One of the most exciting 3D printing technologies available in the market today is SLM 3D printing.
The fact that it can be utilized not only for making rapid prototyping but also for mass production makes it extremely popular.
The SLM process is very beneficial to you if you want to produce metal parts for prototyping in a short span of time.
Apart from making parts with simple geometry, the 3D printing technology also permits you to make extremely complicated parts with dimensional accuracy.
Some of the parts made by SLM 3D printing are impossible to manufacture using traditional manufacturing technologies.
SLM is pretty similar to DMLS, to an extent that some people almost use it interchangeably. However, there is a difference between the two technologies.
And if you were to ask yourself a simple question i.e. what material does SLM melt? And, what material does DSLM melt? You will know the exact difference between them. The answer to the former question is pure metals, whereas the latter one is metal alloys.
Because of the choice of metal alloys available in very vast, SLM is preferred by those who love manufacturing with different materials.
Also, the technology is highly preferred by those who demand parts and functional prototypes of the quality that is obtained by traditional manufacturing techniques.
But what exactly makes a part manufactured using SLM 3D printing, like what is? How does the 3D printing process work? And what are its pros and cons? These are some of the questions, with which our article deals.
What is the Difference Between SLS and SLM?
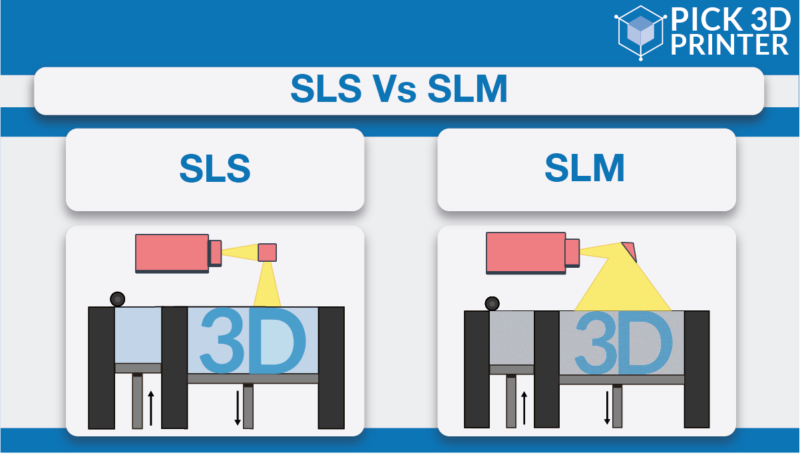
If you happen to know Selective Laser Sintering 3D printing technology, you will not have more difficulty in knowing SLM.
Firstly, both of them fall under the same kind of 3D printing technologies i.e. powder bed fusion.
The difference lies in the kind of feedstock and powder used by them. SLS 3D printing mainly uses Nylon (PA) polymer materials whereas SLM 3D printing uses metal.
A typical SLM 3D printing technology starts with the laser source. The duty of this source is to sinter the powder together.
This, the laser source does layer after layer until the complete model is printed as in the 3D design file.
The process of SLM and SLS can be the same if the powder material used in both the technologies are the same.
However, there is one more difference between these technologies, and this one deals with the nature of support structures.
In SLM 3D printing you will need to add support structures like the ones of FDM 3D printing. Remember overhangs? You are going to need them while printing a part out of the SLM process.
Whereas when you are manufacturing apart from SLS 3D printing technology you do not need any support structures, its powder acts as a support.
Stepwise Mechanism of an SLM 3D Printer
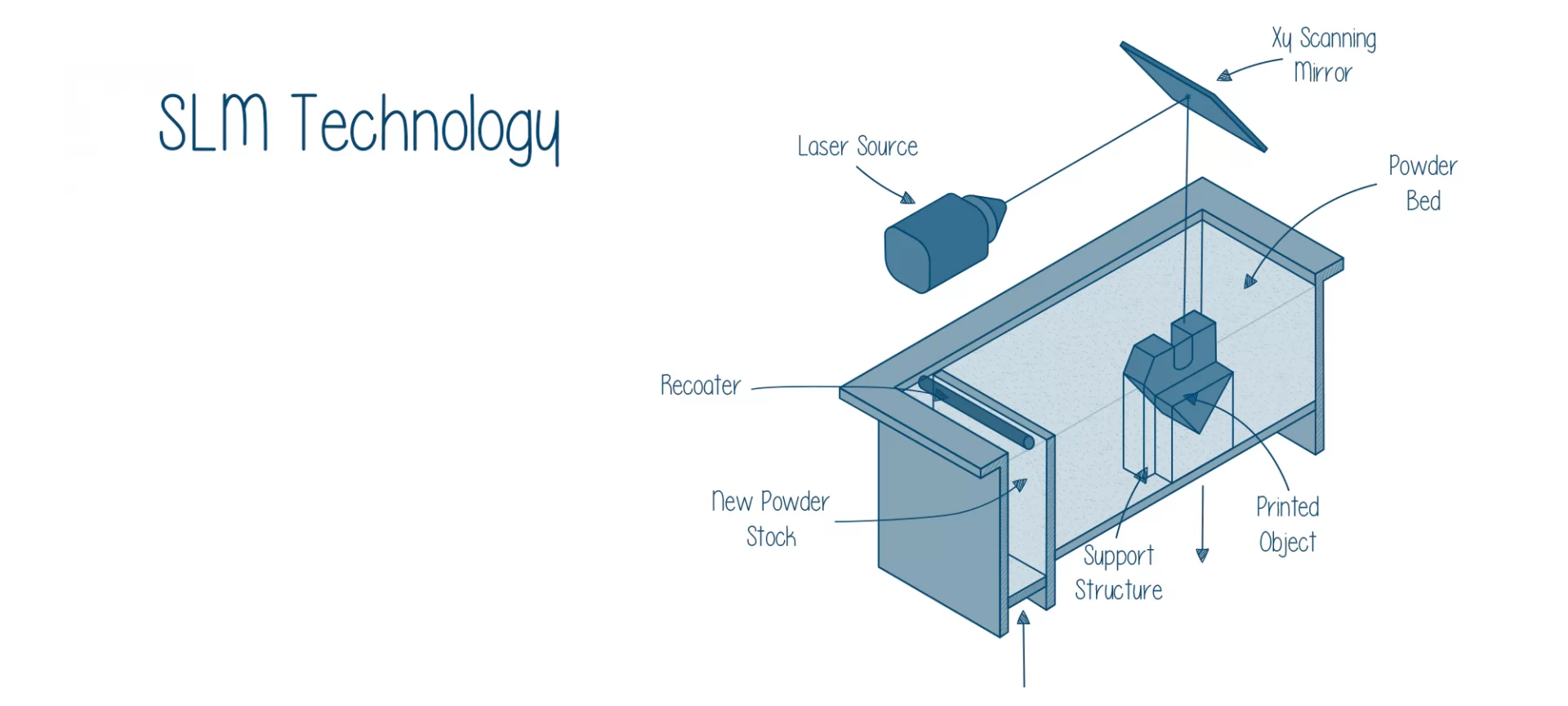
- Any SLM 3D printer’s print chamber has to be completely filled with metal powder. The first step which indicates the start of SLM 3D printing is the spreading of this metal powder. You need to ensure that this powder is spread all across the substrate or build a plate in thin layers by a coater blade.
- Once this is done, the laser source is allowed to step in, not before. A high power laser source starts fusing a two-dimensional slice of the part by selectively melting the powdered material. As soon as this is achieved, the build plate of the printer drops down by the height of one layer, and the coater again spreads a fresh layer of metal powder across the build surface. And this process will be repeated until you get the final part printed.
- All of this process has to be conducted in a controlled environment. So, you cannot have a 3D printer with an open-body ever, for SLM 3D printing. You need an enclosed print chamber that should withstand a certain degree Celsius of temperature.
- After the part is built, it can be removed from the built plate using a bandsaw. As mentioned above, the support material will be of the same material as the part, the post-processing can be a little difficult and time-consuming. And needs to be done with a lot of patience.
- Once you get the parts in your hand you’d notice that the sintered parts are rough and depending on the application you wish to use them for, they will require post-processing. Machining of parts made from this technology for getting finer finish features, surfaces, and holes is a very common practice.
Applications in Which SLM 3D Printed Parts are Used
Mostly the objects created from this technology are made from Aluminum and metal alloys. This implies that these parts can resist high gas pressure and heat that leads.
Due to this feature, SLM 3D printed parts and functional prototypes are used in mechanical engineering and chemical engineering.
Some of the common goals that you can achieve by SLM 3D printing are: saving in weight, high performance, cost reduction, and better handling.
The industry which can directly benefit from parts of such nature is Aerospace and Aerospatial industries.
Apart from that, as mentioned above, mechanical industries such as tooling, fixtures, motor parts such as rotors and impellers, and cooling channels, etc are some of the areas where parts made from SLM can be used.
Other fields include Automotive, research, dental, and medical engineering. And also to mention, the technology is getting more and more adaptable with the passage of time and hence is getting attached to industry after industry. So, the scope of SLM 3D printing is widening with time.
Having stated so, it’s time now to look at the pros and cons of this technology.
Pros and Cons of SLM 3D Printing
Although the technology has some of the greatest benefits that cannot be offered by any other 3D printing technologies, it has its own limitations.
- You’d able to choose from one of the widest range of 3D printing material options. The total number of 3D printing material that you can print using SLM 3D printers is around seventy-nine.
- Using this 3D printing technology you’ll be able to print some of the hardest to imagine complex shapes or internal features that you cannot via traditional manufacturing techniques.
- SLM 3D printing technology reduces lead times, as you require no time for adjusting the tooling.
- This technology allows for part consolidation and production of multiple parts at the same time.
- Allows you to reduce the weight of parts and functional prototypes in various applications.
- You can produce optimized designs using the technology that removes the need for the assembly of parts.
- The technology is very expensive compared to other 3D printing technologies such as SLA and FDM 3D printing. Provided if the parts that are produced using this technology aren’t optimized or designed for the process.
- Not everyone can operate a 3D printer based on SLM 3D printing technology. You need skilled hands and an experienced workman to make sure the parts printed using this 3D printing technology are of high quality.
- This technology is currently limited to producing parts of smaller build volume. You cannot print larger build volumes as you can with FDM or SLA, using an SLM 3D printer.
- All the parts and functional prototypes manufactured using this technology have a rough finish and thus they require lots of post-processing. This increases the overall print time.
SLM Solutions is one of the major producers of SLM 3D printers in the market. At the time of writing this article, it has five printers in this category.
For gaining a better understanding of the technology and how it is directly used in the industry, let’s have a look at these printers and their special features.
SLM 125

It is a compact, and accurate high power 3D printer used for manufacturing parts and functional prototypes of low build volume.
SLM 125 is ideal for various users ranging from rapid prototyping to low volume manufacturing. Its build envelope is 125 mm * 125 mm * 125 mm.
The printer uses a single laser source and can print with multi-material.
Special Features:
- High power laser in the range of 400 Watts for a compact footprint.
- The substrate plate of the printer can be heated up to 200 degrees Celsius.
- PSM Manual powder Sieve.
- Melt Pool Monitoring.
- Laser Power Monitoring.
The variable thickness range offered by SLM 125 is 20 to 75 micrometers. And the maximum scan speed is 10 meters per second.
|
SLM 280 2.0
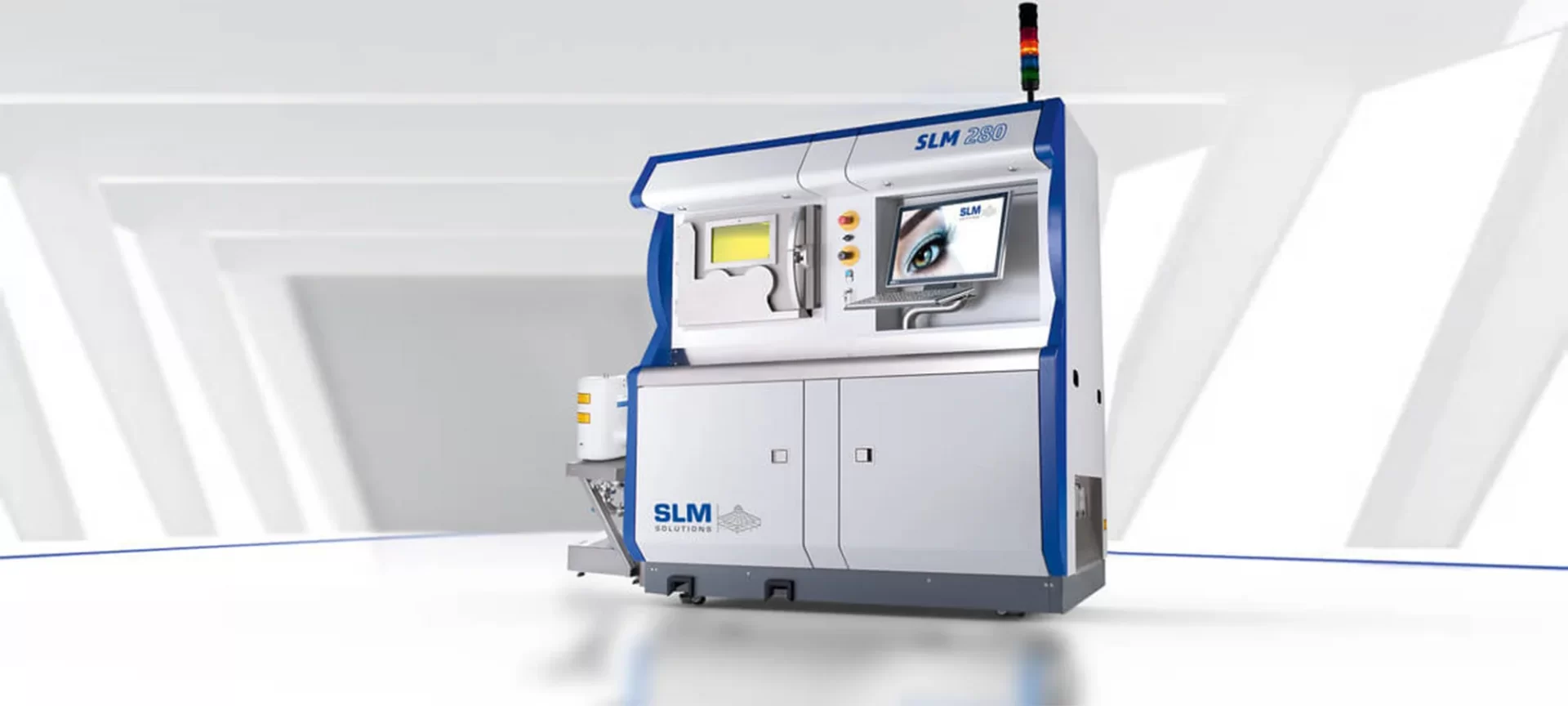

The printer allows you to do metal 3D printing using more than one laser source and closed-loop powder handling.
SLM 280 2.0 is ideal for medium to high volume part production and prototypes. It offers a build volume envelope of 280 mm * 280 mm * 365 mm.
Special features:
- Based on multi-laser technology, SLM 280 2.0 is equipped with two lasers of 700 Watt power each. The printer lets you accelerate the printing process of many metal additive powders.
- The sieving process of this printer runs automatically without influencing the running build process. This reduces ancillary times and support and speeds up the sieving procedure.
- The printer features a re-coater cleaning station that is a stable mount for maintenance, is 730 mm * 310 mm * 250 mm in dimension. It is very safe for storing recoating mechanisms.
- Substrate plates with parts up to 180 kilograms can be easily removed from the process chamber with the printer’s build plate handling device.
SLM 280 2.0 offers a variable layer thickness range of 20 to 75 micrometers. And a maximum scan speed of 10 meters per second.
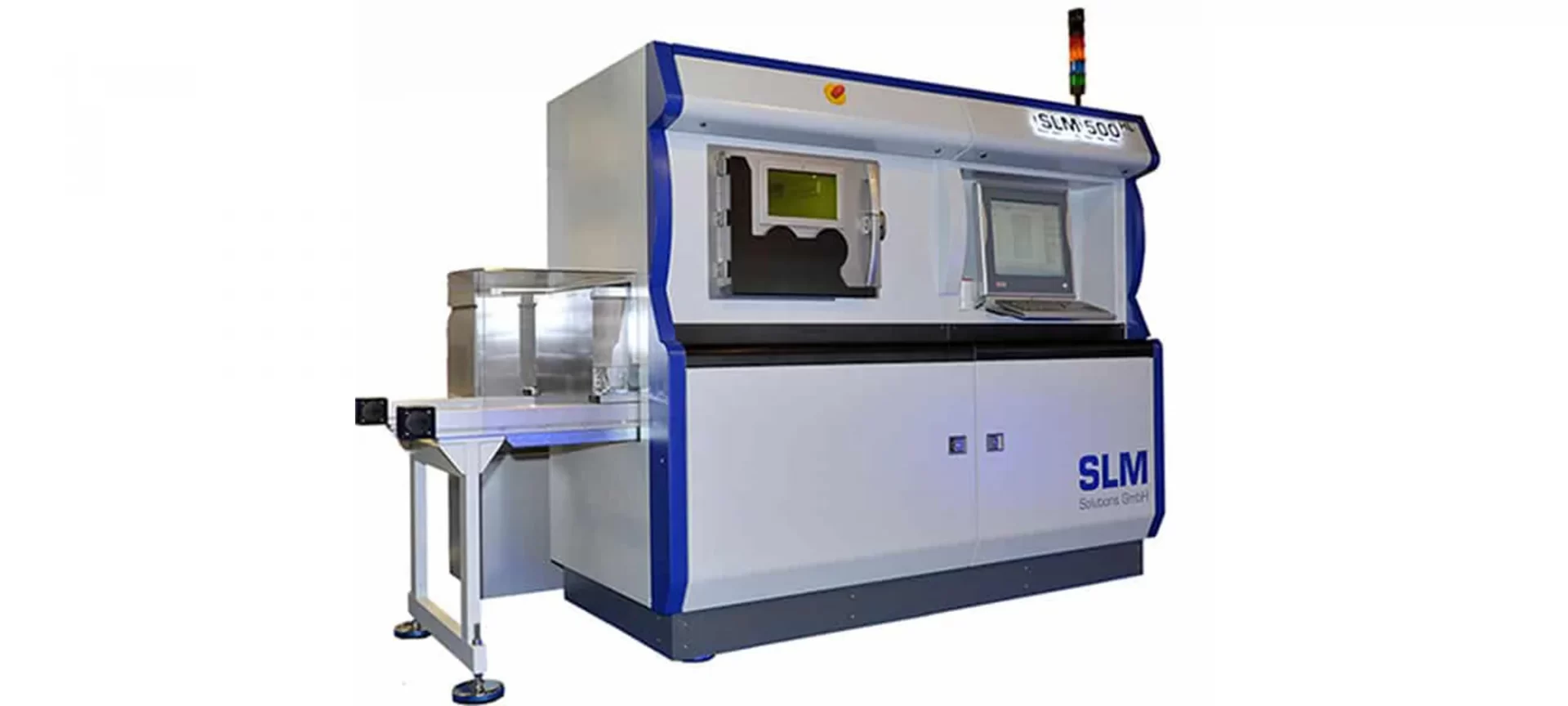
SLM 500
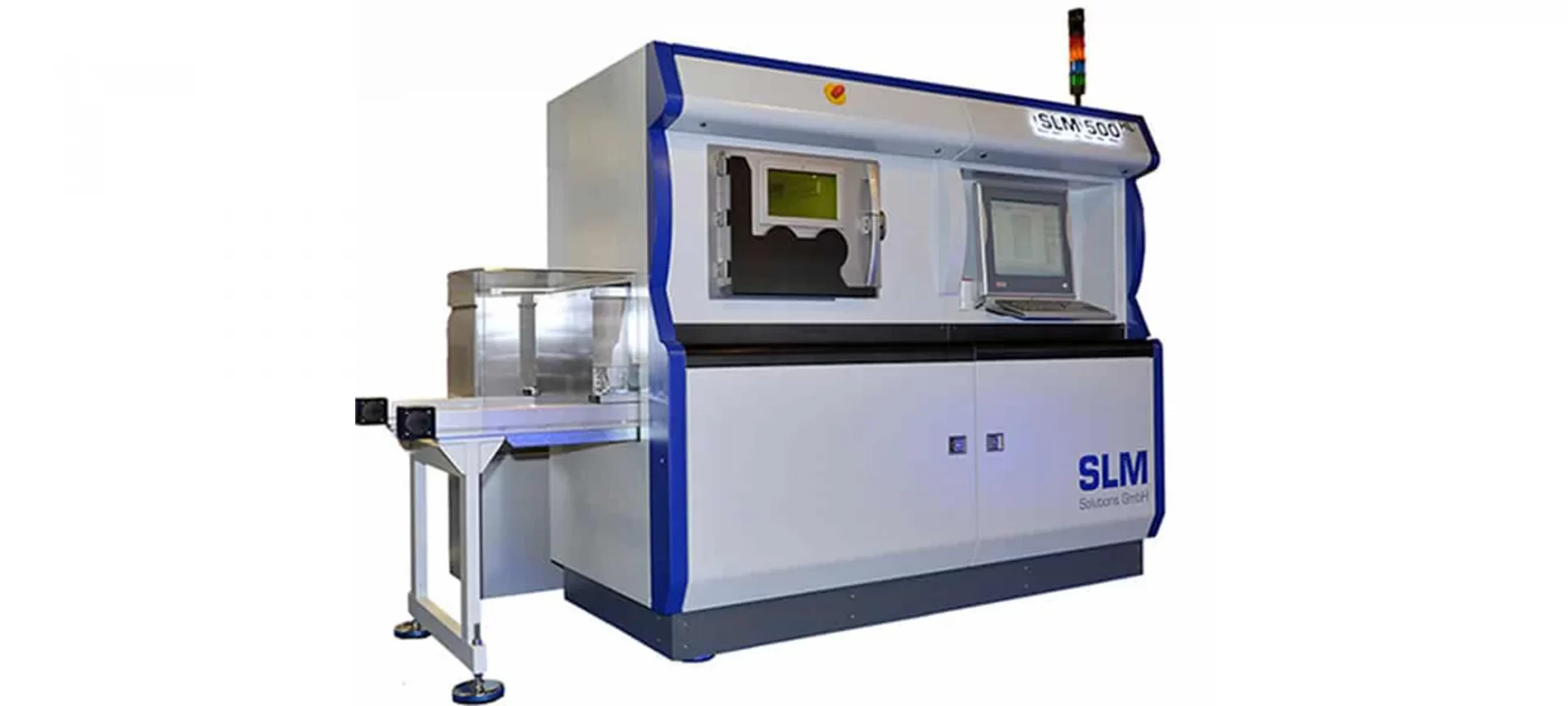

The printer manufacturer boasts about this one as the first 3D printer equipped with the quad-laser metal system.
It can integrate lasers independently or in parallel for increasing build rates by 90 percent over twin laser configurations.
The building envelope offered by this 3D printer is 500 mm * 280 mm * 365 mm. It has an automated powder handling system and a turnkey system that includes a part removal station.
Special Features:
- Designed to ensure operator safety and lower the overall operational costs of manufacturing. It’s automated powder sieve and supply decreases the human effort and separates powder via closed-loop powder handling technology.
- There is a permanent filter in-built in this 3D printer that traps the submicronic soot which is a by-product of the printing process and condensates particles from the process gas.
- The layer preparation tool enables reproducible adjustments to the recoating lip height, independence from the operator with one micrometer, etc. This results in recoating and laser exposure level consistency for every part or functional prototype build on this printer.
- The Laser Power Monitoring features of this printer measures and illustrates nominal and actual power during the ongoing manufacturing process.
The variable layer thickness range in parts and functional prototypes manufactured using this printer is 20 to 90 micrometers.
And the maximum scan speed is 10 meters per second. The beam focus diameter range of the laser source in this printer is 80 to 115 micrometers.
|
The Conclusion
The way in which more and more people are demanding SLM 3D printers is revolutionizing the way in which parts are made.
SLM 3D printing lets you manufacture parts and functional prototypes that are impossible to manufacture with traditional manufacturing techniques.
These parts are very complex in nature and demand laser-sharp precision. Mostly the quality of parts manufactured using SLM 3D printing depends on the coherence of the laser beam used.
That’s why we see more and more companies manufacturing SLM 3D printers with more than one laser source.
It’s all about exposing more areas of the spread powder to the laser beam for the solidification of that powder into a part of the wanted geometry.
This 3D printing technology is yet to reveal its complete potential and overcome the limitations that it is currently facing.













