Currently, there are multiple 3D printing processes in use. Among them, two of them are the most pronounced ones: FDM and SLS 3D printing technologies.
However, it still becomes difficult for users to find out which one is better. When comparing FDM vs SLS 3D printers, individuals often find it difficult to choose the right one for their specific needs.
Therefore, it is important to understand how these technologies differ along with the different benefits and limitations they offer.
Both these 3D printing processes have their own set of perks for the users. While FDM is the easiest of all to learn, SLS comes with a steep learning curve. Moreover, there is a huge difference in their mechanism and operation.
Hence, it is imperative to learn about these differences to better understand the worth of each 3D printing process. And, what could be the best way to do that if not a detailed comparison?
Let’s get to know both of these processes closely and find out which one is better for which application.
What is Fused Deposition Modeling?
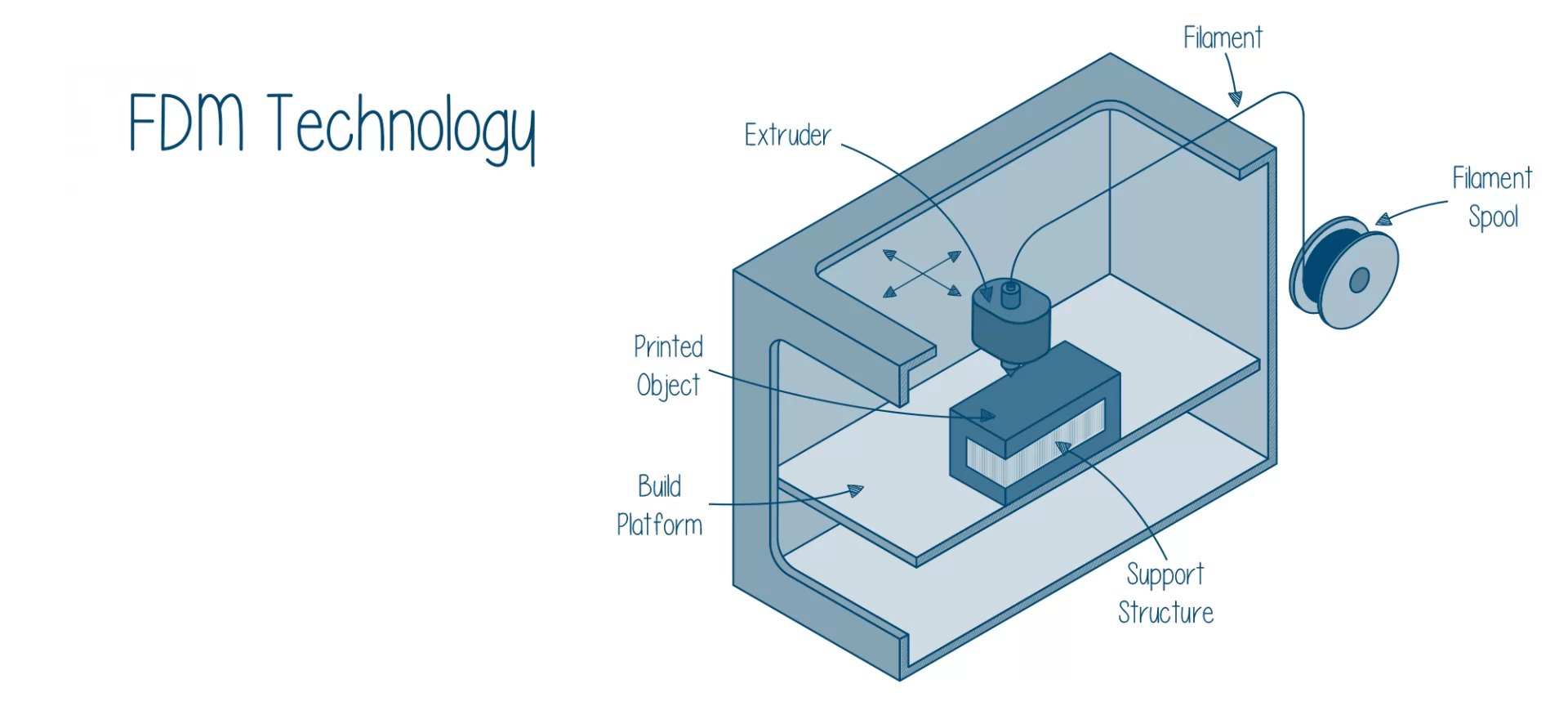
It is a method of additive manufacturing in which layers of materials fused together in a pattern for creating an object.
The 3D printing material employed for 3D printing is melted past glass transition temperature.
After this is done, the material is extruded in a geometry next to or on top of previous extrusions for creating part layer by layer.
An FDM 3D printer utilizes plastic filament and squeezes it through a hot end, melting it and hence depositing it in layers over the print bed.
The layers fuse together, build up throughout the print, and then they form the finished part.
The other name of FDM is Fused Filament Fabrication 3D printing technology. Stratasys, the company discovered it in 1991.
The most common types of materials used for 3D printing using FDM 3D printing technology are thermoplastics, pastes, metal, or wood-infused thermoplastic.
This is the simplest way for 3D printing. It is cheap as well as efficient. FDM 3D printers are the most available 3D printers in the market currently.
Major Applications of FDM 3D Printing

Different types of industries choose FDM 3D printing. The main ones are automotive and consumer goods manufacturing.
To aid their product development, prototyping, and their manufacturing process, they employ FDM 3D printers.
Before developing a product and mass manufacturing them, it is very important to test these objects.
This is why thermoplastics are the primary kind of materials used; as they endure heat, chemicals, and mechanical stress.
FDM 3D printing technology has the capability for creating extremely detailed objects.
Therefore, all the industries that need to create parts have to be tested for fit and form.
FDM 3D printing is also used for manufacturing end-use parts, especially small parts with a lot of details.
Thermoplastics are used in food packaging and drug packaging and also popular technology in the medical industry.
Advantages of FDM 3D Printing
Easy Handling
The 3D printing industry is yet not the main way for creating parts and functional prototypes. However, it will be in the future for many reasons.
The chief one is that it simplifies the manufacturing process and enables manufacturers to test, alters as well as produce the final product faster than traditional manufacturing processes. It is very easy to handle the 3D printing materials.
Cost-efficient
FDM 3D printing technology provides a viable solution designed for helping to keep manufacturing lower costs. Compared to other 3D printing technologies, FDM 3D printing is the cheapest method.
Also, the materials used for 3D printing are cheaper than SLS, and SLA 3D printing technology.
Flexibility in Choice of Materials
A wide range of 3D printing materials can be used to manufacture parts and functional prototypes using this technology.
All of them are accessible and available. Filament spools such as ABS, PLA, TPU, PETG help creating complex objects in a variety of colors.
Post-Processing of Parts is not Much Required
FDM 3D printing technology optimizes production time and saves money. It requires less post-processing hence you do not need to search for expensive liquids, which can be used in other methods. Because it creates a product that is ready to use.
Overall, FDM 3D printing is a technique that is very easy to understand and it delivers product ready for application with the least amount of effort.
If you are willing to start a business and looking for a feasible 3D printing technology option, FDM can be a great choice. Its 3D printing materials and 3D printers are readily available at low cost.
What is Selective Laser Sintering?
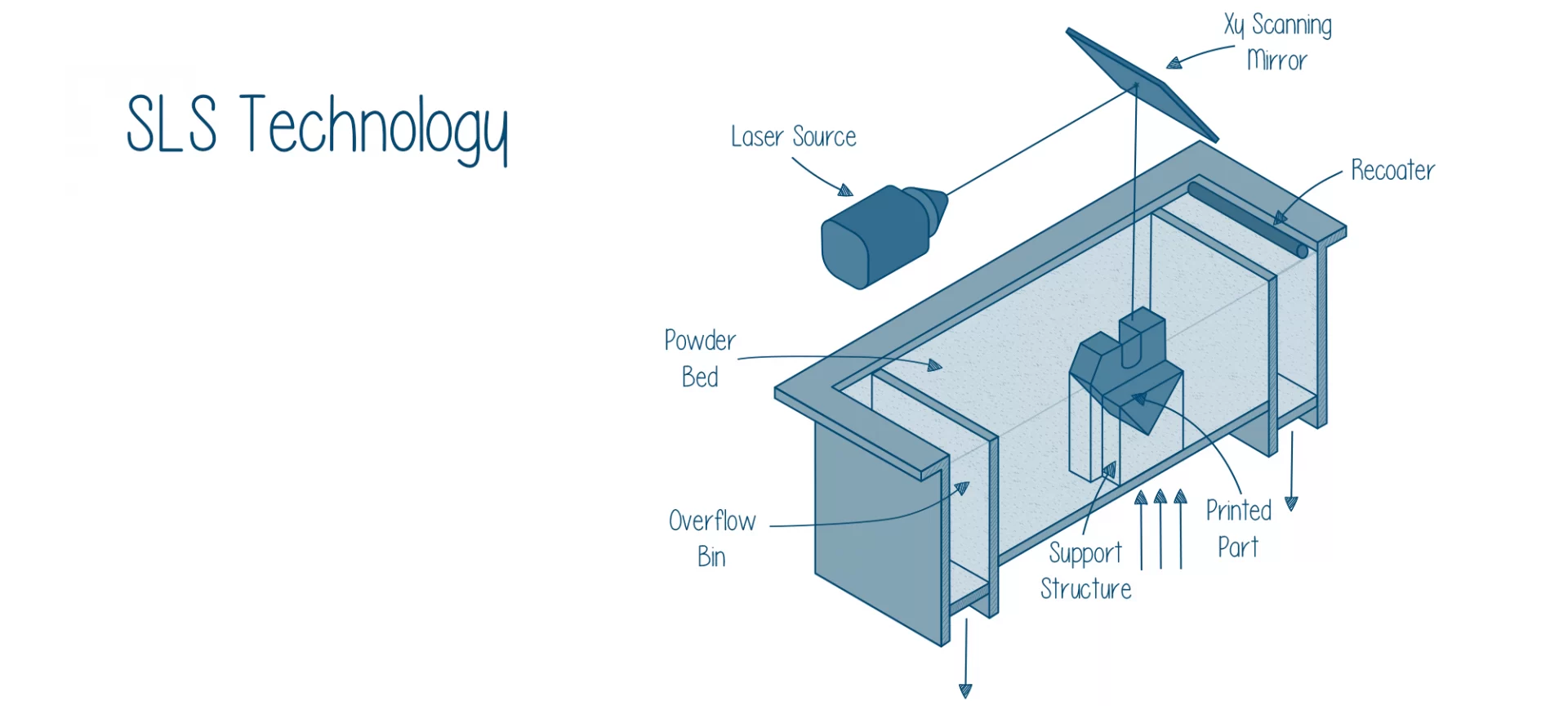
This manufacturing technology belongs to the powder bed fusion category of 3D printing technologies.
In the process of 3D printing, a part or functional prototype using SLS 3D printing a laser selectively sinters the particles from a polymer powder, fuses them together, and builds the part layer by layer. Mostly, the 3D printing material employed in this technology comes in granular form.
Like FDM 3D printing technology, SLS is also used for prototyping functional polymer components as well as small production runs. It offers very high design freedom, parts with higher accuracy and consistent mechanical properties can be produced using this technology.
Working on SLS 3D Printing
- The first step to SLS 3D printing is heating of the powder bin i.e. the equipment in which 3D printing material for 3D printing is kept. The heating stops before the melting temperature of that material is reached. With this, the recoating blade of the 3D printer spreads a thin layer of powder over the build platform.
- In the second step, a laser-based on carbon dioxide scans the contour of the next layer and selectively sinters or fuses the particles of the polymer powder. The complete cross-section of the component is scanned to ensure the part that is built, is solid.
- After the layer is completed, the build platform of the printer moves downwards by the height called layer height. In addition, the blade once again re-coats the surface. This process is repeated until all the layers of the part are printed as mentioned in the 3D design file.
- Once the printing is done, the 3D-printed parts are fully encapsulated in the unsintered powder. The powder bin, which was heated to the melting temperature, needs to be cooled down before unpacking them. Although the process looks simple, it takes as long as twelve hours depending on the 3D printing material you used for 3D printing. Cleaning of these parts with compressed air or other blasting media makes them ready for post-processing while the remaining powder can be reused.
Applications of SLS 3D Printing

SLS 3D printed parts are used as anatomical models in healthcare, dental settings, dummies, and as pre-operative planning models and training aids. They are also employed in architecture for creating designs of various places.
Since SLS can create complex parts, it is used by artists for creating pieces of art that work well in art disciplines such as sculptures and monuments. It can be also be used for verifying engineering designs.
The fashion industry benefits from utilizing this technology for developing clothing in one piece. Clothes are custom-made according to the individual’s body measurements. There’d be no waste material because clothing is printed with exact specifications.
Advantages of SLS 3D Printing
- Parts and functional prototypes manufactured using SLS 3D printing technology are known to have good, isotropic mechanical properties. This is what makes them ideal for functional prototypes.
- Manufacturing a part or functional prototype using this technique requires no support structures even when you are producing complex geometries.
- The manufacturing capabilities of SLS 3D printing are excellent for small to medium batch production.
- Durable functional parts with high complex geometries can be made using this technique.
- It is ideal for parts that need high temperatures for melting and are chemical resistant.
- The process has shorter lead times.
FDM vs SLS – What is the Difference Between FDM and SLS?
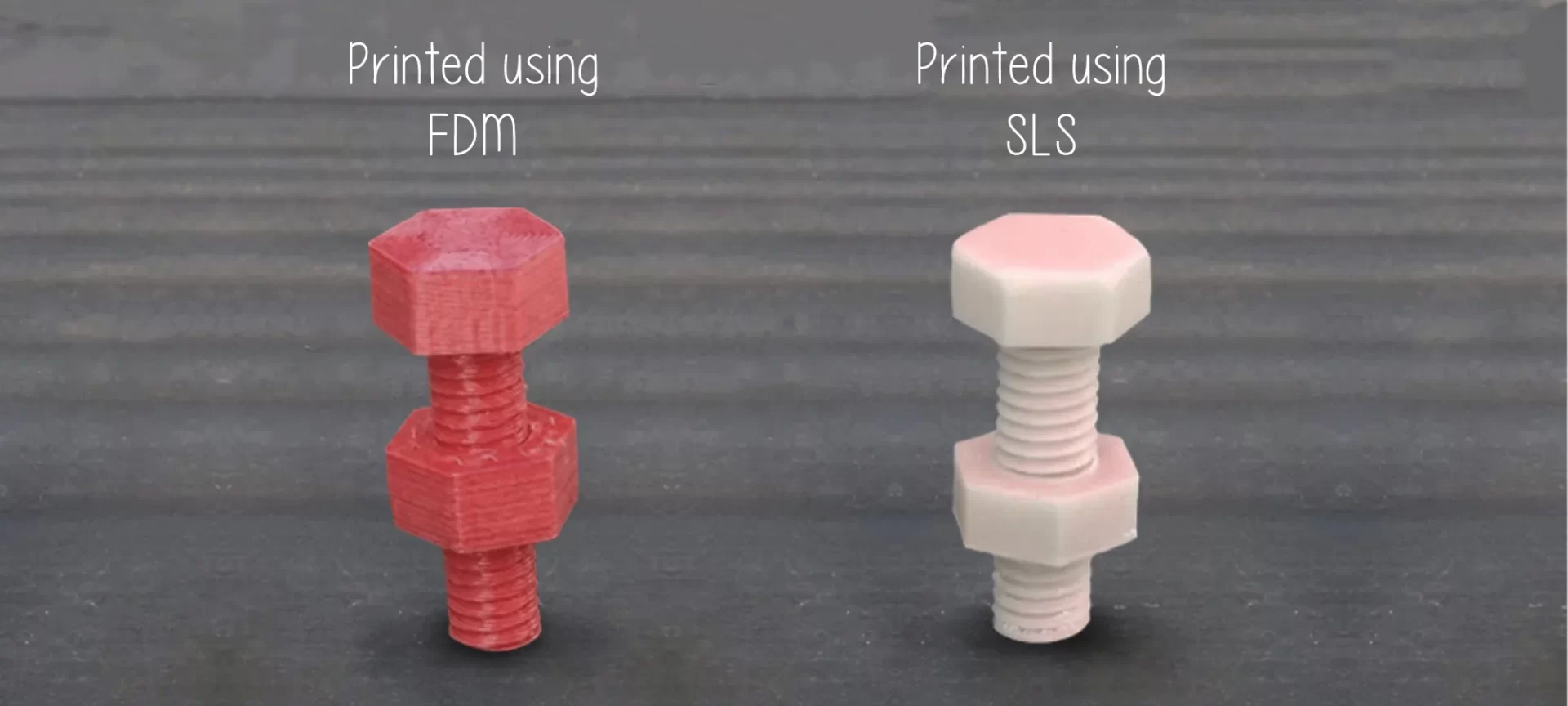
Here is a comparison between FDM vs SLS based on different criteria.
FDM vs SLS in Terms of Equipment Cost
Related to cost, there are three types based on which FDM can be compared to SLS. Starting with equipment cost for both these technologies, SLS 3D printers are on a higher-end when putting it versus FDM 3D printers. Budget FDM 3D printers and kits start from a few hundred dollars.
Even high-quality mid-range desktop FDM 3D printers are available from $2000 whereas industrial 3D printers are available from $15000.
Stating about SLS 3D printers, benchtop industrial systems start from $18,500, whereas traditional industrial 3D printers are available from $100,000.
So, going FDM vs SLS in terms of equipment cost, it is suggested you prefer FDM when do not want to spend much cost.
On the other hand, in applications where you need high quality, even if you are subjected to a higher budget, SLS can be preferred.
It is also to note that as you have desktop 3D printers starting at a cost as low as $200, you do not have such an option with SLS 3D printing.
FDM vs SLS in Terms of Material and Labor Cost
Moving on to material costs, most standard engineering FDM filaments start from $50 per kilogram and end up being as high as $150 per kilogram. Whereas for support material, the cost ranges from $100 to $200 per kilogram. SLS on the other hand requires no support structures.
However, stating about 3D printing material employed by the technology, it is $100 per kilogram from Nylon. So overall, FDM vs SLS on a material cost level, you can say there is a tie.
You can use a lower cost of $50 3D printing material with lowering costing support structure material and the cost will equivalent to that of printing a part or functional prototype with SLS 3D printing.
The post-processing process of FDM 3D printing is lengthier than that of SLS 3D printing. Also, the process of material removal is manually done when printing with desktop 3D printers. Whereas it is easy to remove parts and excess powder using SLS 3D printing.
FDM vs SLS in Terms of 3D Printing Technologies
FDM is known for 3D printing with low-cost consumer machines and speedily. Whereas SLS is known for printing strong functional parts, with design freedom, without any support structures.
The amount of accuracy offered by FDM 3D printers is low, there is lesser detailing in parts and functional prototypes printed using this technology. While in SLS 3D printing you can expect rough surface finishes, but of course, the choice of 3D printing with a variety of 3D printing materials is not possible with it.
Stating about the print volume of parts and functional prototypes, in FDM it is around 300 mm * 300 mm * 600 mm, on average for the desktop to benchtop 3D printers. For SLS 3D printing, it is 165 mm * 165 mm * 300 mm for benchtop industrial SLS 3D printers.
The materials employed for making a part using FDM are standard thermoplastics such as ABS, PLA, and other blends. For SLS, it is Nylon 11, Nylon 12 and their composites.
FDM vs SLS in Terms of Training, Facility Required, and Ancillary Equipment
Minor training in build setup, machine operation, finishing, and moderate training on maintenance is required for FDM 3D printing.
Whereas moderate training on build setup, machine operation, and finishing is required for SLS 3D printing.
The surrounding required for FDM 3D printers is typically ventilated, air-conditioned environment for desktop machines.
Whereas a workshop environment with moderate space is required for benchtop SLS 3D printers.
Stating about support removal systems, you need machines with support systems as far as FDM 3D printers are concerned.
While for SLS 3D printers, post-processing stations for part cleaning and material recovery are required.
The Conclusion
Well, this is where the comparison ends. And, if you are thinking about which one is better, it’s better to find out what you are looking for.
In case, you need to enjoy a smoother surface without worrying about the extra effort needed for post-processing,
SLS is the best choice. However, if your application requires faster printing, with not much attention to the high resolution, FDM is the best pick.
In short, both technologies are great. So, you must underline your needs before comparing FDM vs SLS to choose the right 3D printer sufficing your needs.







