There are many such things in the world, the frontend of which we know, but not the backend. Almost all of us are familiar with metal products, but not all of us are familiar with injection molding.
The majority of the metal products that you see around yourself are manufactured by Metal Injection Molding. Fabrication of these molds is a very expensive and time-consuming process.
And in the search for a cost-effective process of making small and complex metal parts for production, manufacturers were gifted with 3D printing technology.
From the time it was first discovered, to date, MIM 3D printing has come a long way. Currently, MIM 3D printing is a core manufacturing technology that is widely used for making small components in various industries.
Markets such as medical, firearms, general industry, and many others use components developed from this 3D printing technology.
From the economy’s perspective, when a part’s design is not likely to change in the next five to ten years, and the volumes of it are to be manufactured in hundreds, thousands, or millions, that is when MIM tooling can come handy.
Before starting to explore the core of this process, let’s look at the overview of Injection Molding to understand the process from which Metal Injection Molding 3D printing is derived.
Metal Injection Molding 3D Printing: When Metal Injection Molding Met 3D Printing
Injection Molding is one of the most common methods of manufacturing. The molten metal is injected into a mold cavity. This liquid metal hardens as it cools.
When it is completely cooled, the mold is opened and hard metal pieces are taken out. Injection Molding is typically favored when you wish to produce pieces in huge masses because of its high design, test, and tooling cost.
Preparing the mold in which the plastic is to be injected, takes a lot of effort so when you have pieces that are to be manufactured in a lot of amounts, this method is very favorable. The unit price drops very much when the amount is very huge.
3D printing is a process of manufacturing parts and functional prototypes layer by layer as per the 3D design file. Once the design file is ready, it is sliced and converted into g-code which is then fed into the 3D printer.
And after that, it’s all about setting your 3D printer for ensuring a perfect print. That is exactly how injection molds in which you feed in the feedstock for metal injection molding can be 3D printed.
The process that you need to follow is:
- Prepare the design of injection molds with CAD software such as AutoCAD or Fusion 360.
- Save the design file in STL file format or any other that your 3D printer is compatible with.
- Print the molds layer by layer using a 3D printer based on processes such as SLA, FDM, Material jetting, and SLS.
- Fit the molds into the metallic frames and be ready for the process of injection molding.
It is to be noted how, by 3D printing injection molds, the cost of designing and the efforts are significantly reduced because of the digitization.
A real-life example of this was provided by Athlone Institute of Technology who designed an injection mold of their college’s logo and the whole process took even lesser than 24 hours.
And the cost was very low compared to the cost of manufacturing traditional injection molds.
Stepwise Process of Metal Injection Molding 3D Printing
There are five steps of this process.
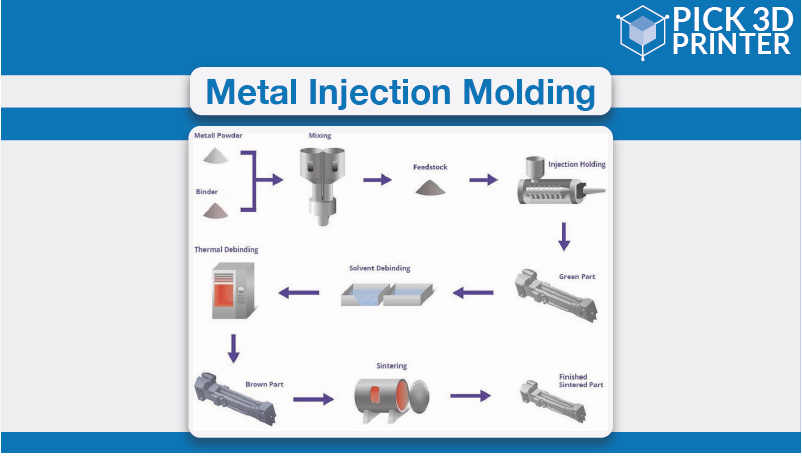
- Feedstock preparation: It starts with feedstock preparation wherein a fine metal powder which is less than 20 microns in particle size, mixed with thermoplastic and wax binders in pre-decided amounts. The ratio of metal powder to binder is 60:40. The prepared blend is then placed in special mixing equipment that is then heated to a temperature. This process is to ensure that the binder has melted. Until the metal powder particles are uniformly coated with the binders, the mass is mechanically mixed. It is then cooled and granulated into free-flowing pellets which are passed on to the 3D printer.
- Injection Molding: The pelletized feedstock is fed into a machine that is capable of doing injection molding. Here the feedstock is heated and injected into a mold cavity at high pressure. When the injection is completed, the molded part is allowed to cool and ejected from it. The process is repeated till the feedstock completes. Only the binders melt after this process that happens at about 200 degrees Celsius. The size of the mold cavity is kept around 20 percent more for ensuring it fits even after shrinkage occurs during sintering. For doing so, the shrinkage capacity of each material is precisely known.
- Binder Removal Process: Now that the main process i.e. formation of the geometry of the part or functional prototype is done, it’s time to remove it. This process is called Debinding or binder removal. In this process, the binder materials that we ensured get bind to metal powder, are to be removed from the prepared MIM component. It is conducted in several steps starting from removing the majority of this before the sintering step. And leaving behind only enough binder for handling the parts into the sintering furnace. Among the many processes that can be employed for binder removal; the most employed one is solvent extraction. After you have removed the binder, the part is semi-porous, allowing the remaining binder to flee during the sintering process.
- Sintering: The parts that have been removed are placed on ceramic setters that are loaded into a high-temperature controlled sintering furnace. For driving out the remaining binders, the brown parts will then be heated in a protective atmosphere. After the binders evaporate, the metal part is heated to even higher temperatures where the void space between them is eliminated because they will fuse together. This will make the part shrink to its design dimensions and transform into a dense solid. The sintered parts’ density is generally greater than its theoretical value which gives it properties similar to wrought materials.
- Finishing: To have this included or excluded will depend upon the final requirements of the part or functional prototype you require. For improving the physical property of the manufactured part you can do some heat treatment over it. Any type of machining operation can be performed on the MIM manufactured part for making it more precise. Processes such as cold working or welding can also be used, depending on the final geometry of the part you need.
Pros of Metal Injection Molding 3D Printing
- As you can sense from reading the above write-up, a major advantage of using metal injection molding 3D printing is the cost reduction. Compared to traditional injection mold manufacturing, it is cheaper and less time and effort-consuming. Also, traditional mold manufacturing can only be achieved using precise machinery and expertise from mold makers. If you are using 3D printing, it is very cheaper and has a simple way of manufacturing that does not need much expertise apart from making the 3D model and operating the 3D printer. According to records making 3D printed molds can save up to eight percent costs.
- Parts and functional prototypes that cannot be manufactured with traditional injection molding because of their design complexities can be manufactured using 3D printing. In case the result of 3D printing is not as efficient as you determined it would be, you can easily change the design to print another one. This kind of flexibility and efficiency was not possible using traditional injection molding. Also, the time taken for making the design is notably reduced.
- When you manufacture molds using 3D printing, it is not necessary to mass-produce them. As your initial costs of design are reduced, it is possible to customize the production even for small quantities. Even when mass production is not involved, making 3D-printed molds are cheaper to make compared to traditional molds.
Cons of Metal Injection Molding 3D Printing
- 3D printed injection molds are subjected to the issue of shrinkage which is a common problem while cooling. So, you need to be precise with the method of cooling as well as when to start cooling, according to the dimensions of the final part.
- The two main processes employed for MIM 3D printing that is DMLS and SLM have the highest price points. The materials as well as machines employing these 3D printing processes are expensive and have a slow printing rate.
- The finished parts are porous compared to the melted metal part. The complete porosity cannot be eliminated but only controlled in the post-processing.
- Most of the 3D printers employed in making parts using metal injection molding have smaller build volumes compared to other 3D printing processes.
What Are the Applications of Metal Injection Molding?

The industries that benefit majorly from this technology are the medical, dental, and aerospace industries.
In the field of Medicine
To replace portions of bones lost in an accident or a disease, custom prosthetics can be modeled and 3D printed using MIM. Materials such as titanium alloys are used for the creation of custom prosthetics.
They are high in strength, attack-resistant, and porous. Each prosthesis can be customized to the patient’s biology and that’s the main benefit.
In the field of Dentistry
Parts such as bridges, crowns, and partial dentures can be modeled specific to the patient and then printed from materials such as cobalt chrome. They can custom fit, have long-term durability, and have high strength.
In the field of Aerospace
One main benefit of MIM 3D printing is that they reduce part count, creates complex geometries, and reduces weight. All of that it does by maintaining the part strength and reliability.
Because of these benefits, it is extremely helpful while making a commercial rocket and aircraft parts. Imagine complex turbine parts and probes, rocket exhausts, all these can be made using metal injection molding 3D printing.
A Company That is Completely Into MIM 3D Printing
ExOne makes Metal 3D printers, metal materials as well as binders that are suitable for metal injection molding 3D printing.
Their printing systems are ideal for complex or low-run series production, prototyping designs, metal production lines, and reducing lead time.
To ensure you have complete reliability, predictable parts, starting from 3D printing to the final sintering, they have a range of qualification processes.
Its R & D team works day in, day out with new materials in their machines and routinely partners up for developing specific materials.
To date, Exone has declared five single alloy metals, and three metal composites as third-party qualified materials.
They have declared nine single alloy metals, six ceramics, two ceramic-metal composites and three metal composites as customer-qualified materials and the list is increasing.
For Metal Injection Molding 3D printing, ExOne offers five different 3D printing systems;
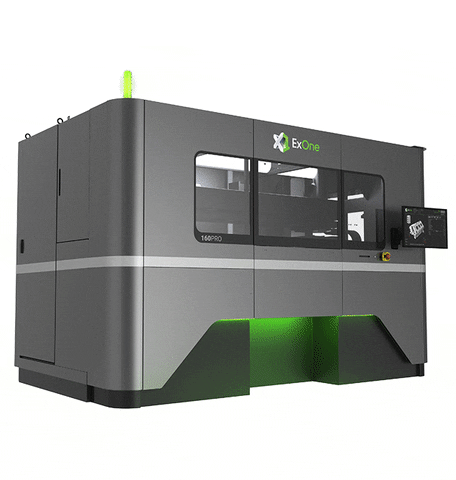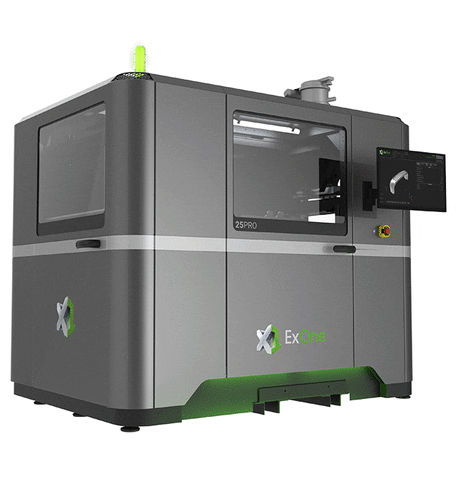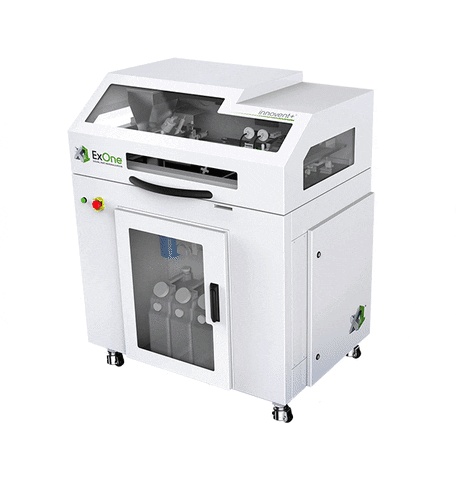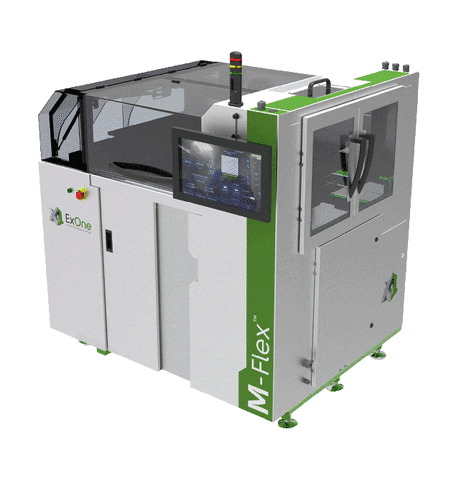
- X1 160 Pro: Offers build volume of 800 mm * 500 mm * 400 mm and a layer height of 30 to 200 micrometers. The build rate of this printer is more than 10,000 cc per hour.
- X1 25 Pro: Offers build volume of 400 mm * 250 mm * 250 mm and a layer height of 30 to 200 micrometers. The build rate of this printer is around 3600 cc per hour.
- Innovent Pro 3L: Comes in two build volume options, either three or five-liter, and has a layer height of 30 to 200 micrometers with a build rate of more than 700 ccs per hour.
- Innovent+: Offering a build volume of 160 mm * 65 mm * 65 mm, a layer height of 30 to 200 micrometers, and a build rate of 166 ccs per hour.
- M-Flex: The maximum build volume you can print on this printer is 400 mm * 250 mm * 250 mm, layer height is 50 to 200 micrometers, and build rate is 1600 cc per hour.
The Conclusion
Because of the invention of 3D printing, it has gotten easier to create parts using metal injection molding. Complex parts and functional prototypes can be made in lesser time, cost, and energy than before.
However, the technology is very expensive and so are machines based on it. But with the passing of time, the cost will reduce and the technology will be more accessible.







