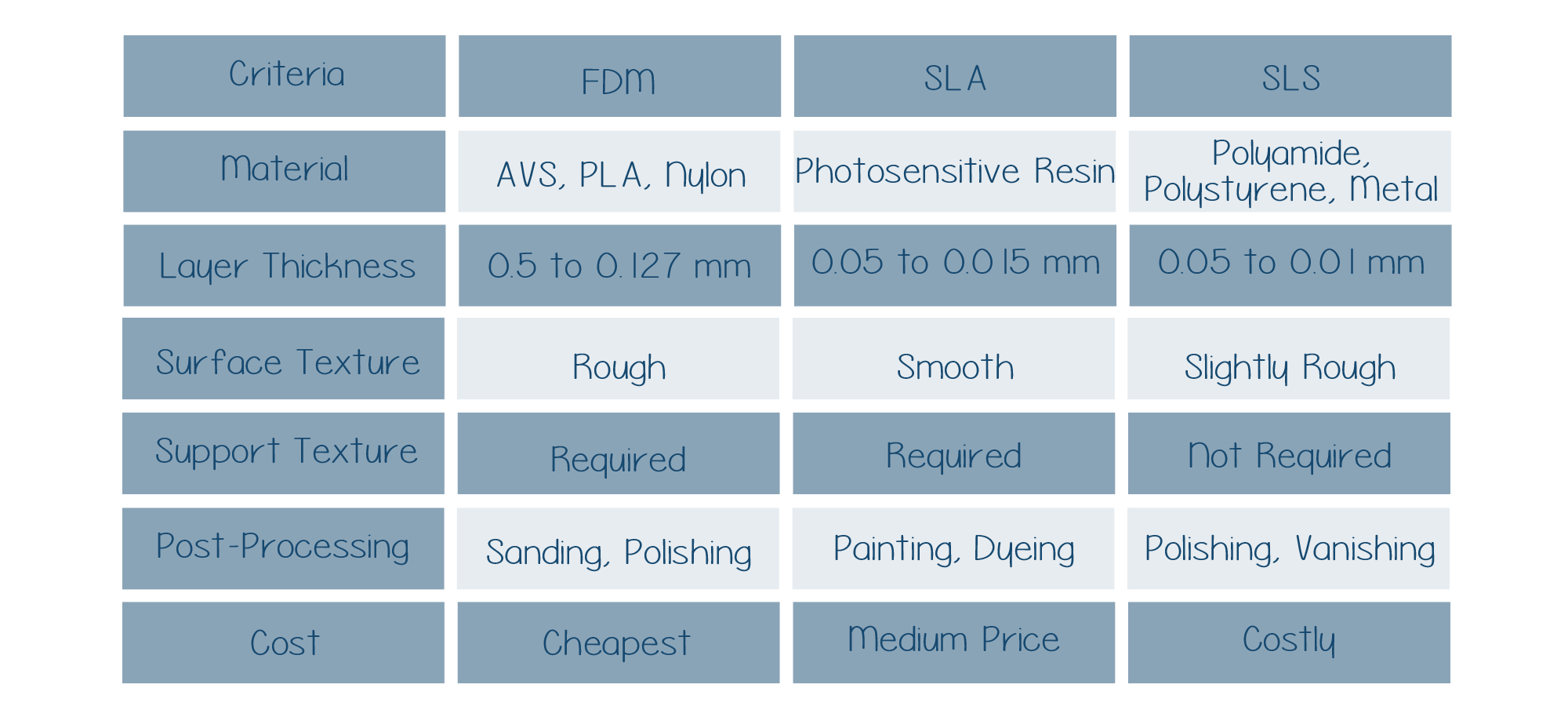
FDM 3D printing technology offers a low to medium quality surface finish. The parts or functional prototypes made using this method possess a layer thickness ranging from 0.5 mm to 0.127 mm and a minimum wall thickness of 1 mm.
Whereas, objects made using SLA 3D printing technology have a high level of surface finish. The layer thickness range of parts manufactured using this technology is 0.05 mm to 0.015 mm and a minimum wall thickness is 5 mm.
Just like SLA 3D printing technology, SLS too offers a high-level surface finish. Parts made using this technology possess a layer thickness ranging from 0.05 mm to 0.01 mm and a minimum wall thickness of 0.8 mm.
So, if you are willing to make parts and functional prototypes with a high-level surface finish prefer buying an SLS 3D printer over the other two. Overall, while comparing SLA vs SLS vs FDM concerning print quality SLS beats SLA and FDM by a fair margin because it provides minimum wall thickness and less layer thickness range.
Type of Material

FDM 3D printing technology offers the freedom of playing with standard thermoplastics such as ABS, PLA, PVA, PETG, Nylon, and many other blends. Also, advanced FDM 3D printers allow users to print with high-strength materials such as Carbon Fiber, PEEK, Ultem, and much more. All these materials are used in a solid filament spool while printing with an FDM 3D printer.

SLA 3D printing technology uses varieties of resins like thermosetting plastics, standard engineering ABS-like, PLA-like plastics as well as flexible, heat resistant plastics, and the rarely used castable, dental and medical as well as bio-compatible materials for creating parts that are put into application in various industries.

SLS 3D printing technology makes use of Engineering thermoplastics such as Nylon 11, Nylon 12 and their composites. Also, advanced SLS machines allow 3D printing with Polystyrenes, Thermoplastic polyurethane, and Metals.
Overall, FDM and SLA 3D printing technologies permit the use of more 3D printing materials than SLS 3D printing technology. So, construing SLA vs SLS vs FDM as to the type of material you get the most materials to play while 3D printing a part with FDM.
Cost of Printers as well as 3D Printing a Part
This criterion will hint you about the running as well as investment cost of FDM, SLA, and SLS 3D printers.
Starting with FDM 3D printers: they are the most inexpensive 3D printers while making the comparison of SLA vs SLS vs FDM. Also, compared to SLS and SLA, FDM 3D printing materials i.e., solid filament spools are much lower in cost compared to resins or powdered materials.
SLA 3D printers are neither the most budget-friendly printers nor on the very higher end. They are much on the medium side. Having stated so, the printing materials used in SLA 3D printing technologies i.e., resins can be expensive.
Stating about SLS 3D printers, they are on a much higher-end compared to SLA and FDM 3D printers. Whereas, the 3D printing materials i.e., polyamides, polystyrenes, thermoplastic polyurethane are not extremely expensive compared to resins and plastic filament spools.
Overall, it can be derived that the running as well as investment cost of SLS 3D printers while doing SLA vs SLS vs FDM 3D printing technologies is higher. But on the other hand, it is also able to deliver fantastic quality prints with an excellent surface finish.
Post Processing
After you are done 3D printing a part or functional prototype using FDM 3D printing, generally on average many post-processing processes such as polishing, painting, sealing, smoothing with acetone vapor is needed.
On the other hand, while printing an object using SLA 3D printing technology, you rarely need post-processing. A little bit of painting just to enhance the complete parts’ beauty is sufficient. Because the surface finish of 3D printed parts is such that requires no more touch-ups.
Whereas, after creating parts with SLS 3D printing technology, generally users can opt for polishing, smoothing, beautifier, varnishing, dyeing, and painting. Post-processing of objects makes them application-ready.
So, in terms of post-processing, while doing SLA vs SLS vs FDM 3D printing technology, SLA manages to take a lead compared to SLS and FDM 3D printing technology.
Pros and Cons
FDM

FDM 3D printing technology produces parts and functional prototypes at low cost and consumes minimal time. Not only its 3D printing material but also its machines demand low one-time investment and hence is a beginner-friendly 3D printing technology. Also, its mechanism is very easy to understand even for a person with a non-technical background. So, even newbies find their comfort while printing a part using FDM.
The darker side of FDM 3D printing technology is that it is not able to print highly accurate 3D printing parts. Also, a lot of detailing is not possible via FDM 3D printing. It offers limited design compatibility and users have to design support structures in case they wish to print parts with a lot of intricate geometries.
SLA

SLA 3D printing technology offers high print resolution and is a lot more automated than FDM 3D printing technology. It offers great value for money and can print highly accurate parts and functional prototypes. Moreover, objects 3D printed using SLA 3D printing technology are known to have smooth surface finishes.
SLA 3D printed parts are sensitive to long exposure to UV light. Also, SLA 3D printing materials are not as varied as FDMs’ are. Moreover, SLA 3D printers require high maintenance costs compared to FDM 3D printers.
SLS

Using SLS 3D printing technology you can print parts and functional prototypes without using any support structures. They offer the freedom of printing high-quality prototyping and movable parts. Also, functional parts of high strength can be created using SLS. The technology offers a commendable amount of design freedom.
SLS 3D printing technology has very little stock of material options that you can choose from. Also, it consumes much more 3D printing time compared to FDM or SLA 3D printing technology.
The Conclusion
While choosing anyone from SLA, SLS or FDM 3D printing technology, be clear about your 3D printing task. Ask yourselves some basic questions, the factual answers of which allows you to come to a decision.
For example, if your 3D printing project is to print a part with huge build volume, decent print quality at a good level of print speed with multiple materials, and under strict budget constraints, it’s wise to favor FDM 3D printing technology.
In case the requirement is to print a functional prototype with high detailing, sharp edges, curves, and complex geometries and time and budget are not any constraints, SLS would be the most favorable choice if the material option is available.
While, SLA 3D printing technology is an appropriate choice in conditions wherein the build volume required is considerable, good surface finish, intricate geometries and design freedom to print support structures, and budget constraint is also not a huge deal.
So, understand your print job well to benefit by implementing the about mentioned comparison of SLA vs SLS vs FDM 3D printing technology based upon the seven most general parameters. Also, understand that each one of them is accessible up to a certain extent. And FDM is the most accessible 3D printing technology, so you’d find FDM 3D printers costing under $200.
The same applies to SLA 3D printers as well, but its accessibility is still not as much as FDMs’. Whereas, even desktop SLS 3D printers are very expensive. For an instance, you can get a desktop SLA at the same price as intermediate or even sometimes mid-level industrial FDMs.
Moreover, there are application-specific 3D printers available in each of the 3D printing technologies. So, even after doing SLA vs SLS vs FDM be wise while taking your call of which technology to employ when.







